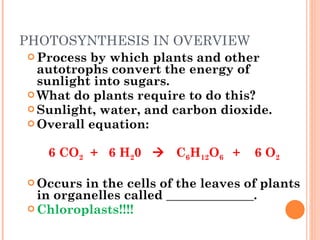
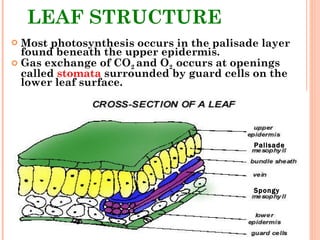
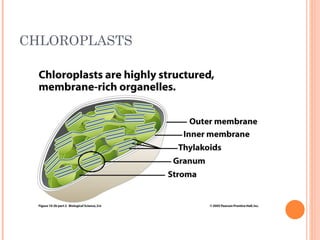
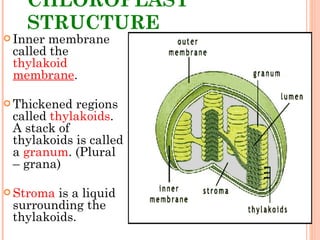
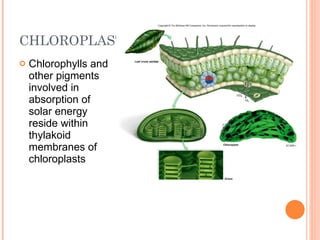
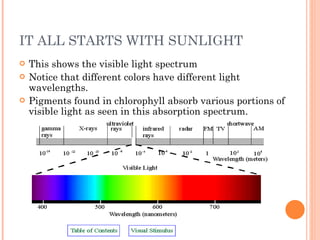
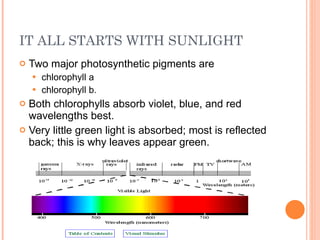
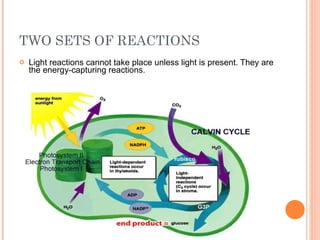
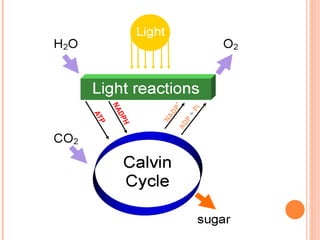
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants and other autotrophs convert sunlight, water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and energy-rich organic molecules like glucose. It occurs in chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll and other pigments. Chlorophyll absorbs blue and red light during the light-dependent reactions, which capture energy from sunlight to produce ATP and NADPH. These products are then used in the light-independent Calvin cycle to fix carbon from carbon dioxide into glucose.