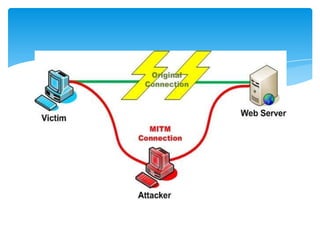
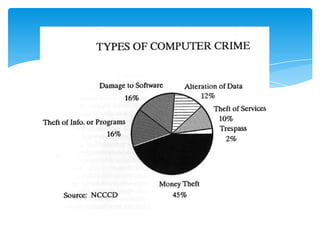
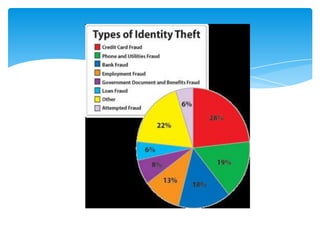
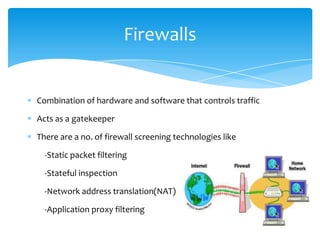
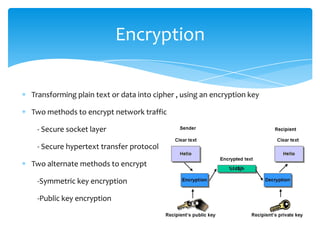
The document discusses system security and tools used to protect information resources. It covers topics like system vulnerability and abuse, as well as technologies and tools used for protection. One section summarizes a group project on this topic led by Karan Bhandari, Gurshawn Singh, and Nishad Prabhu. The document then explains why systems are vulnerable and various security threats like malicious software, hackers, spoofing, denial of service attacks, and identity theft. It concludes by describing technologies like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, anti-virus software, encryption, and ways to ensure system availability.