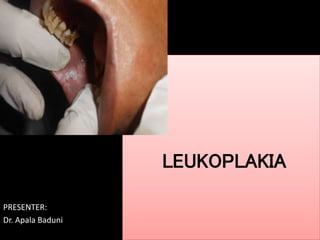
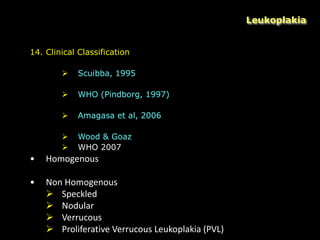
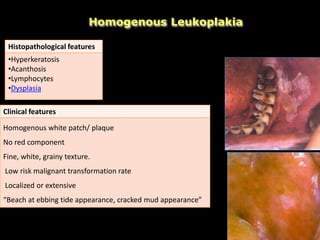
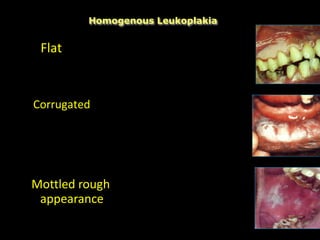
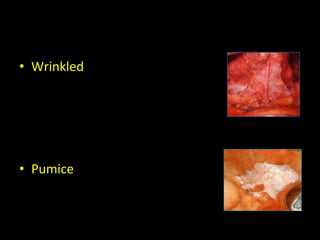
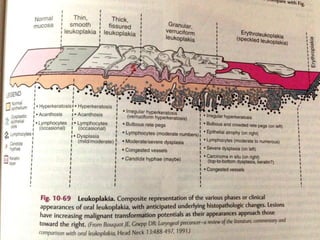
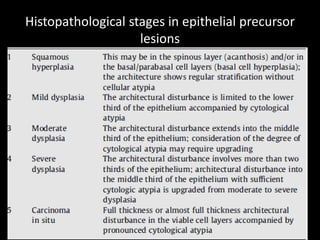
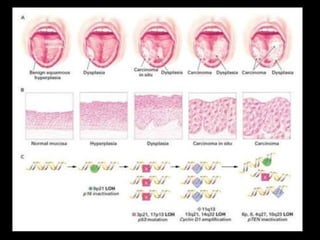
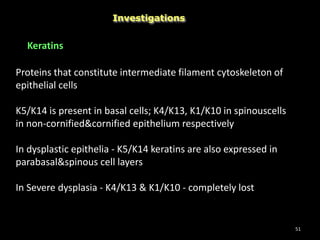
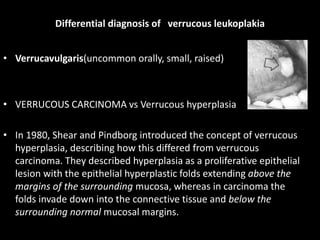
Leukoplakia is a predominantly white lesion of the oral mucosa that cannot be characterized as any other definable lesion. It is most commonly caused by tobacco use. Leukoplakia can be classified as homogenous or non-homogenous. Homogenous leukoplakia appears as a flat, white patch and has a low risk of malignant transformation, while non-homogenous leukoplakia contains red areas and has a higher risk of becoming cancerous. Diagnosis is made through biopsy and examination under light microscopy to check for epithelial dysplasia. Treatment involves eliminating possible irritants and monitoring for signs of malignant transformation.







![• Hereditary
• Reactive/ Inflammatory
Burket’s
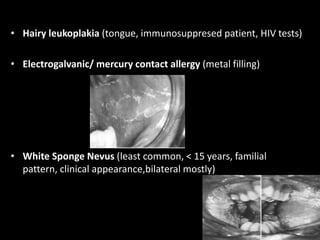
1.Leukoedema
2.White sponge nevus
3.Heriditary benign
intraepithelial dyskeratosis
• Linea alba [white line]
• Frictional [traumatic] keratosis
• Cheek chewing
• Chemical injuries of the oral
mucosa
• Actinic keratosis [cheilitis]
• Smokeless tobacco –induced
keratosis
• Nicotine stomatitis
• Sanguinaria –induced
leukoplakia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leukoplakia-150320142728-conversion-gate01/85/Leukoplakia-9-320.jpg)

































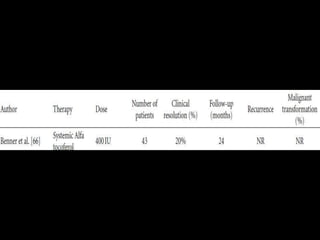
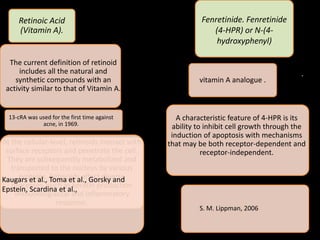

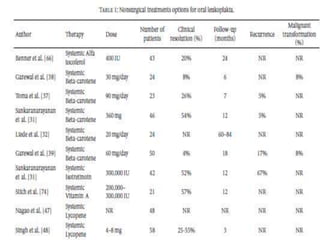
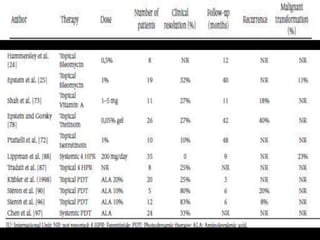



























![Reference Material
1. Burket’s Oral Medicine by Malcolm Lynch, 11th Edition
2. Oral Diseases in the Tropics by Prabhu& Wilson
3. Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions by Goaz& Wood, 5th Edition
4. Dental clinics of north America - Oral soft tissue lesions. Jan 2005, vol 49, no.1
5. Cawson’s essential’s of Oral pathology & Oral medicine, 7th edition. Cawson, Odell
6. Mehta et al; report on investigations of oral cancer & precancerous conditions in indian rural populations 1966-
1969 munksgardcopenhagen.
7. Nielsen et al., 1996; Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol32(B):264-270.
8. Praetorius, 1997; HPV-associated diseases of oral mucosa. ClinDermatol15:399-413.
9. Jepsen and Winther, 1965; ActaOdontol Scand 23:239-256.
10. Renstrup, 1970; ActaPatholMicrobiol Scand [B] MicrobiolImmunol78:421-424.
11. Bánóczy and Sugar, 1972 J Oral Pathol1:265-272.
12. The results of CO2 laser surgery in patients with oral leukoplakia: a 25 year follow up . P.S. van der Hemet al
Oral Oncology (2005) 41, 31–37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/leukoplakia-150320142728-conversion-gate01/85/Leukoplakia-107-320.jpg)
