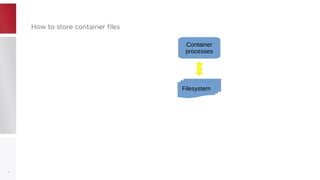
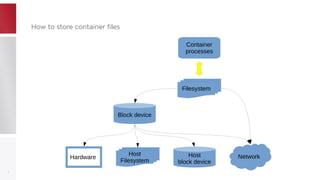
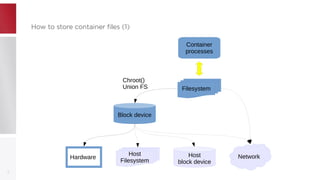
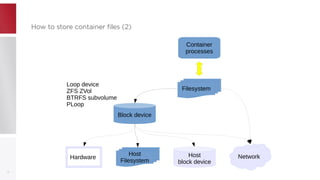
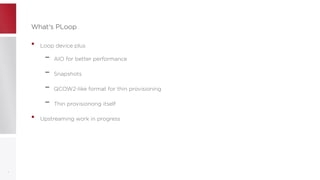
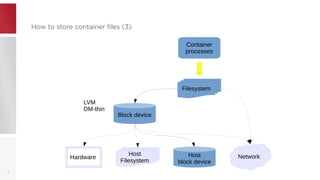
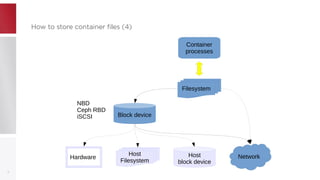
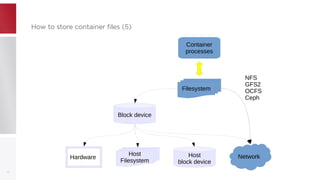
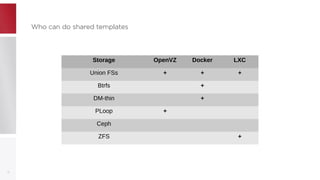
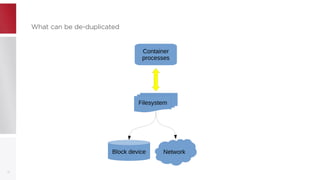
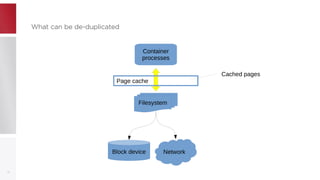
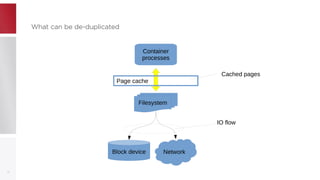
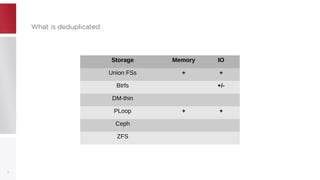
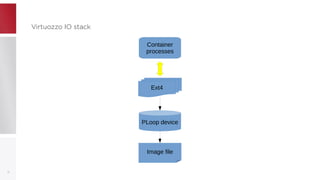
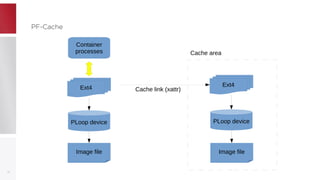
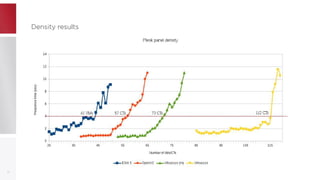
This document discusses using PFCache to improve storage density for container files by deduplicating identical data. PFCache uses a cache area to store deduplicated file contents, referenced via cache links in container image files. Evaluation showed PFCache improved storage density. Future work includes upstreaming PLoop for containers and pursuing IO deduplication in the Linux kernel for additional benefits.