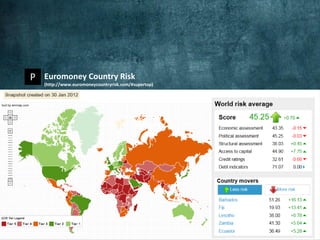
The document outlines various types of political risks that can affect multinational enterprises (MNEs) at the firm, country, and global levels. It emphasizes the importance of analyzing these risks, including governance and cultural factors, to prepare and negotiate effectively, while also highlighting the challenges of predicting events like terrorism. Additionally, it discusses the implications of corporate social responsibility and sustainable development in relation to these risks.