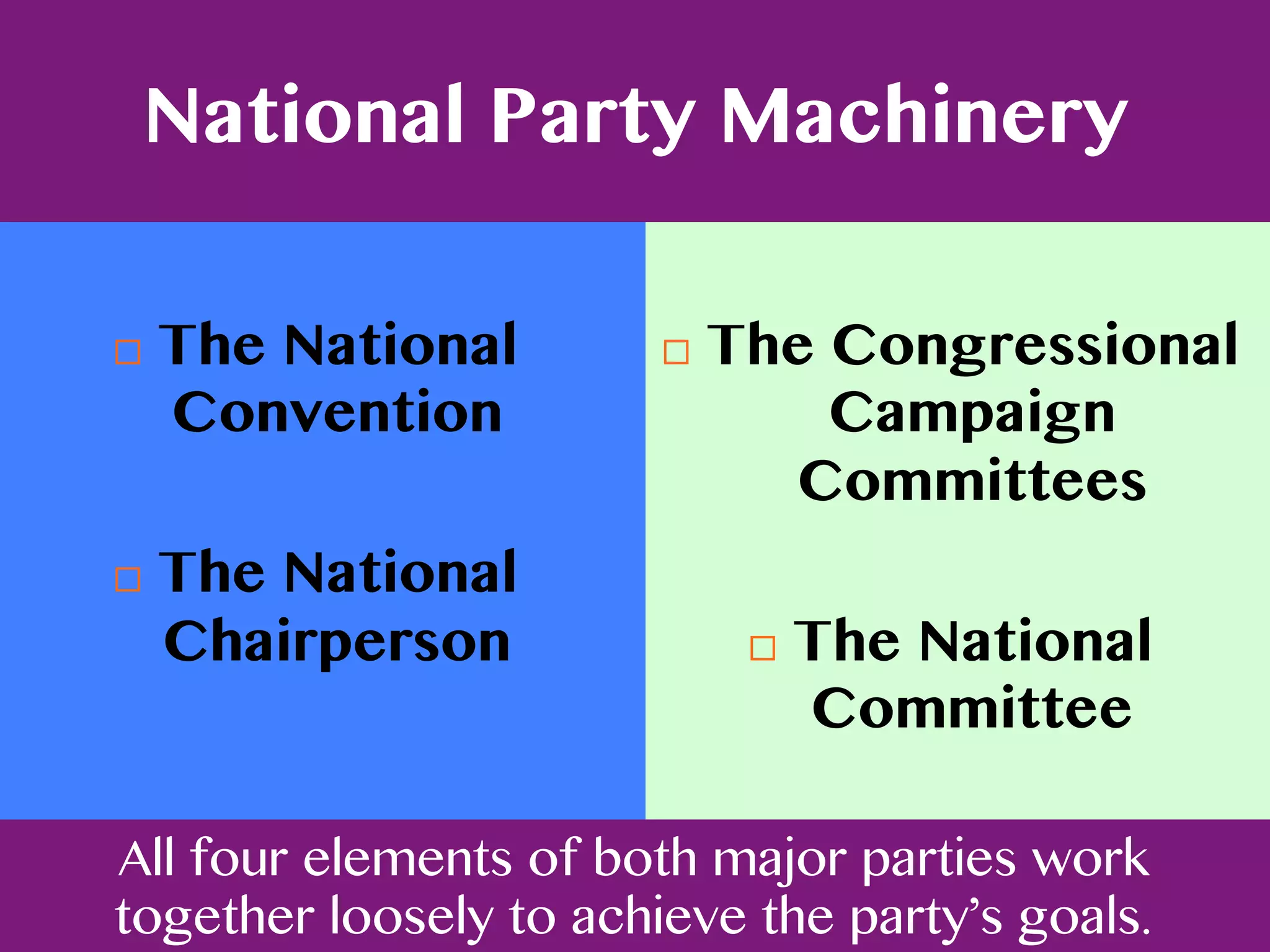
Political parties in the Philippines are diverse in ideology and numerous. Most parties lack grassroots membership and are led by political figures. There are three main types of party systems - one-party, two-party, and multi-party. The Philippines has a multi-party system where no single party gains majority control, requiring coalitions between parties. Major parties are decentralized with national and local machinery coordinating candidates and policies across branches of government.




























![These parties won more than 2% of the vote
Philippine
name
Party-lists represented in Congress
English
translation
Abbr. #1 nominee
Seats in the lower
house (PL only)
Notes
1st Consumers Alliance for
Rural Energy
1-CARE
Edgardo
Masongsong
2 / 58
Abono Fertilizer Abono Conrado Estrella III
2 / 58
Advocacy for Teacher
Empowerment Through Action,
Cooperation and Harmony
Towards Educational Reforms
A TEACHER Mariano Piamonte, Jr.
2 / 58
Agricultural Sector Alliance of
the Philippines
AGAP Nicanor Miral Briones
2 / 58
Akbayan
Citizens'
Action Party
Akbayan Walden Bello
2 / 58
Member of the Progressive
Alliance;
Consultative member of the
Socialist International;
Allied with Team PNoy
Ako Bicol
Political
Party
I am Bicol
Political Party
AKB
Christopher Co or
Emilio Ubaldo, Jr.
2 / 58
An Waray
The Waray
[people]
An Waray
Neil Benedict
Montejo
2 / 58
Bayan Muna Nation First Bayan Muna Neri Colmenares
2 / 58
Member of the Bagong
Alyansang Makabayan
Buhay
Hayaan
Yumabong
Life be
Allowed to
Prosper
Buhay Michael Velarde, Jr.
3 / 58
Citizens' Battle Against
Corruption
CIBAC
Sherwin Tugna or
Luis Lokin, Jr.
2 / 58
Cooperative NATCCO Network
Party
Coop-
NATCCO
Cresente Paez
2 / 58
GABRIELA Women's Party GABRIELA Luzviminda Ilagan
2 / 58
Member of the Bagong
Alyansang Makabayan
Magdalo
para sa
Pilipino
Cheer for
Filipinos
Magdalo Gary Alejano
2 / 58
OFW Family Club OFW Family Roy Señeres, Sr.
2 / 58](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/politicalpartiescopy-140920193330-phpapp01/75/Philippine-Political-Parties-29-2048.jpg)