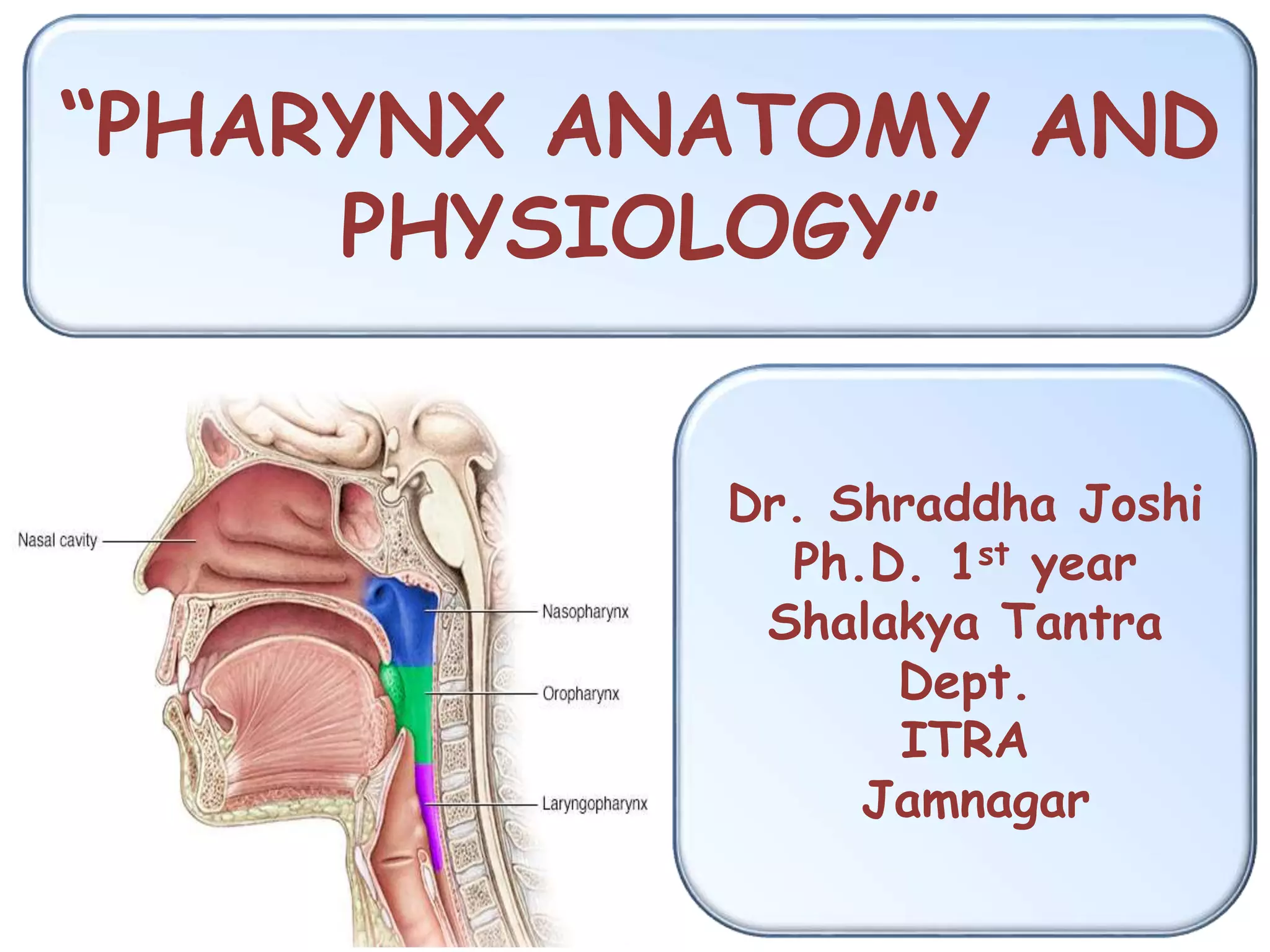
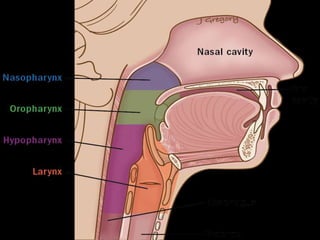
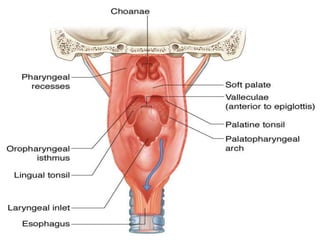
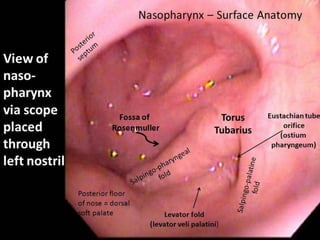
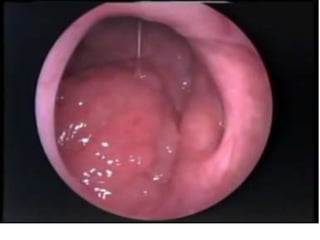
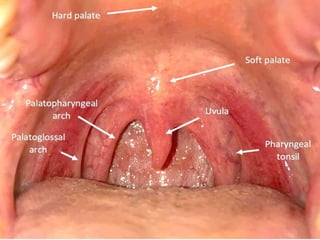
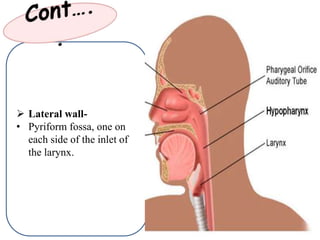
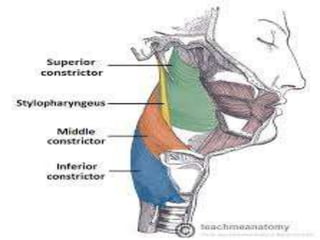
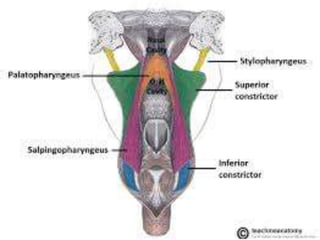
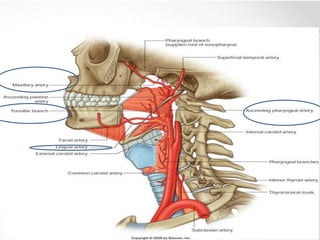
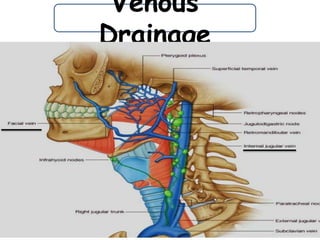
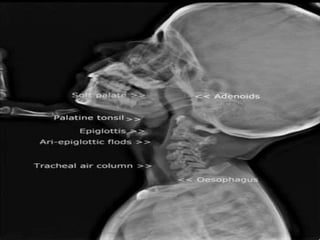
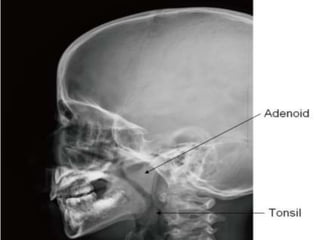
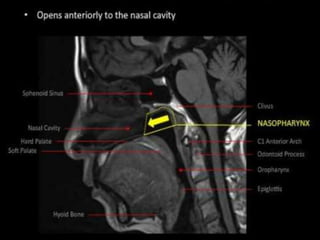
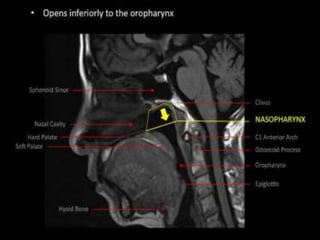
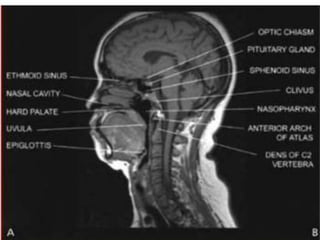
The pharynx is a muscular tube located behind the nose, mouth, and larynx. It is divided into three parts: the nasopharynx behind the nose, the oropharynx in the middle, and the hypopharynx behind the larynx. The pharynx has rigid walls and connects the nasal, oral, and laryngeal cavities. It is lined with squamous epithelium and contains three constrictor muscles between fascial layers. Blood supply comes from branches of the external carotid artery and veins drain into the retropharyngeal and deep cervical nodes. The pharynx is innervated by the pharyngeal plexus formed from the vagus, glossopharyngeal,