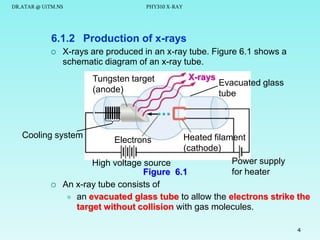
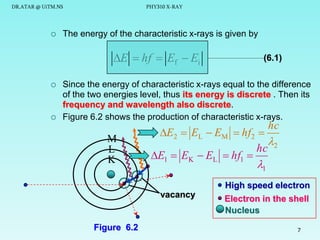
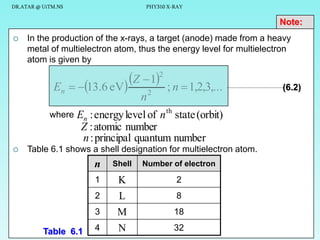
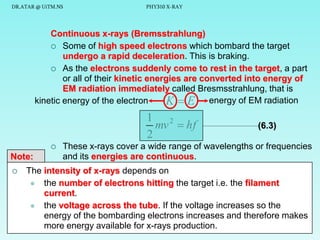
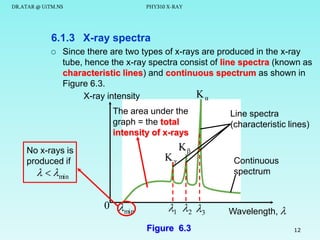
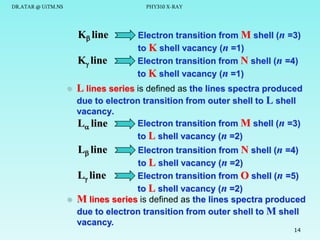
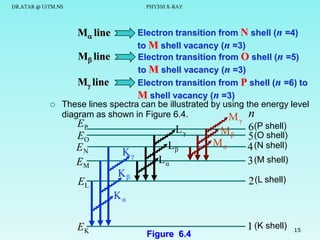
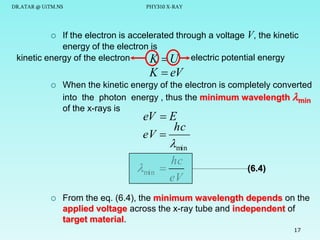
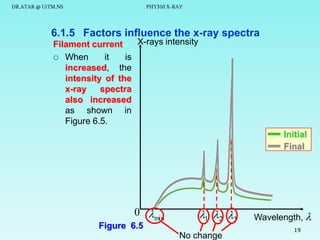
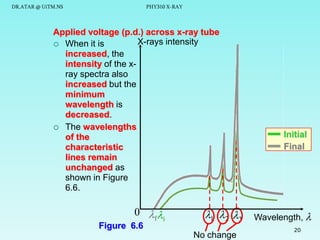
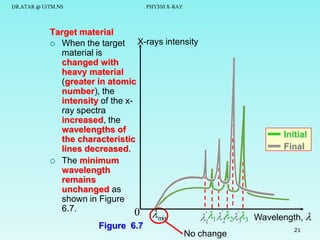
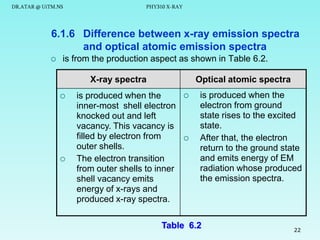
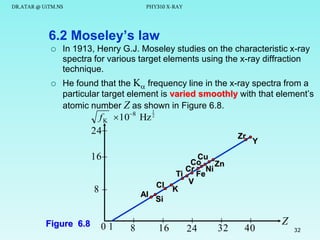
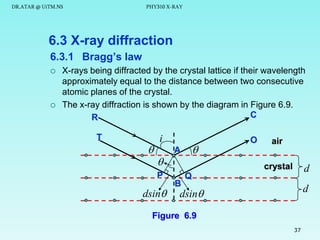
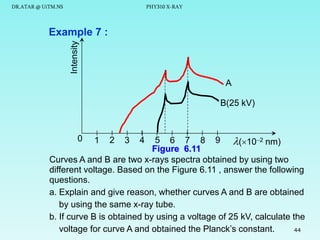
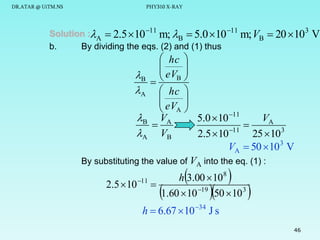
The document discusses x-rays and their production and spectra. It begins by defining x-rays as electromagnetic radiation with shorter wavelengths than UV produced when high-energy electrons bombard atoms. It then discusses how x-rays are produced in an x-ray tube through two mechanisms: characteristic x-rays produced via electron transitions in atoms, and continuous x-rays produced when electrons are decelerated. The document outlines the key components of an x-ray tube and the factors that influence x-ray spectra such as voltage, current and target material. It also compares x-ray emission spectra to optical atomic emission spectra.