1. A pH-rate profile plots the log of the observed degradation rate constant (kobs) versus pH. It identifies the pH at which a drug is most stable by determining how the degradation rate changes with pH.
2. Just a 1 pH unit shift can cause a 10-fold change in a drug's degradation rate. pH-rate profiles are constructed to locate the optimum pH range for maximum stability.
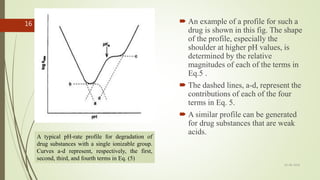
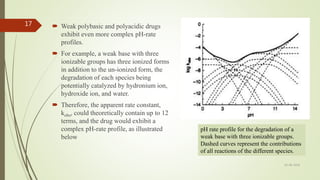
3. pH-rate profiles can indicate whether a drug's degradation is catalyzed by acid, base, or water. More complex profiles result for drugs with ionizable groups, as the degradation of each ionized form must be considered.




![-dc/dt = k1 [H+]c + k2 c + k3 [OH-]c …………….(1)
Rearranging the above equation,
-dc/c.dt = k1 [H+] + k2 + k3 [OH-]
(-dc/c.dt = kobs )
Therefore,
kobs = k1 [H+] + k2 + k3 [OH-]
k1 and k3 are second order constants
k2 is pseudo first order constant
02-08-2018
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phstabilityprofile-180802054148/85/pH-stability-profile-6-320.jpg)
![The pH v/s rate profile is constructed by one by one considering one
of the three kinetic terms predominanting.
When, k1 [H+] >>> k2 + k3 [OH-]
kobs = k1 [H+] and log kobs =log k1 – pH…… (2)
When, k2 >>> k1 [H+] + k3 [OH-]
kobs = k2 and log kobs =log k2 …… (3)
When, k3 [OH-] >>> k1 [H+] + k2
kobs = k3 [OH-] and log kobs =log k3 + pH…… (4)
02-08-2018
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phstabilityprofile-180802054148/85/pH-stability-profile-7-320.jpg)

![ If the contribution of first and second term is larger than third
term, the pH rate profile shown below is obtained (acid catalysed)
02-08-2018
9
kobs = k1 [H+] + k2 + k3 [OH-]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phstabilityprofile-180802054148/85/pH-stability-profile-9-320.jpg)