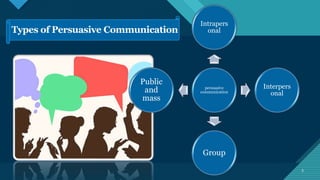
The document defines persuasive communication as messages aimed at influencing others' responses, emphasizing the three pillars: ethos (credibility), pathos (emotion), and logos (logic). It outlines various types of persuasive communication, including intrapersonal, interpersonal, group, and public/mass communication, along with steps to effectively persuade an audience. Additionally, it highlights common errors to avoid and the importance of establishing trust and a good working environment.