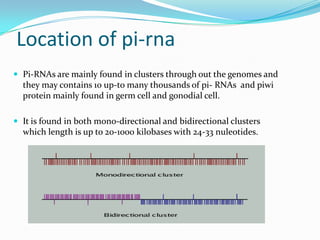
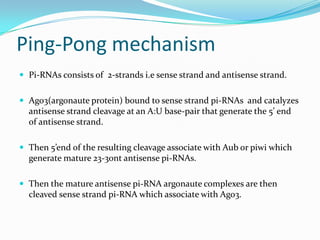
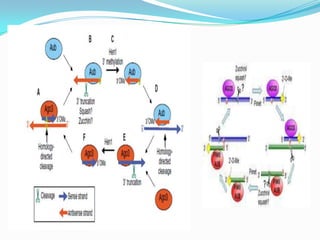
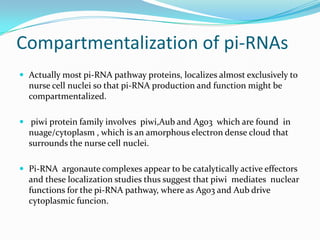
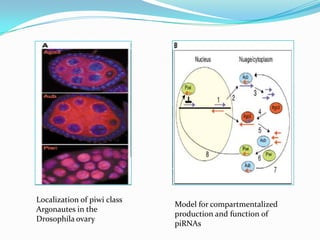
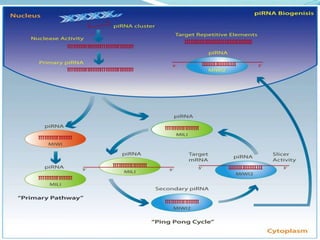
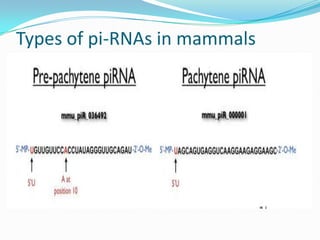
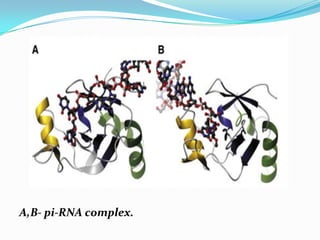
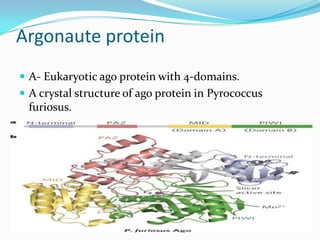
This document discusses PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs), a class of small non-coding RNAs that interact with PIWI proteins. It describes how piRNAs were discovered in Drosophila and their role in silencing transposons in the germline. The document outlines piRNA biogenesis, including their location in clusters in genomes and the "ping-pong" mechanism of biogenesis. It also discusses compartmentalization of the piRNA pathway and functions of piRNAs in maintaining genome integrity, transposon silencing, and fertility.