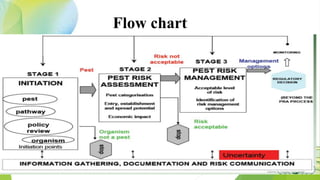
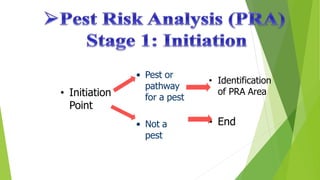
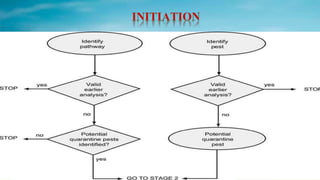
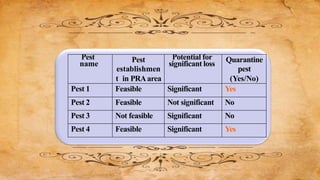
The document summarizes the process of pest risk analysis (PRA). PRA involves three stages: initiation, pest risk assessment, and pest risk management. During pest risk assessment, pests are categorized and the probability of introduction, establishment, and spread are evaluated. Potential economic impacts, including environmental and social impacts, are also assessed. The overall risk is then determined. Pest risk management identifies risk management options to address risks identified in the assessment. PRA must be conducted for any new imports of plants or plant materials not already approved to ensure biosecurity and minimize trade impacts.