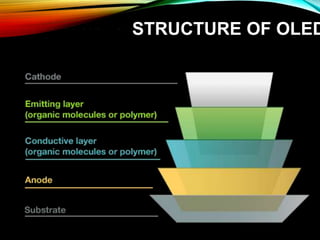
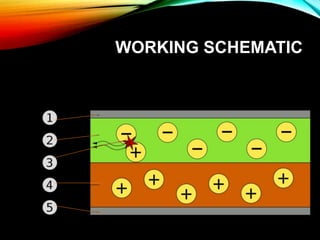
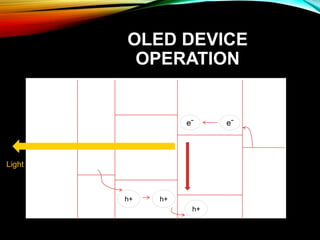
OLED (organic light-emitting diode) is a solid-state lighting technology that uses thin films of organic compounds that emit light when electric current is applied. OLEDs do not require backlighting, can be made to be flexible and lightweight, and have high contrast ratios. The basic structure consists of an anode, organic layers including a conductive layer and emissive layer, and a cathode. When voltage is applied, electrons flow through the organic layers and combine with holes to emit photons that produce light. Major applications of OLEDs include use in TVs, mobile phone displays, and flexible screens.