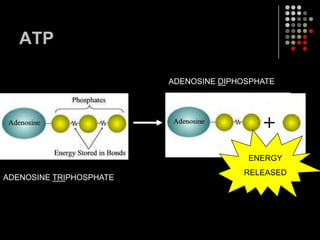
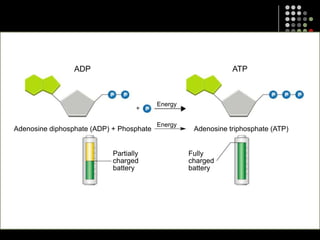
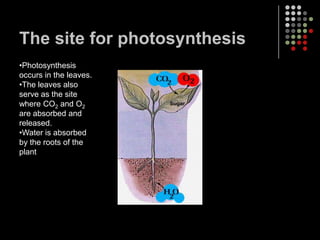
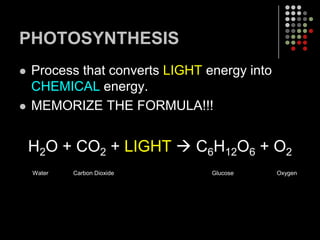
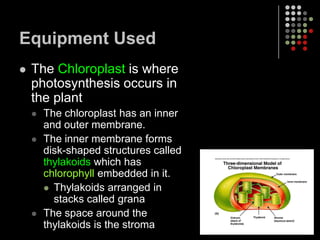
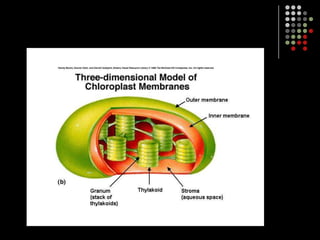
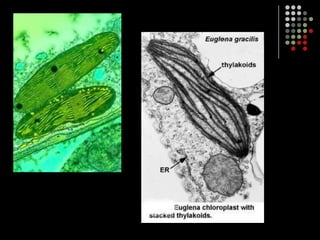
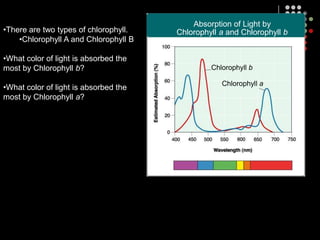
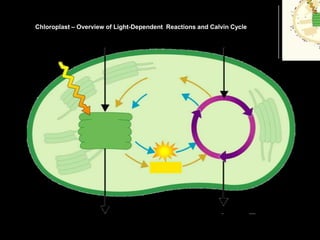
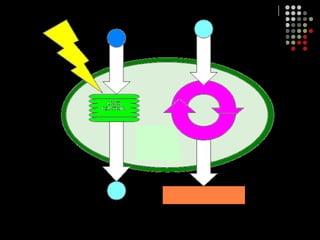
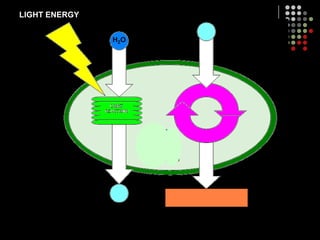
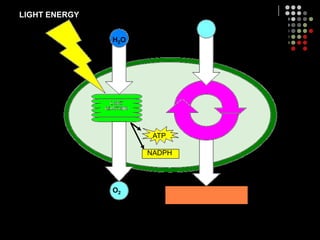
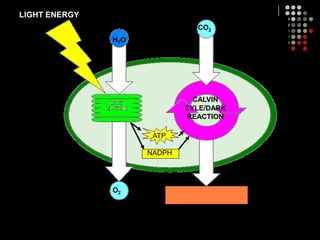
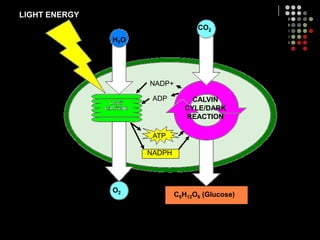
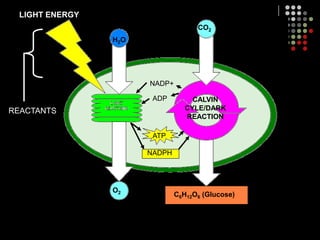
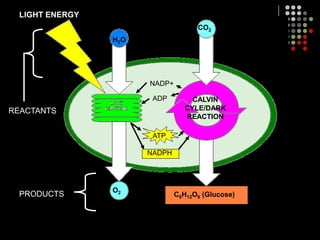
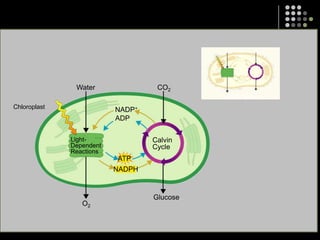
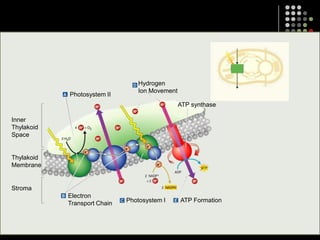
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of glucose. It occurs in two stages: the light-dependent reactions in which light energy is absorbed and used to produce ATP and NADPH, and the Calvin cycle where ATP and NADPH fuel the building of glucose molecules from carbon dioxide. Chlorophyll and other pigments are key to absorbing sunlight during the light-dependent reactions, which also produce oxygen as a byproduct. The energy-carrying molecules like ATP and NADPH are then used in the dark reactions to fix carbon from carbon dioxide into organic compounds like glucose.