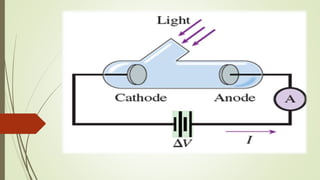
This document summarizes the photoelectric effect. It begins by discussing Hertz's observation that sparks occurred more readily when ultraviolet light was directed onto a light ball. Einstein later proposed that light is made up of discrete packets of energy called photons. The energy of a photon is given by E=hν, where h is Planck's constant and ν is the photon's frequency. When photons of sufficiently high frequency strike a metal surface, they can eject electrons from the metal in what is called the photoelectric effect. The document describes the experimental setup used to study the effect and provides the mathematical description relating the maximum kinetic energy of ejected electrons to the photon frequency and the metal's work function.