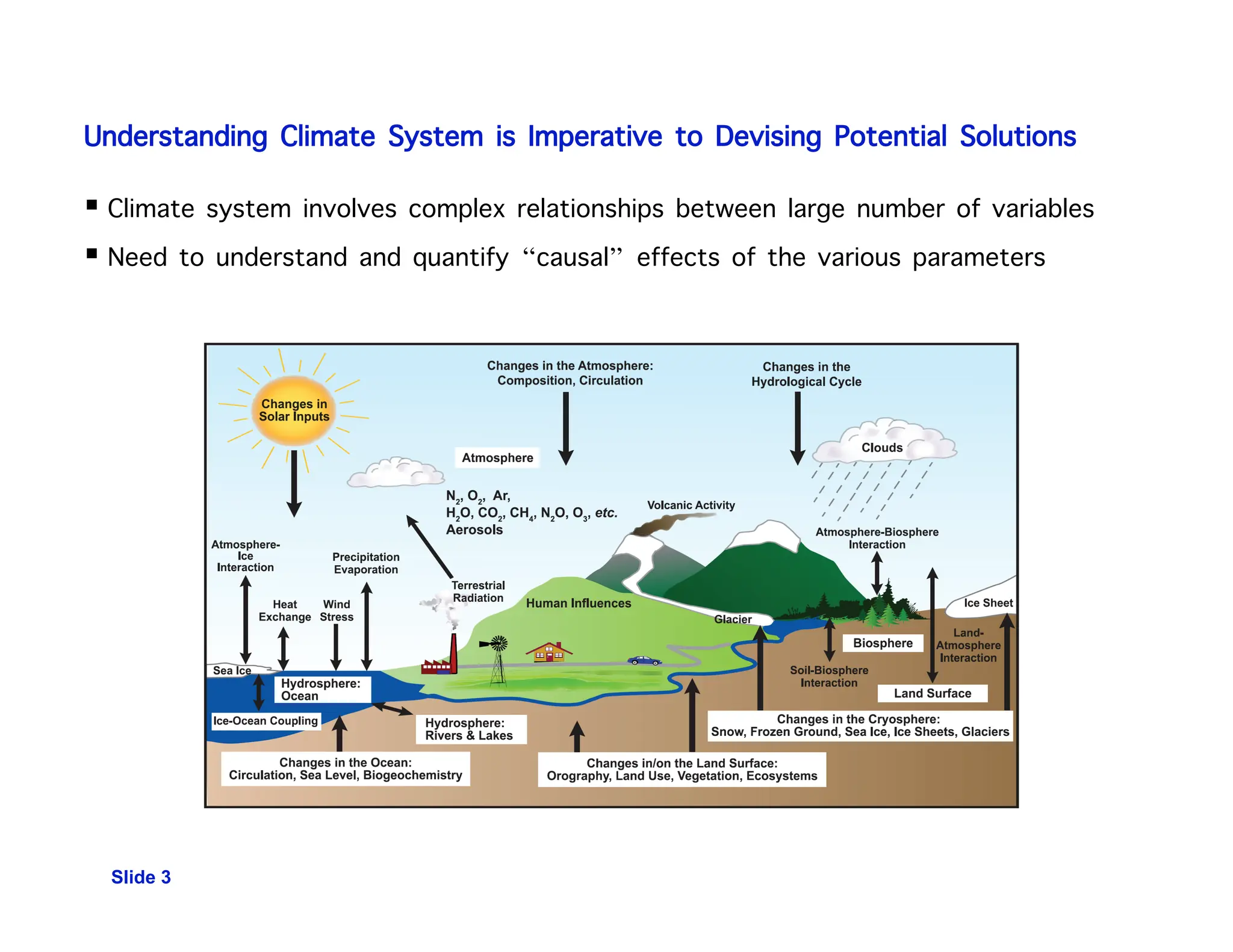
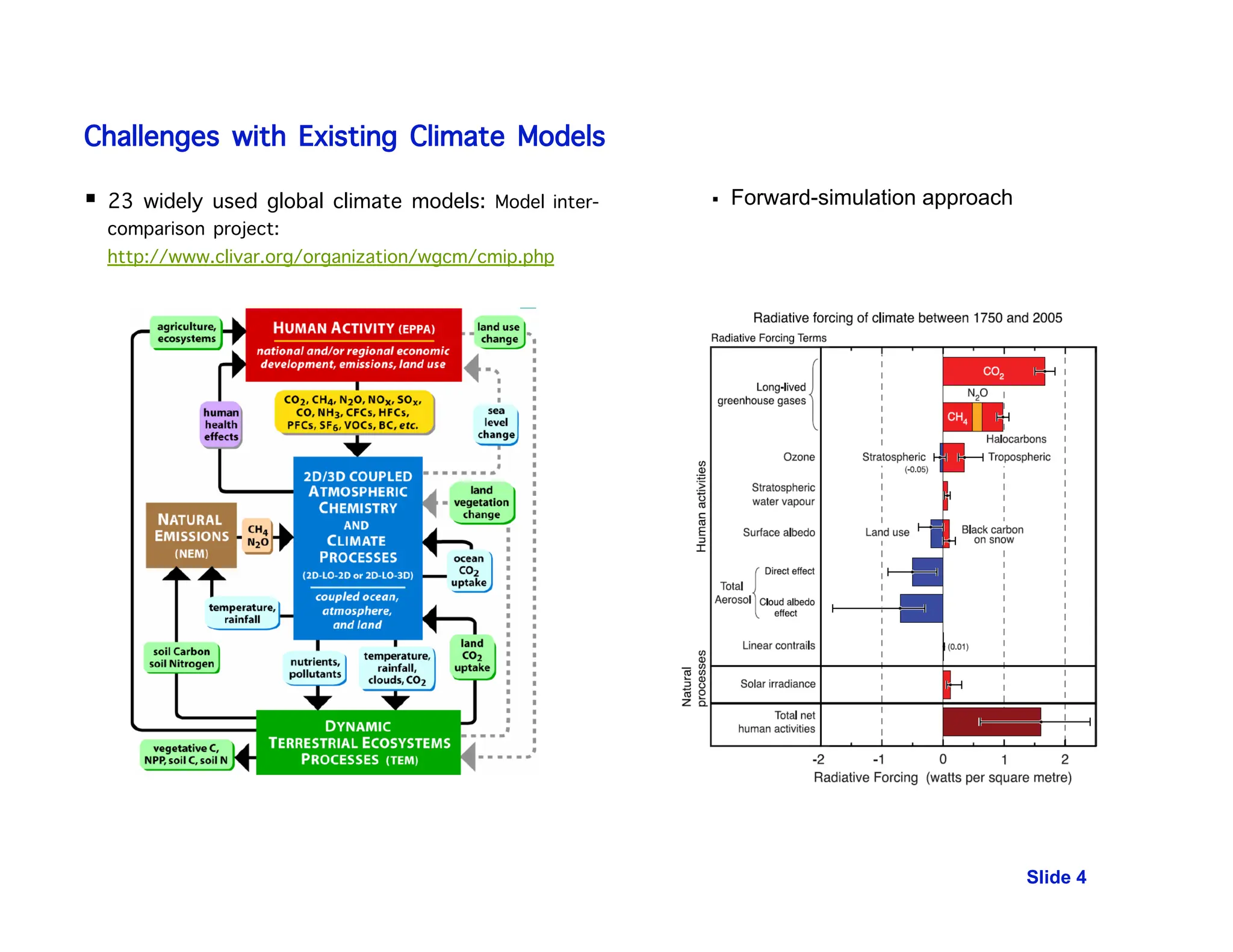
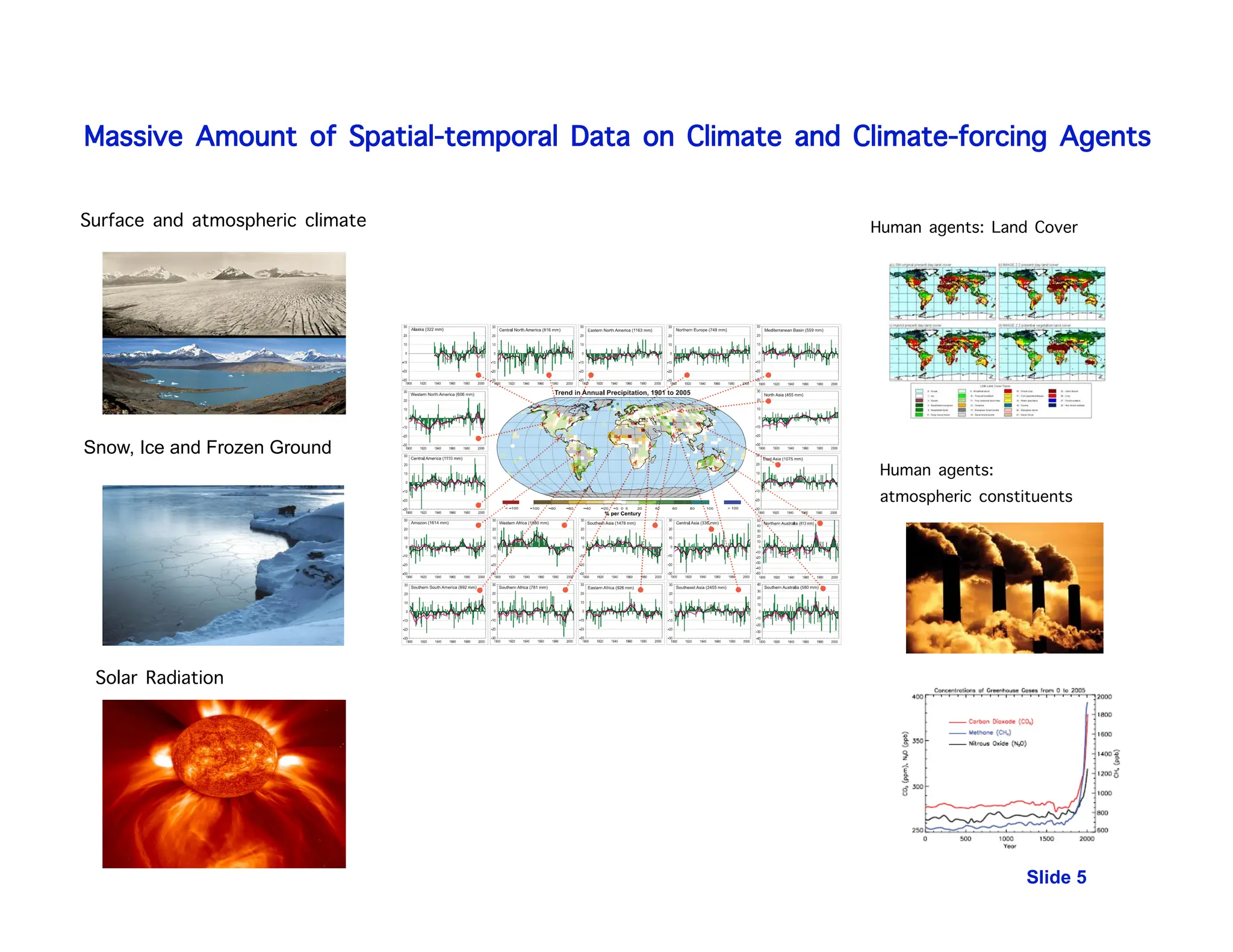
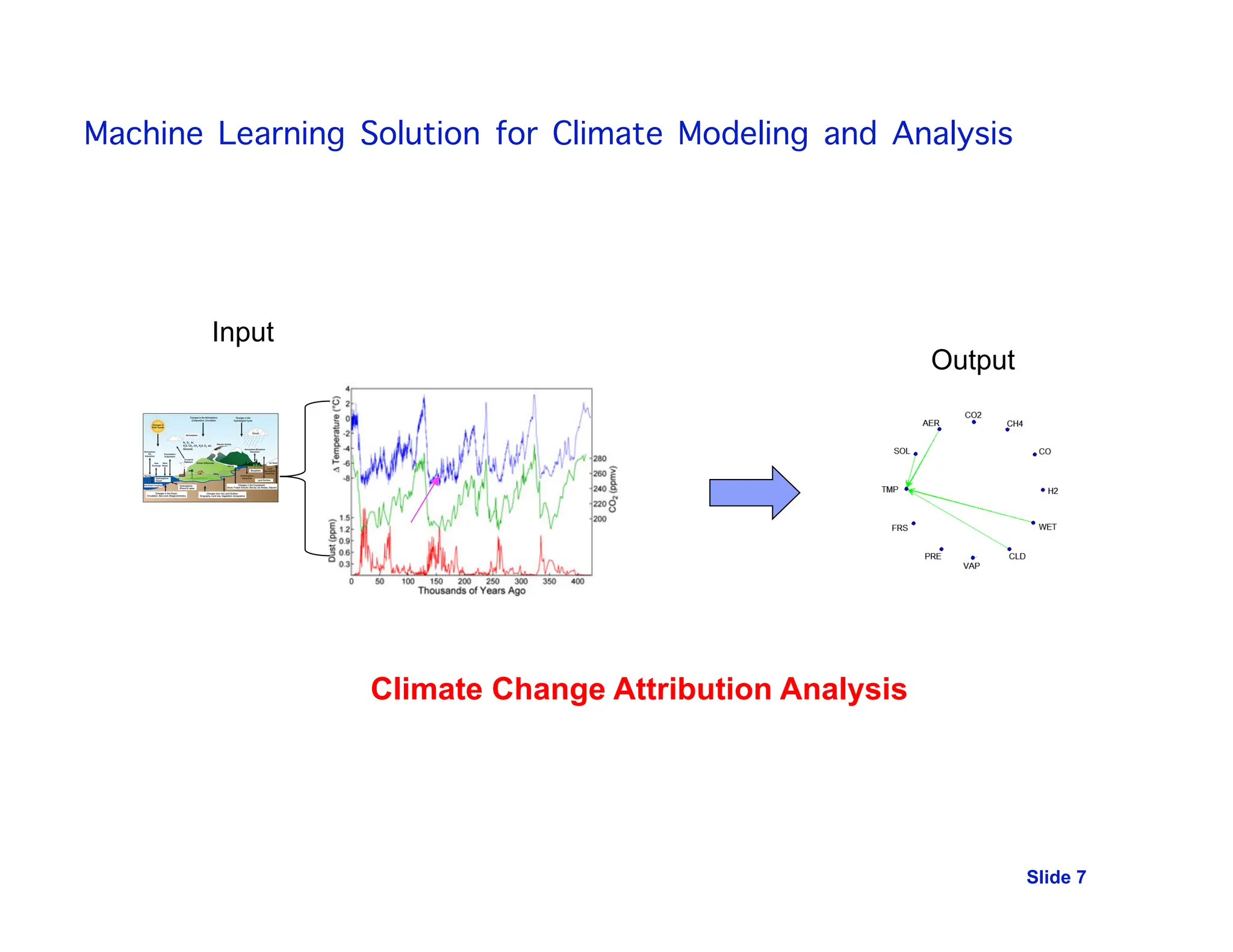
This document discusses the use of temporal causal models, specifically Granger graphical models, for analyzing massive time-series data in climate change attribution and other applications. It highlights the complexity of climate systems and the challenges with existing models, proposing machine learning solutions for better analysis and prediction, including hierarchical Bayesian models for extreme weather events. The research also emphasizes the significance of discovering causal relationships in multivariate time-series data, particularly within the context of gene regulatory networks.




![Graph Structure Learning
Graph Structure learning [Heckerman, 1995] has been an active research area
for decades
Recent progress on L1-penalized regression method for graph structure learning
LASSO regression for neighborhood selection [Meinshausen and Bühlmann, Ann. Stat. 06]
Consider the p-dimensional multivariate normal distributed random variable:$ $
The neighborhood selection can be solved efficiently with the LASSO
Block sub-gradient algorithm for finding precision matrix [Banerjee, JMLR 08]
Efficient fixed-point equations based on a sub-gradient algorithm [Friedman et al.,
Biostatistics 08]
Slide 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datamgmt-liu-231013144707-b6fe7b57/75/Data-Mgmt-Liu-pdf-11-2048.jpg)
![Generic Temporal Causal Modeling Method [KDD 2007 joint work with Arnold, Abe]
Slide 12
An example of REG can be Lasso [Tibshirani, 1996] Granger Causality
Neighborhood
selection
Structure learning is possible even when the number of variables is
significantly larger than that of the samples](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datamgmt-liu-231013144707-b6fe7b57/75/Data-Mgmt-Liu-pdf-12-2048.jpg)
![Temporal Causal Modeling for Time-series Data Analysis
Natural grouping of variables
Group Lasso and group boosting [KDD 2009; ISMB 2009, with Lozano, Abe and Rosset]
Non-stationary
Dynamic linear system [KDD 2009, with Kalagnanam and Johnsen]
Non-linear time-series
Non-parametric approach [AAAI 2010, with Chen, Liu and Carbonell]
Spatial time-series
Spatio-temporal regression via group elastic net [KDD 2009, with Lozano et al.]
Relational time-series
Hidden Markov random field [Snowbird, ICML 2010, with Niculescu-Mizi, Lozano and Lu]
Extreme event modeling
Spatial-temporal extreme value models [KDD 2009, with Lozano et al; NIPS 2011 in
preparation]
Slide 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datamgmt-liu-231013144707-b6fe7b57/75/Data-Mgmt-Liu-pdf-13-2048.jpg)

![Slide 15
Example 1: Relational Multivariate Time-Series Data [ICML 2010, Liu et al]
Input: multivariate time-series X(1), …, X(M) and relational graph GM
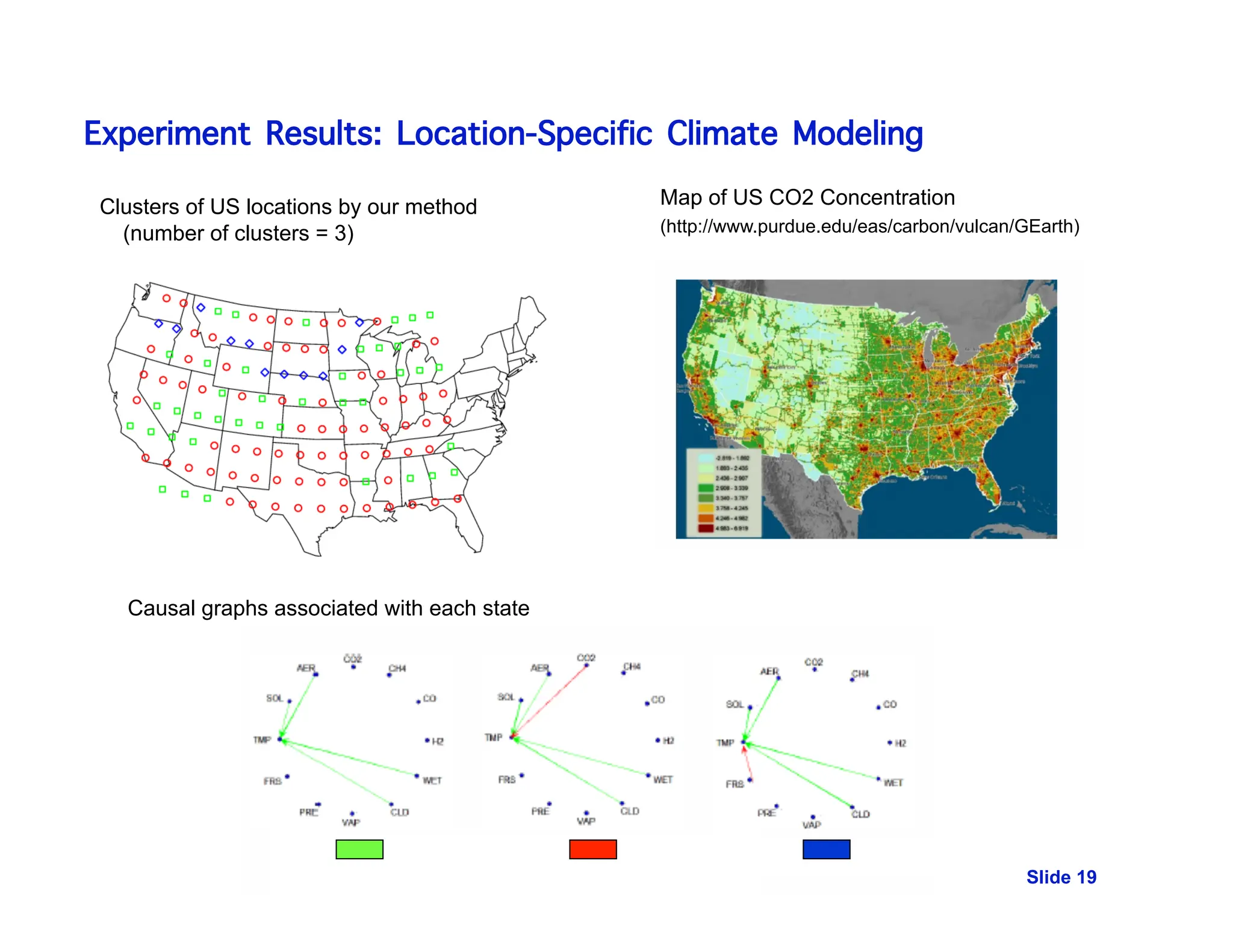
Goal: learn a reasonable temporal causal graph for each location/species ..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datamgmt-liu-231013144707-b6fe7b57/75/Data-Mgmt-Liu-pdf-15-2048.jpg)



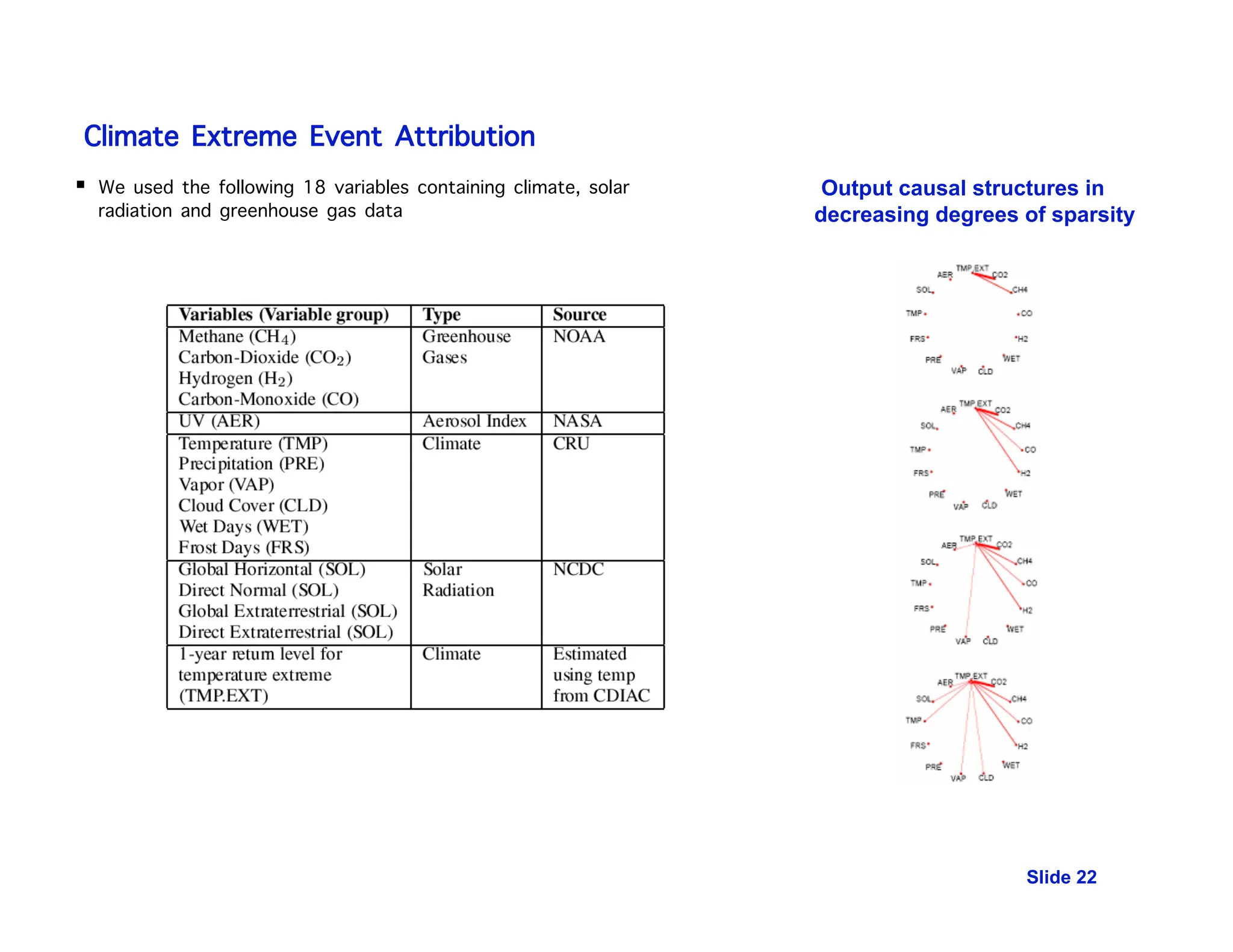
![Gene Regulatory Network Discovery [ISMB 2010]
Slide 24
Causal graphs discovered by our method
Evaluation against BioGRID
BioGRID
Recent Literature
Precision Recall F1
Our method 0.50 0.72 0.59
Sambo et al. (2008) 0.36 0.44 0.40
Gene expression regulatory networks for the human cancer cell HeLa S3 [Whitfield
et al., 2002]
Existing methods in the literature are unable to
Accommodate lags greater than one
Handle causality tests involving a large number of genes simultaneously
Our method addresses both limitations, achieved higher accuracy, and was able
to uncovered previously uncaptured relationships
CCNA2 to PCNA verified in [Liu, et al 2007]
CCNE1 to ETF1 verified in [Merdzhanova, et al 2007]
CCNE1 to CDC6 verified in [Furstenthal, et al 2001]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datamgmt-liu-231013144707-b6fe7b57/75/Data-Mgmt-Liu-pdf-24-2048.jpg)

