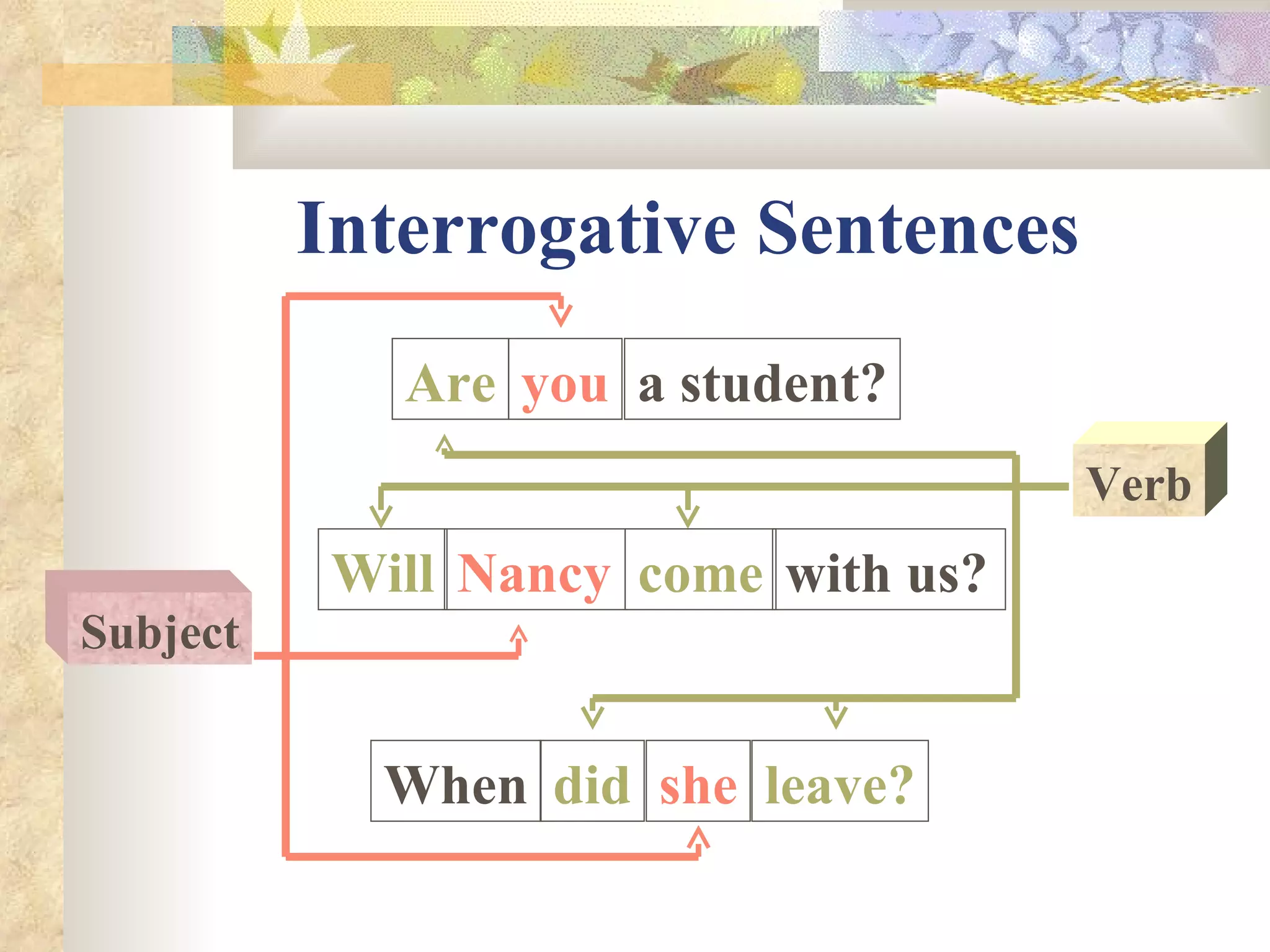
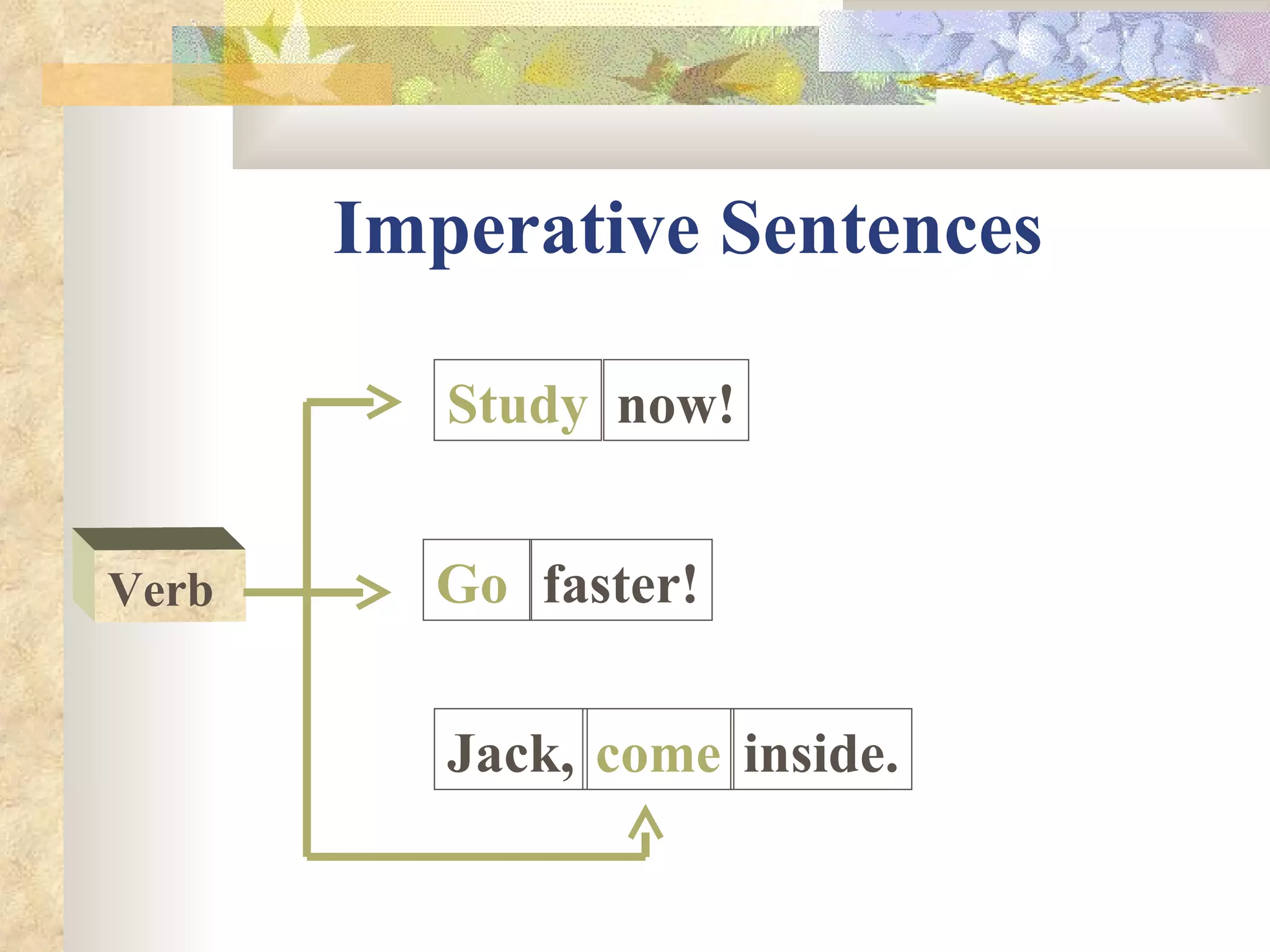
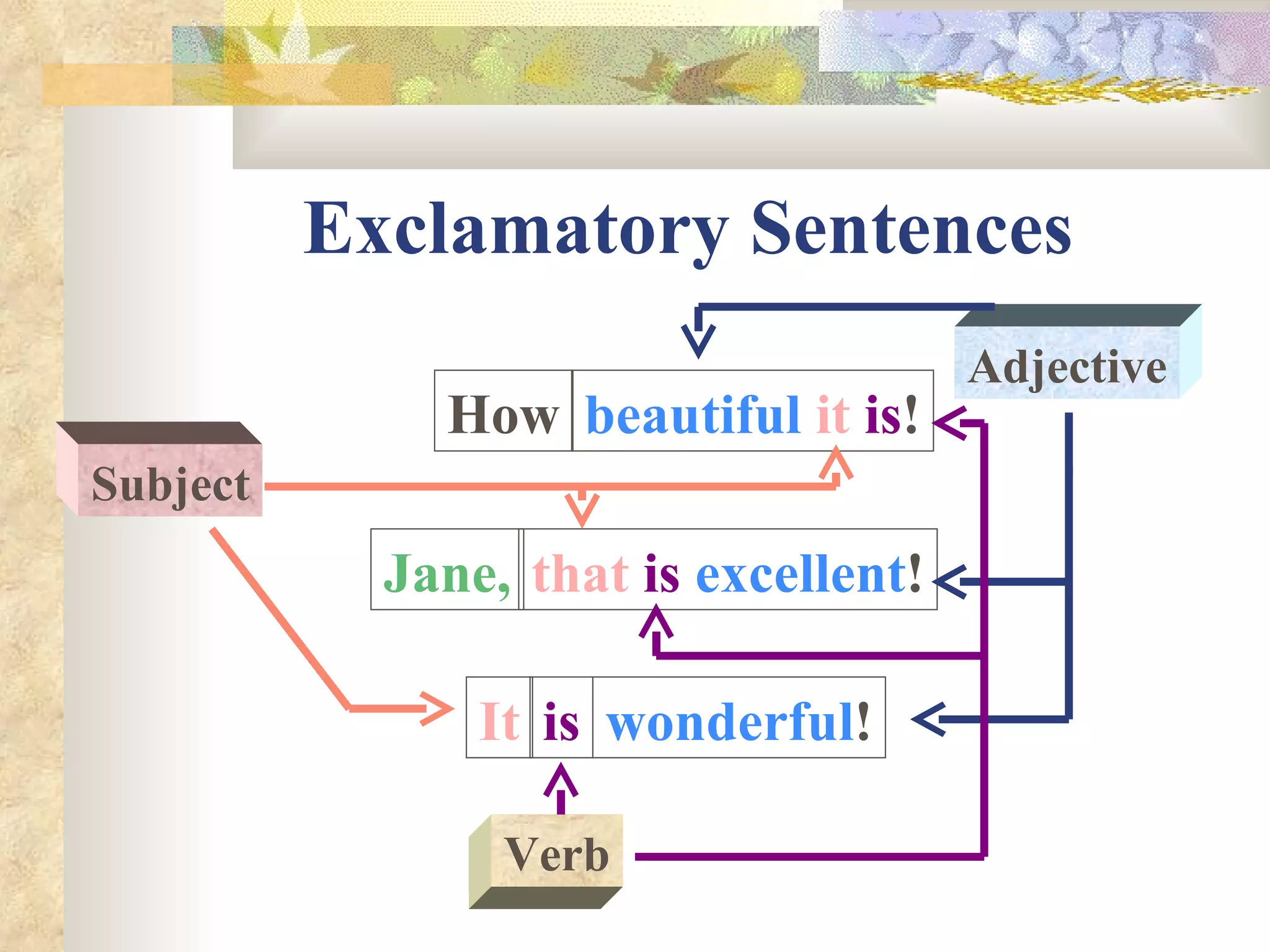
The document describes different types of sentences and how the subject and verb are positioned within each type. It defines declarative, interrogative, imperative, and exclamatory sentences. Declarative sentences place the subject before the verb, interrogative sentences place the subject after or between the helping and main verb, imperative sentences omit the subject which is always "you", and exclamatory sentences can be statements or commands with the subject and verb in varying positions. Examples are provided for each sentence type.