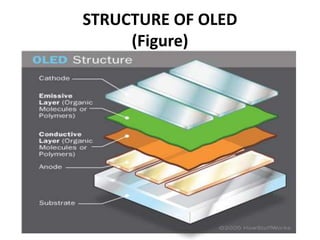
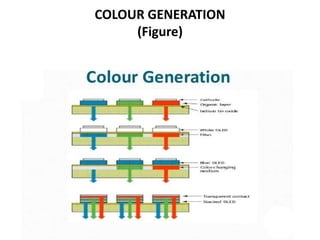
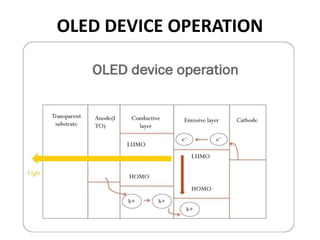
This presentation provides an overview of OLED technology. It discusses that OLEDs are made of thin films of organic materials that emit light when electric current is applied. The history of OLED development from 1987 to recent announcements of AMOLED displays is presented. The key features of OLEDs are their flexibility, light weight, high contrast and brightness from all viewing angles. The common types of OLEDs and their applications in televisions, phones and laptops are also summarized along with the advantages of OLEDs over LCDs and some current disadvantages that researchers are working to improve.