Embed presentation
Downloaded 88 times







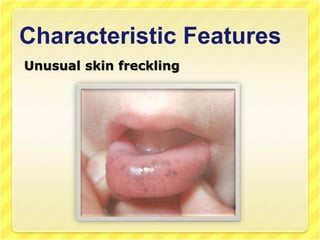
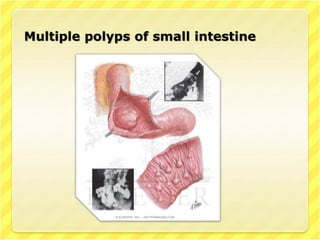
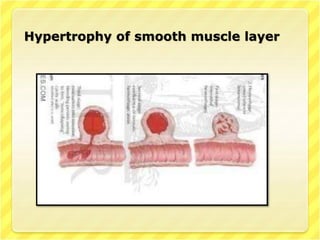
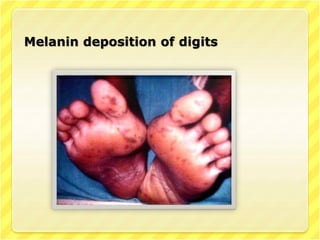








This document discusses Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, a rare genetic disorder characterized by benign polyps in the gastrointestinal tract and pigmentation of the mouth and skin. It is caused by a mutation in a tumor suppressor gene and is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. Symptoms may include abdominal pain, blood in the stool, and intestinal blockage. Diagnosis involves family history, clinical examination finding polyps and pigmentation, and genetic testing. Treatment involves surgery to remove polyps and endoscopic screening, while prevention involves genetic counseling.


















