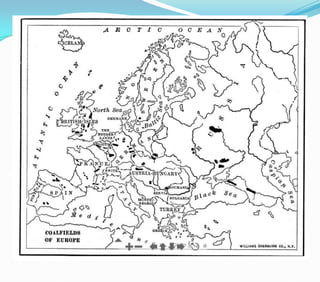
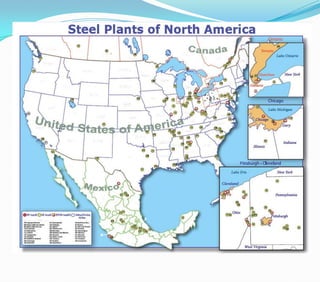
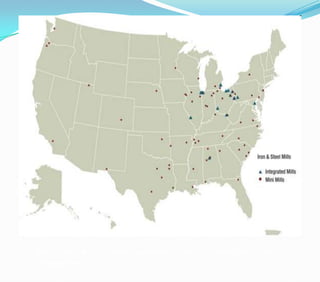
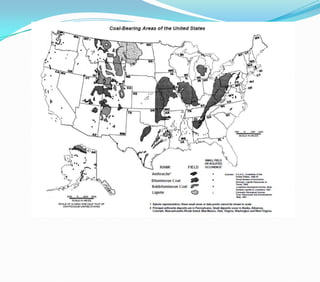
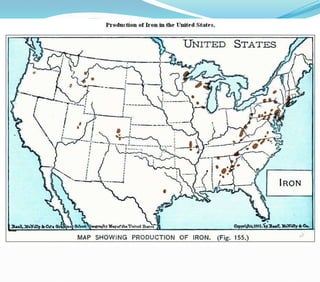
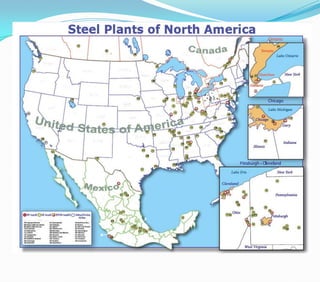
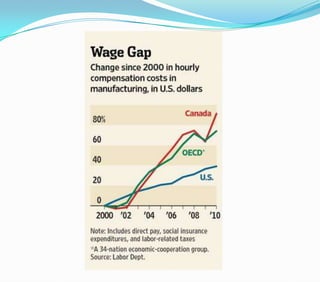
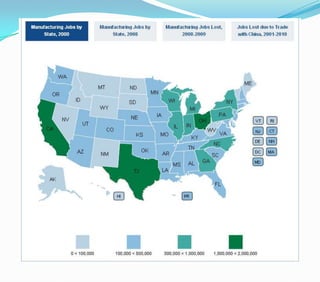
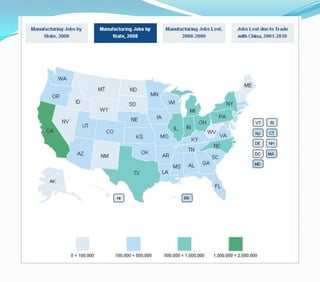
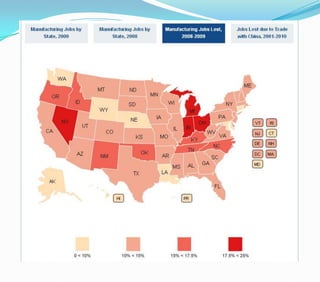
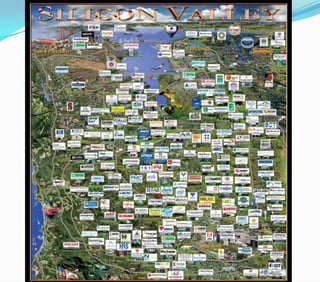
This document discusses factors that influence the location of industrial activity, including primary industries locating near resource deposits and secondary industries considering transportation costs of raw materials and finished goods. It summarizes Alfred Weber's least cost theory of industrial location and describes how transportation, labor, infrastructure, energy, agglomeration, and other political and environmental factors affect site selection. Silicon Valley is provided as an example of an industrial agglomeration influenced by proximity to a university, skilled labor, and natural resource abundance.