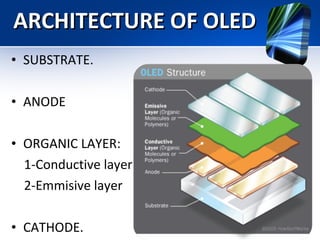
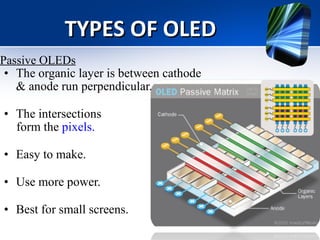
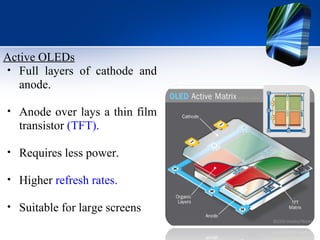
The document outlines the fundamentals and history of Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs), highlighting their construction, types, advantages, and disadvantages. It discusses their applications in various devices like TVs, smartphones, and flexible screens, as well as the challenges in manufacturing and longevity. Future prospects for OLED technology include improving efficiency and lifespan, while also exploring innovative applications such as curved displays and data glasses.