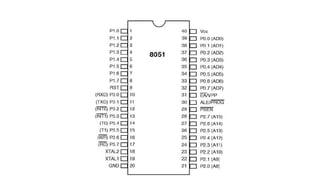
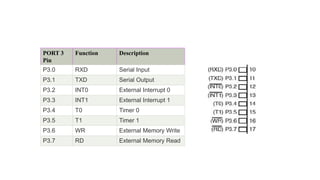
The document provides a detailed pin configuration and function description for the 8051 microcontroller, which consists of 40 pins. It outlines various ports, including bidirectional I/O ports and their special functions, reset input, ground connection, and voltage supply. The document serves as a guide to understanding the key functionalities associated with each pin of the microcontroller.