Embed presentation
Downloaded 153 times


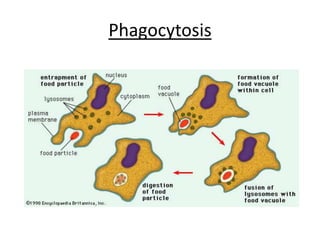

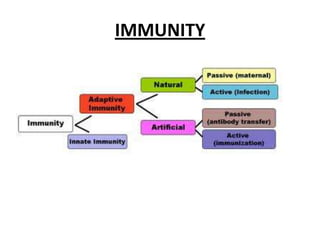



A phagocyte engulfs bacteria by fusing its cell membrane around the bacteria to form a vacuole. Enzymes are then secreted into the vacuole to digest the bacteria, and the soluble substances diffuse into the phagocyte's cytoplasm. Immunity can be either active, where an individual produces their own antibodies after infection or vaccination, or passive, where ready-made antibodies are received from another source such as a mother or laboratory animal serum.







