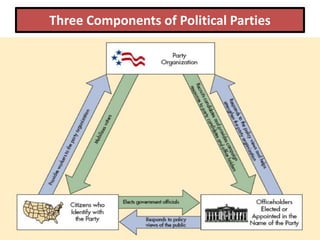
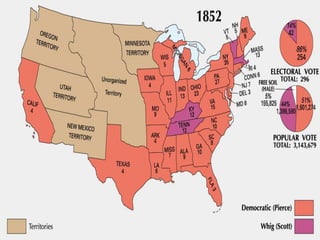
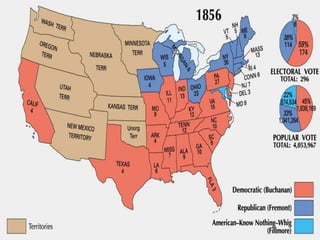
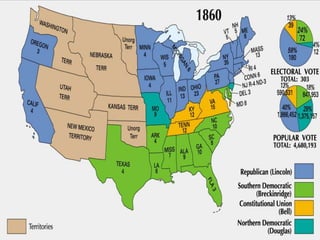
The document provides an overview of political parties, differentiating them from interest groups and outlining their functions, such as recruiting candidates and mobilizing citizens. It discusses the dominance of the two-party system in the U.S., the role of minor parties, and historical developments including realignment and dealignment of party loyalties. Additionally, it addresses the evolution of party conventions and the impact of gerrymandering on political representation.