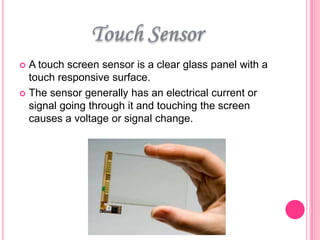
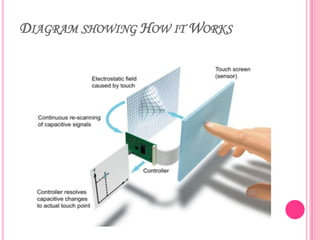
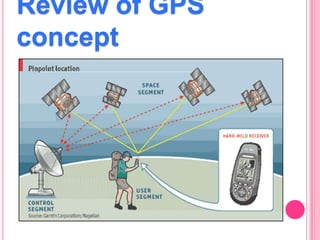
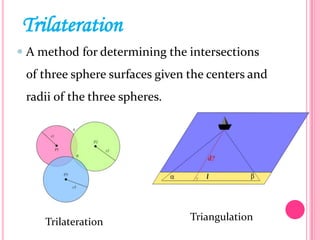
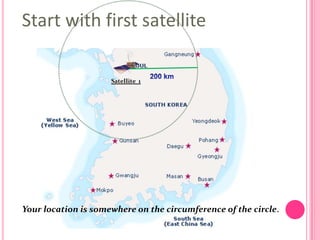
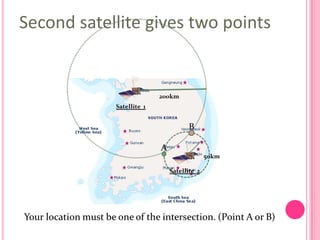
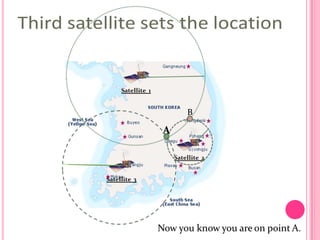
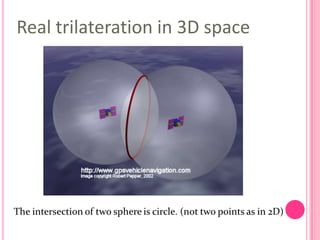
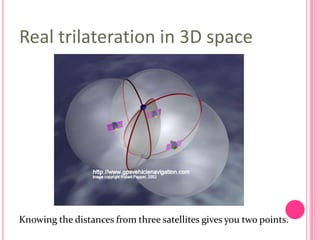
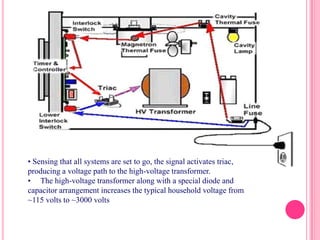
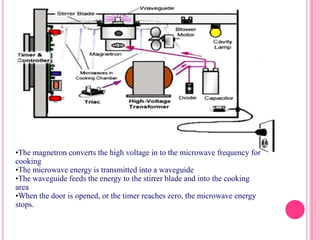
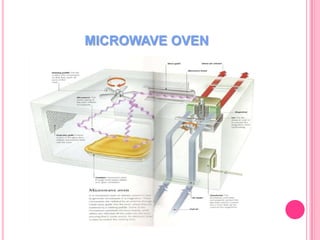
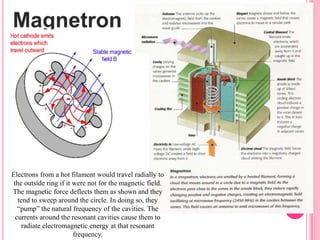
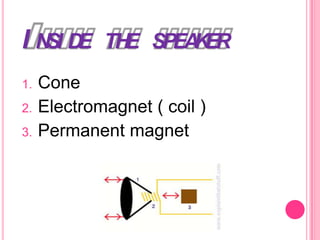
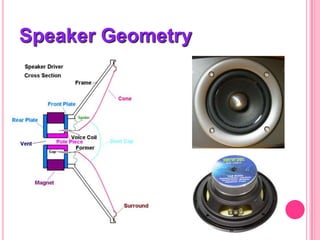
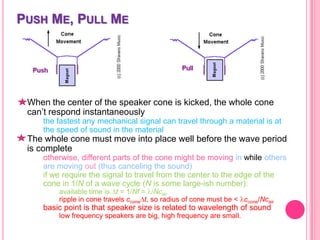
This document summarizes information about several physics projects: a touch screen, GPS, microwaves, bike pumps, and speakers. It provides details on how each system works through explanations of components and diagrams. The touch screen section describes the main parts of a touch screen including the sensor, controller and driver. It explains that touching the sensor causes a voltage change that is detected by the controller. GPS is described using the concept of trilateration to determine location from distances to multiple satellites. Microwaves are used to heat food by oscillating water molecules. Bike pumps compress air that is stopped from exiting by a one-way valve. Speakers work by an electromagnet vibrating a cone to create pressure waves in