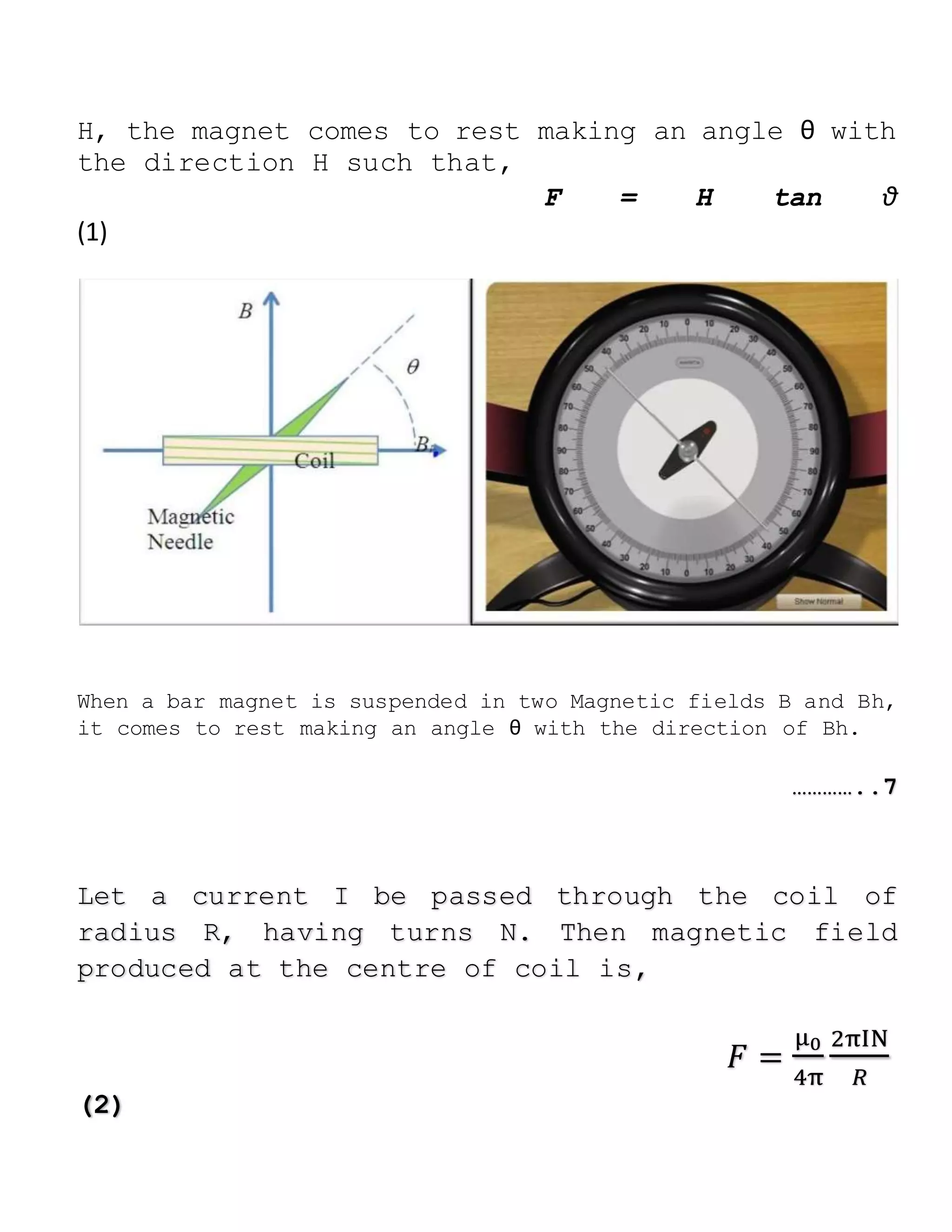
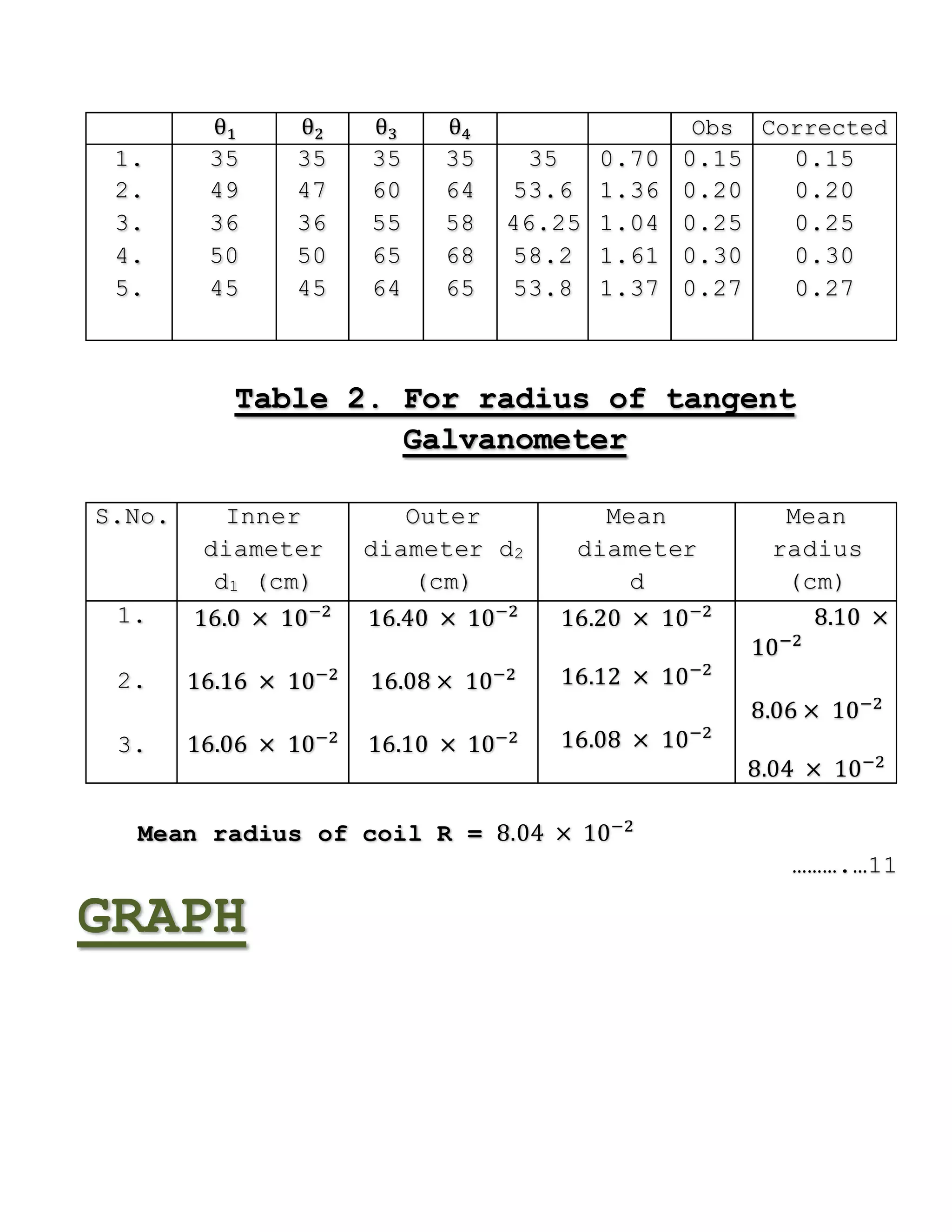
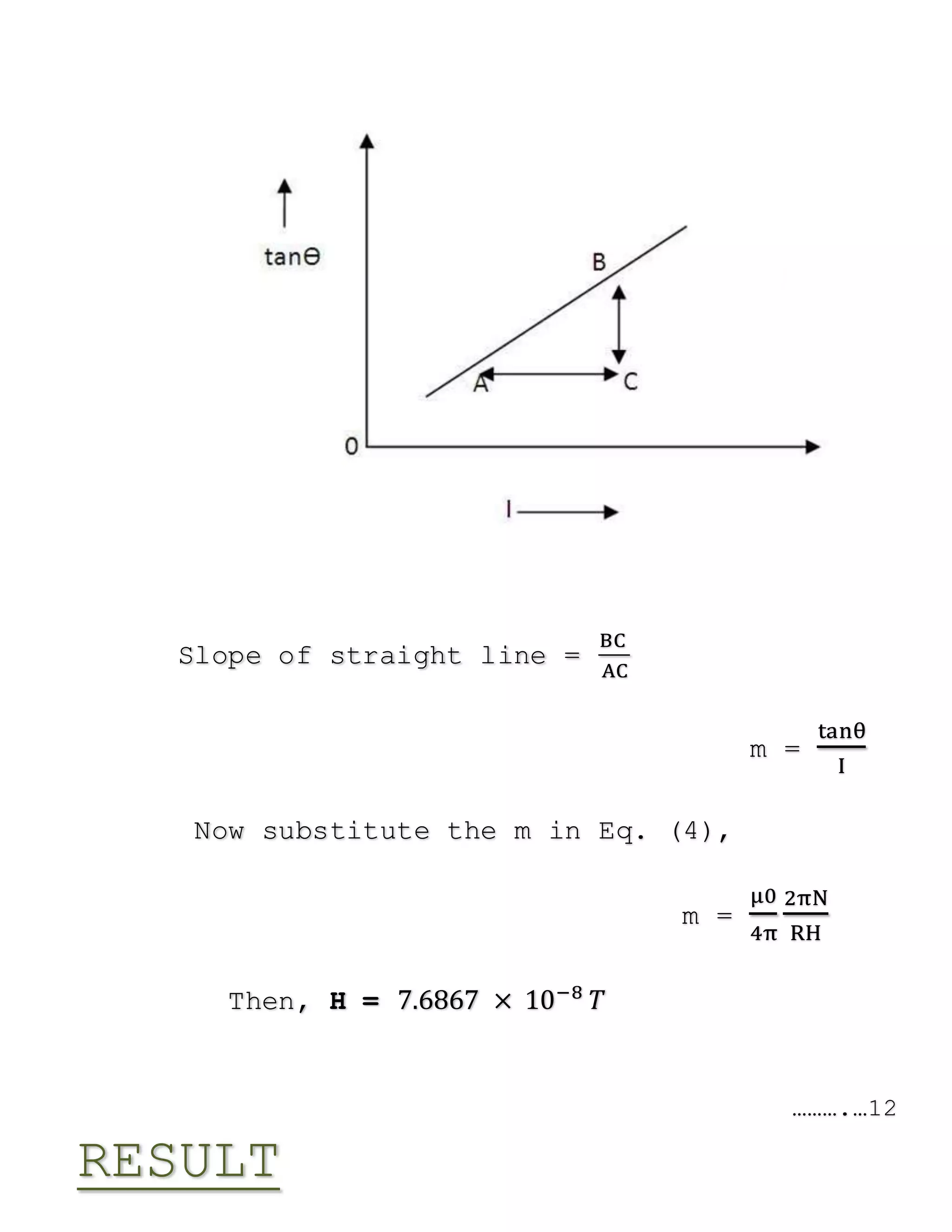
The document outlines a physics project focused on studying the Earth's magnetic field using a tangent galvanometer. It includes acknowledgments, an overview of the galvanometer's history and functioning, project aims, apparatus required, theoretical background, procedure, observations, results, precautions, sources of error, and applications. The final result approximates the value of the Earth's magnetic field at 7.6867 × 10−8 T.