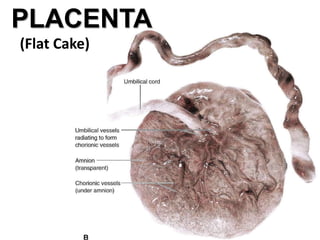
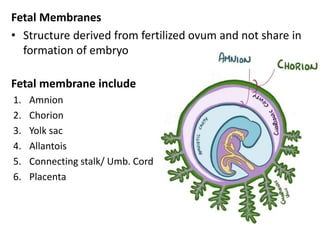
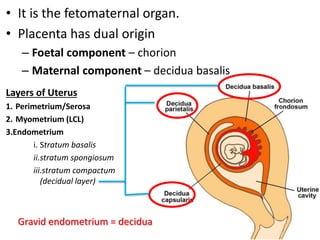
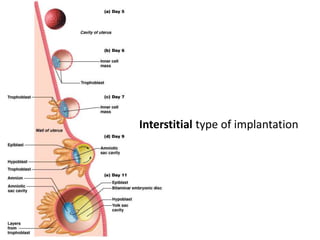
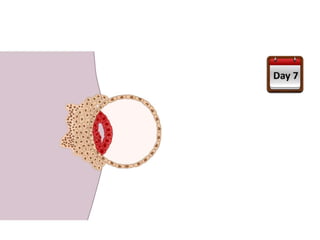
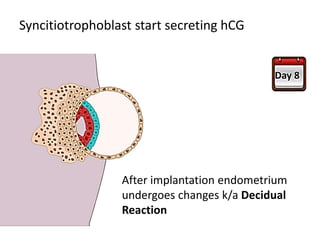
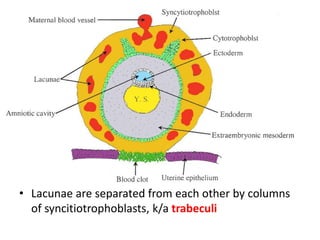
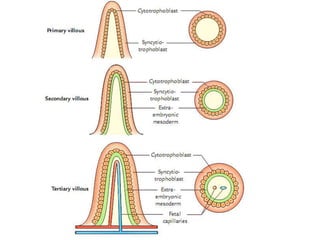
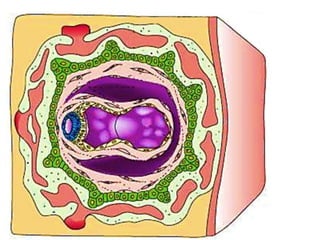
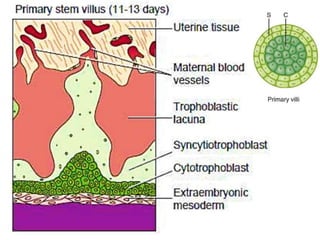
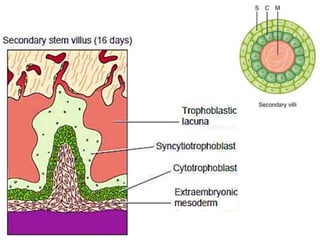
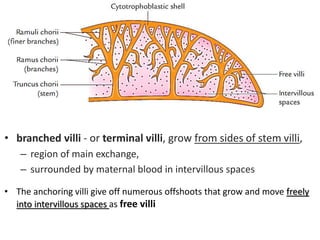
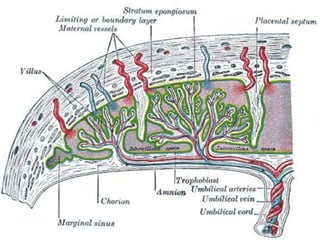
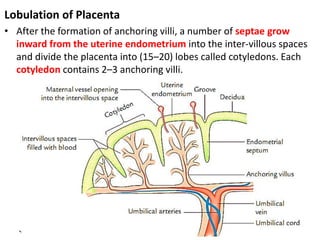
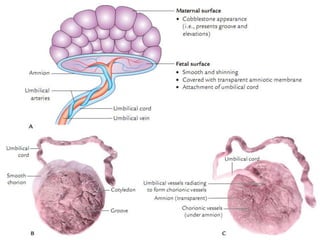
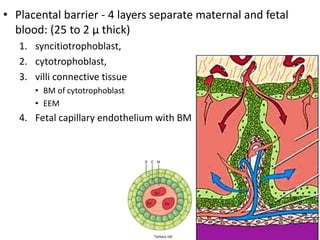
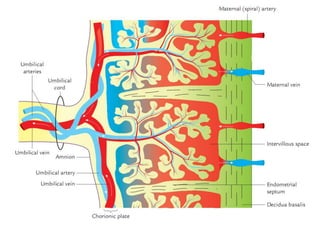
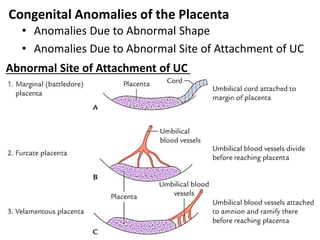
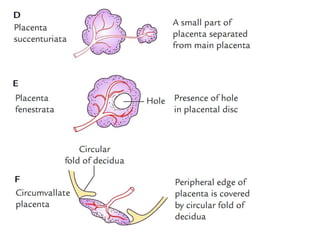
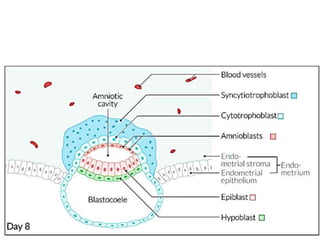
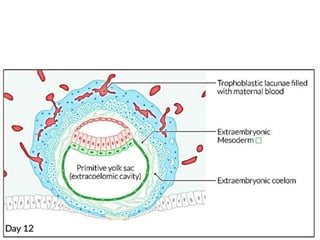
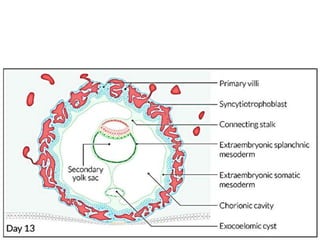
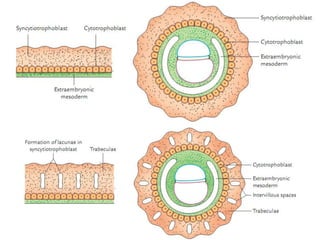
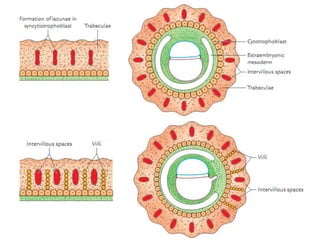
The placenta functions to exchange gases, transport nutrients and waste, and transmit antibodies between the mother and fetus. It is formed from fetal membranes originating from the fertilized ovum. The placenta has a dual origin from the fetal chorion and maternal decidua basalis. Chorionic villi invade the endometrium and develop into stem villi that anchor the placenta and give rise to branching terminal villi for main nutrient exchange with the maternal blood in the intervillous spaces. The placenta develops lobes and circulates both maternal and fetal blood to facilitate transfer between the two.