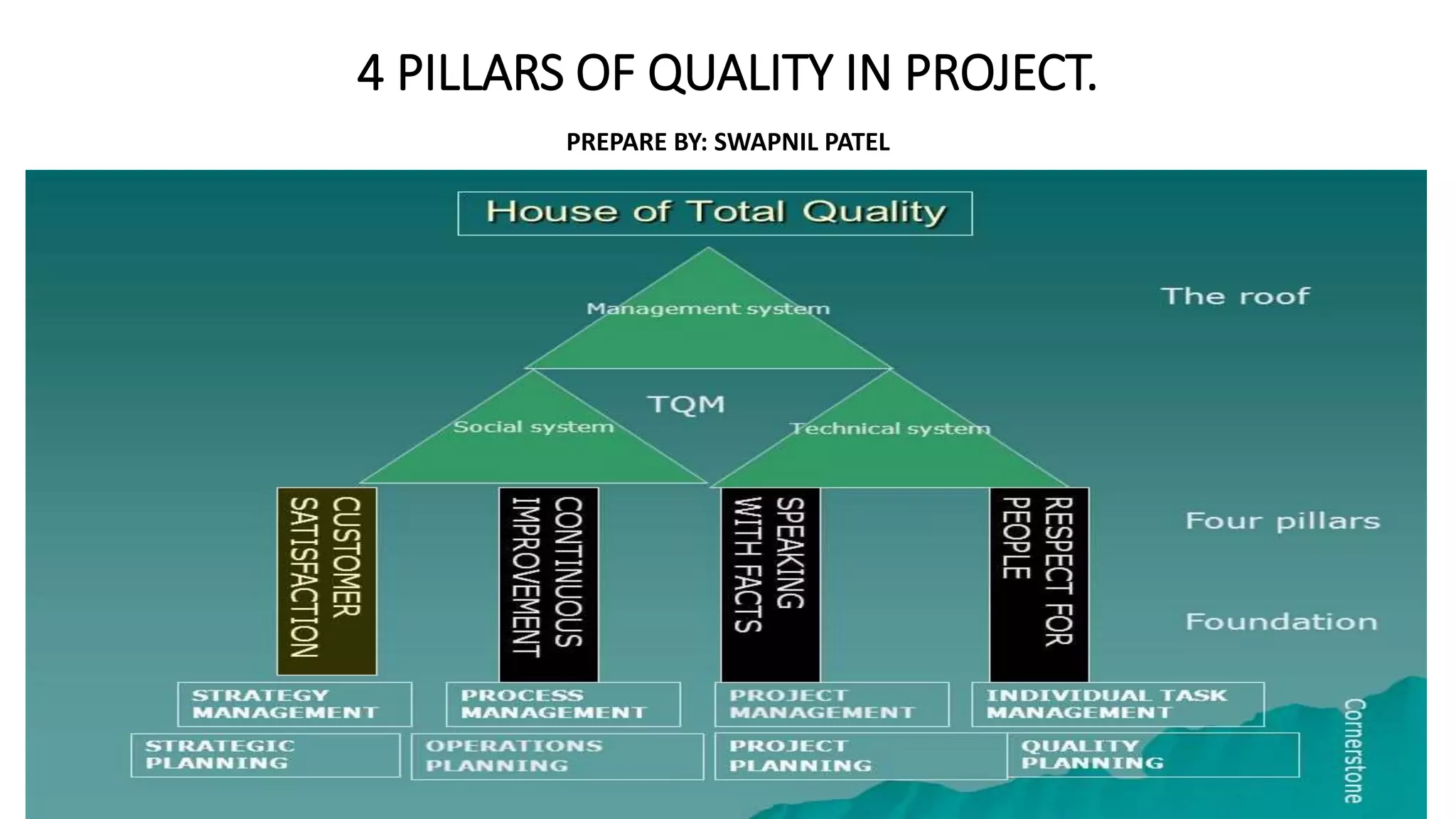
The document outlines the four pillars of quality in project management: (1) customer satisfaction, (2) continuous improvement, (3) fact-based management, and (4) respect for people. It describes each pillar in detail, including identifying stakeholders and their requirements for pillar 1, using PDCA and SIPOC models to manage processes for pillar 2, measuring variation and collecting data for pillar 3, and empowering and respecting individuals for pillar 4. The overall goal is to establish a culture focused on quality throughout all levels and functions of an organization's projects.