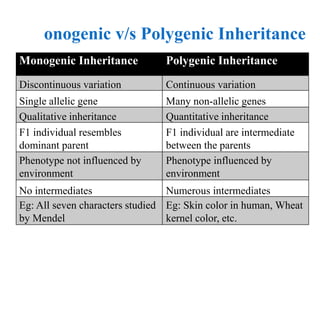
This document discusses polygenic inheritance, which is when multiple non-allelic genes contribute to a quantitative trait. Several key points:
- Polygenic traits do not follow Mendelian ratios and show continuous variation rather than discrete traits. Environmental factors can also influence polygenic traits.
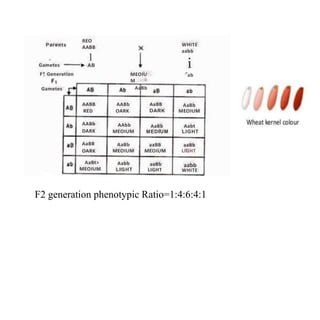
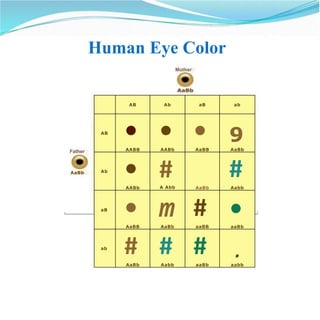
- Examples of polygenic traits include human skin color, wheat kernel color, and human height. These traits involve the additive contributions of several genes.
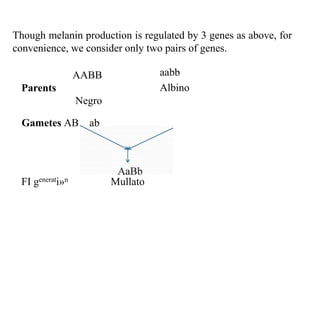
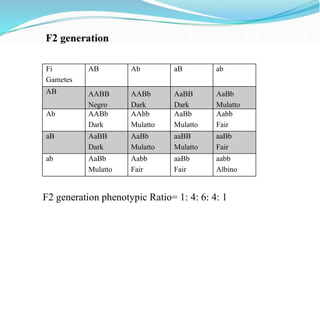
- The inheritance of human skin color is regulated by three genes but the document simplifies it to two gene pairs for demonstration purposes. The distribution of skin colors in populations depends on the number of dark versus light alleles individuals possess.