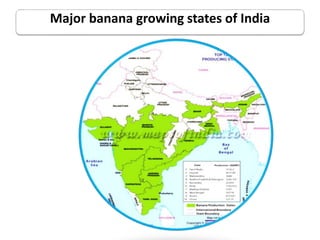
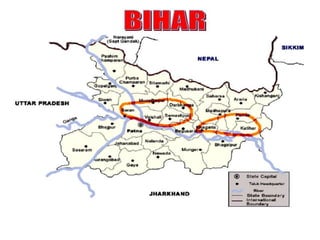
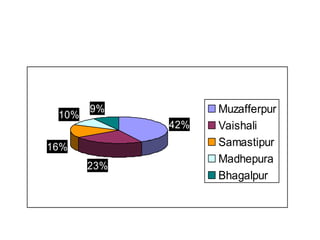
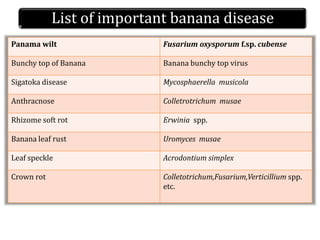
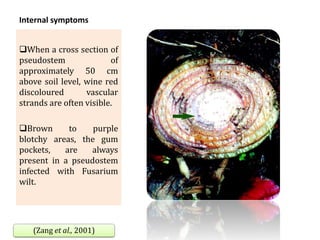
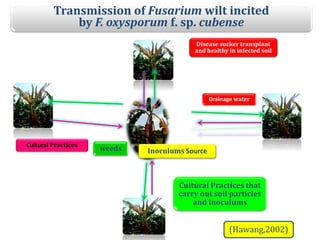
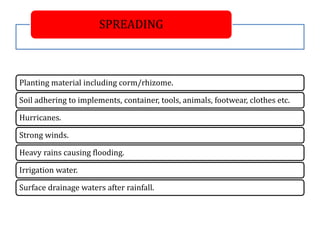
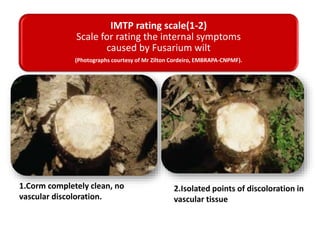
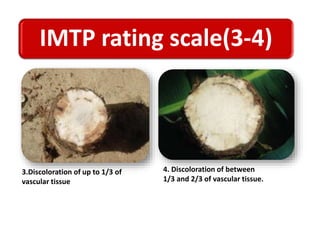
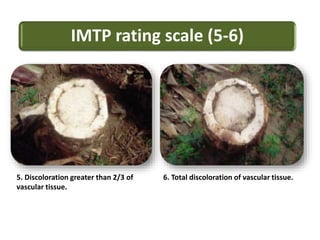
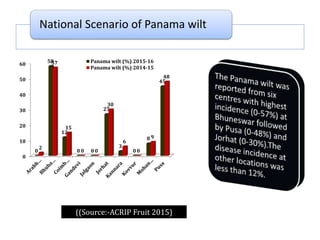
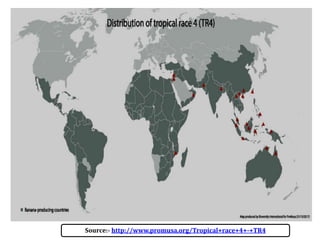
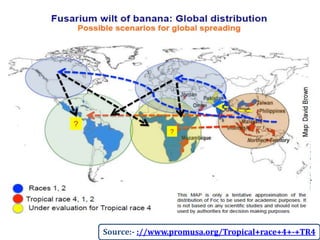
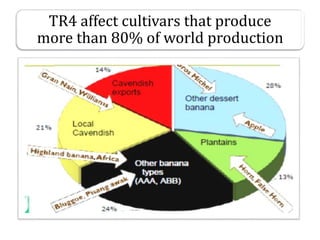
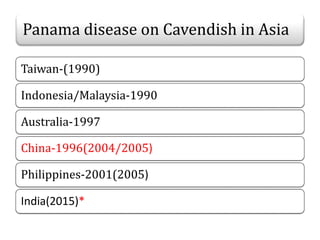
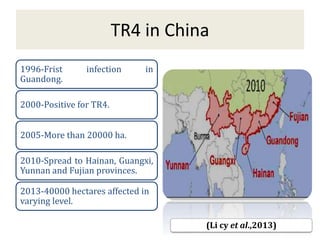
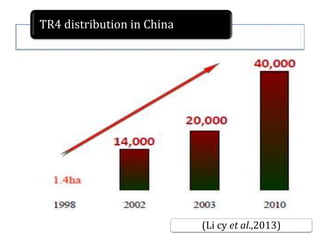
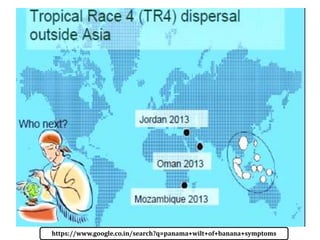
This document summarizes a doctoral seminar presentation on Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cubense race TR4, a new threat to banana cultivation in Bihar, India. The presentation covers key details about banana cultivation in Bihar and India, important banana diseases, symptoms and spread of Panama wilt caused by Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cubense, races of the pathogen, its international spread and impact on banana production worldwide, and management strategies for fields infected with race TR4.