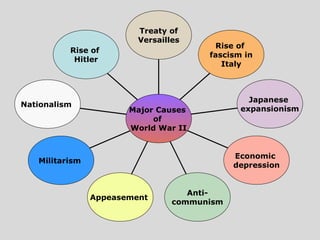
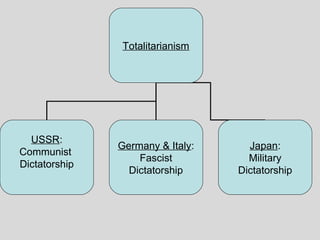
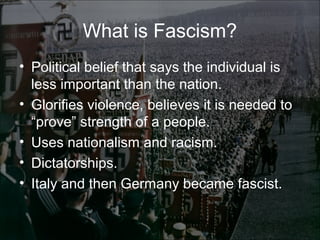
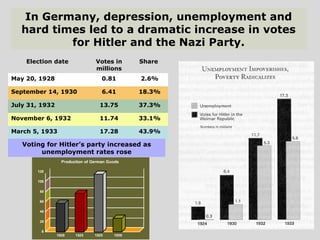
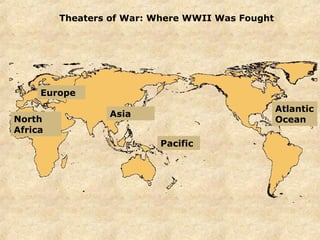
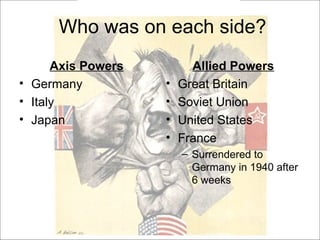
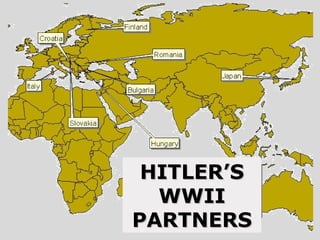
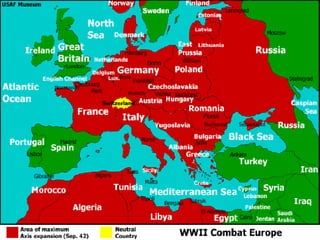
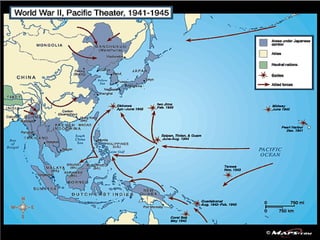
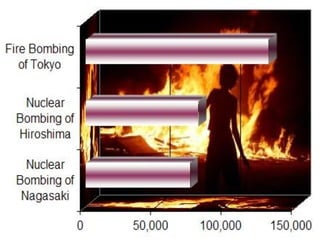
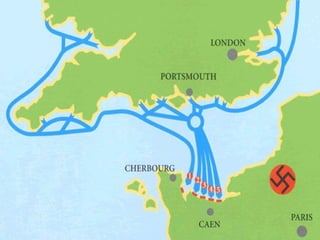
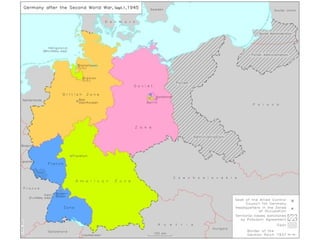
World War II was the largest and deadliest war in history. It began in 1939 after Germany invaded Poland and lasted until 1945. Key causes of the war included the Treaty of Versailles which punished Germany after WWI, the rise of totalitarian regimes like Nazi Germany and fascist Italy, Japanese expansionism, and the policy of appeasement by Western nations. The war was fought globally and involved over 30 countries organized into the Allied and Axis powers. Over 70 million people died making it the most devastating conflict in modern history.