This document discusses various pharmacopoeias from around the world. It defines a pharmacopoeia as an official book that sets quality standards for drugs. Key points include:
- Pharmacopoeias are published by governmental authorities and include monographs defining drugs' identity, purity, and specifications.
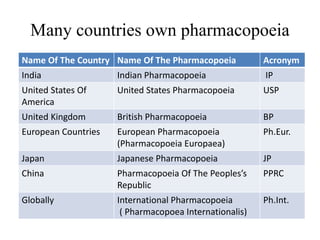
- Major pharmacopoeias discussed are those of India, United States, United Kingdom, European Union, Japan, and an International Pharmacopoeia.
- A monograph identifies a drug and includes tests for purity, strength and limits on impurities. It defines the standard for that substance.
- Pharmacopoeias are updated periodically to add new drugs and remove outdated ones. They help ensure uniform quality of