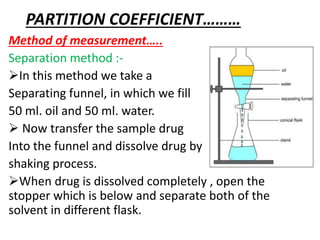
The document discusses the partition coefficient, which is a measurement of a drug's lipophilicity or hydrophilicity. It defines the partition coefficient as the ratio of the amount of unionized drug distributed between the organic and aqueous phases at equilibrium. It describes how the partition coefficient is measured by dissolving a drug into two immiscible solvents - an organic and aqueous phase - and determining the amount of drug dissolved in each. It outlines a separation method using a separating funnel to dissolve and separate the drug into the two phases, then using analytical techniques like UV spectroscopy to determine the drug concentration in each phase and calculate the partition coefficient.