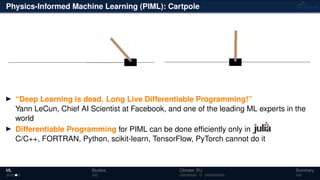
This document summarizes research on physics-informed machine learning methods for data and model analysis. Key points include:
1) The methods couple data and model analytics to extract common hidden features using techniques like nonnegative tensor factorization.
2) Physics constraints are incorporated to identify important processes in datasets and model outputs.
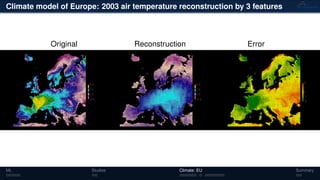
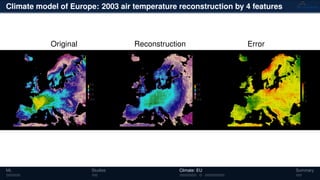
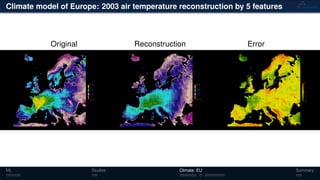
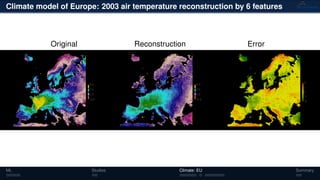
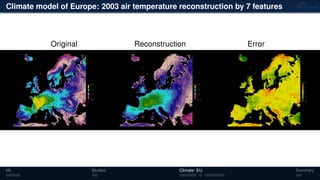
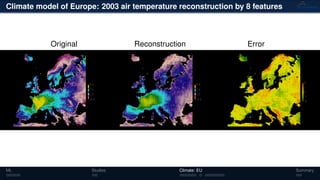
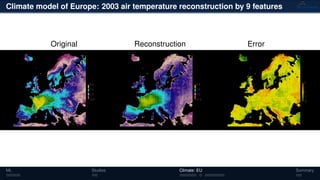
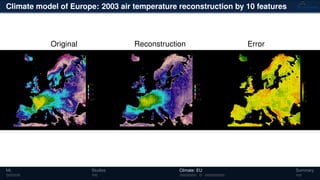
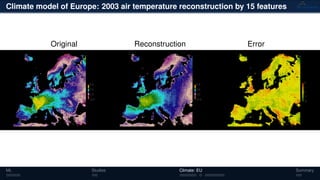
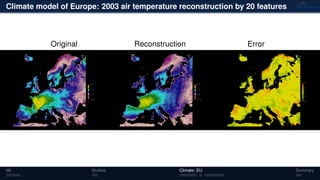
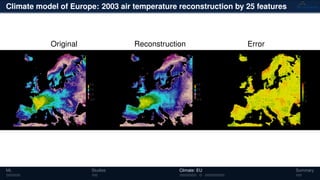
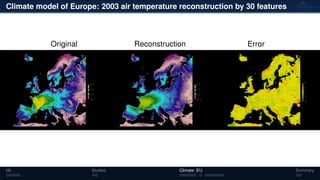
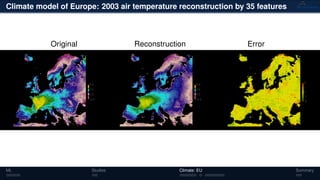
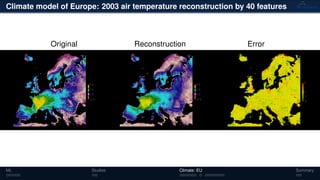
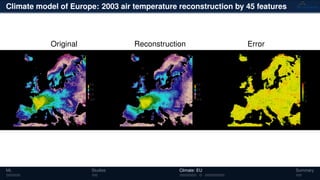
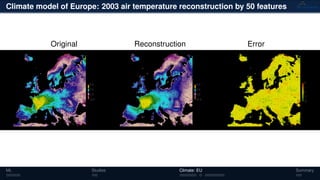
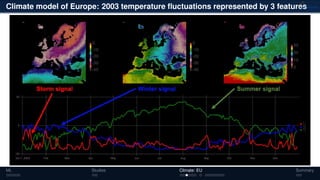
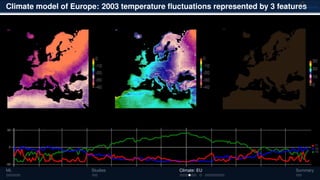
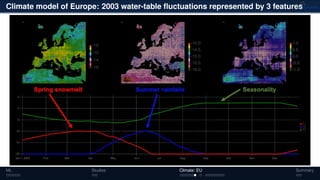
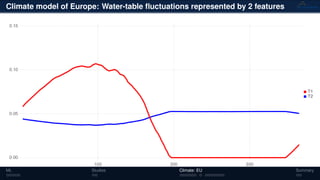
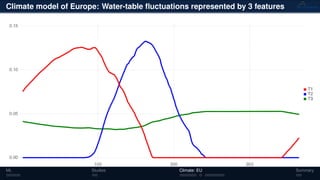
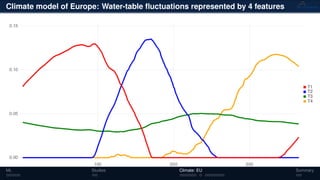
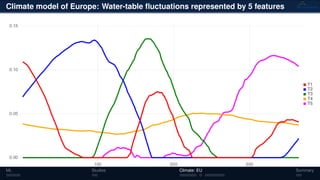
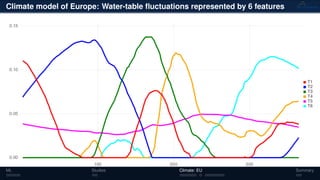
3) The methods have been applied to analyze climate model outputs from Europe to identify dominant patterns in air temperature and water tables over time.




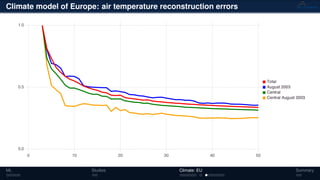
![Climate model of Europe: 2003 air temperature
Daily fluctuations in the air temperature
[◦
C]
Tensor: (424 × 412 × 365)
(columns × rows × days)
NTFk applied to extract dominant
hidden (latent) features
ML Studies Climate: EU Summary](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isr2019-190516201930/85/Physics-Informed-Machine-Learning-Methods-for-Data-Analytics-and-Model-Diagnostics-10-320.jpg)
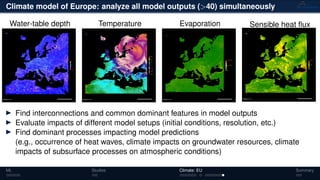
![Climate model of Europe: 2003 water-table depth
Daily fluctuations in the water-table
depth [m]
Tensor: (424 × 412 × 365)
(columns × rows × days)
NTFk applied to extract dominant
hidden (latent) features
ML Studies Climate: EU Summary](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isr2019-190516201930/85/Physics-Informed-Machine-Learning-Methods-for-Data-Analytics-and-Model-Diagnostics-13-320.jpg)
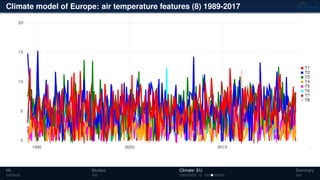
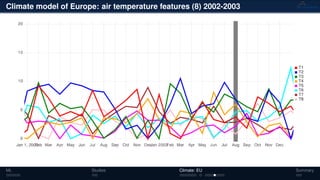
![Climate model of Europe: air temperature 1989-2017
Monthly fluctuations in the air
temperature from 1989 to 2017 [◦
C]
Tensor: (316 × 316 × 348)
(columns × rows × months)
NTFk applied to extract dominant
hidden (latent) features
ML Studies Climate: EU Summary](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isr2019-190516201930/85/Physics-Informed-Machine-Learning-Methods-for-Data-Analytics-and-Model-Diagnostics-20-320.jpg)