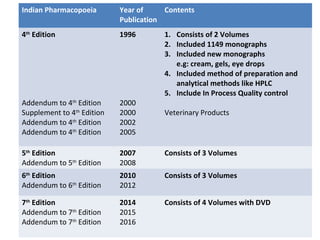
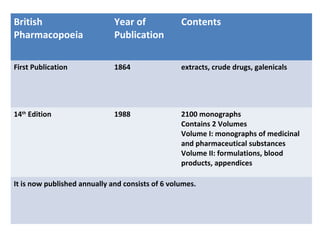
This document discusses various pharmacopoeias and formularies used around the world to set standards for drugs. It provides information on what pharmacopoeias and formularies are, how they differ, examples of major national and international ones like the Indian Pharmacopoeia, British Pharmacopoeia, United States Pharmacopoeia, and others. It also summarizes the history, contents and purpose of these important drug references.