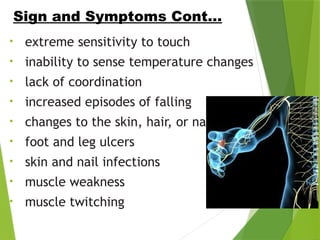
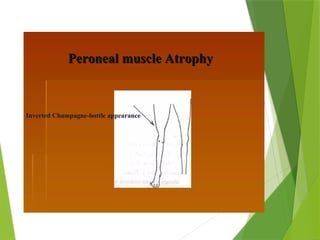
Polyneuropathy is a condition characterized by inflammation and degeneration of multiple peripheral and cranial nerves, leading to sensory, motor, or autonomic nerve impairment. Symptoms include tingling, numbness, muscle weakness, and coordination issues, with diagnosis based on medical history, physical exams, and various tests. Treatment options encompass medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.