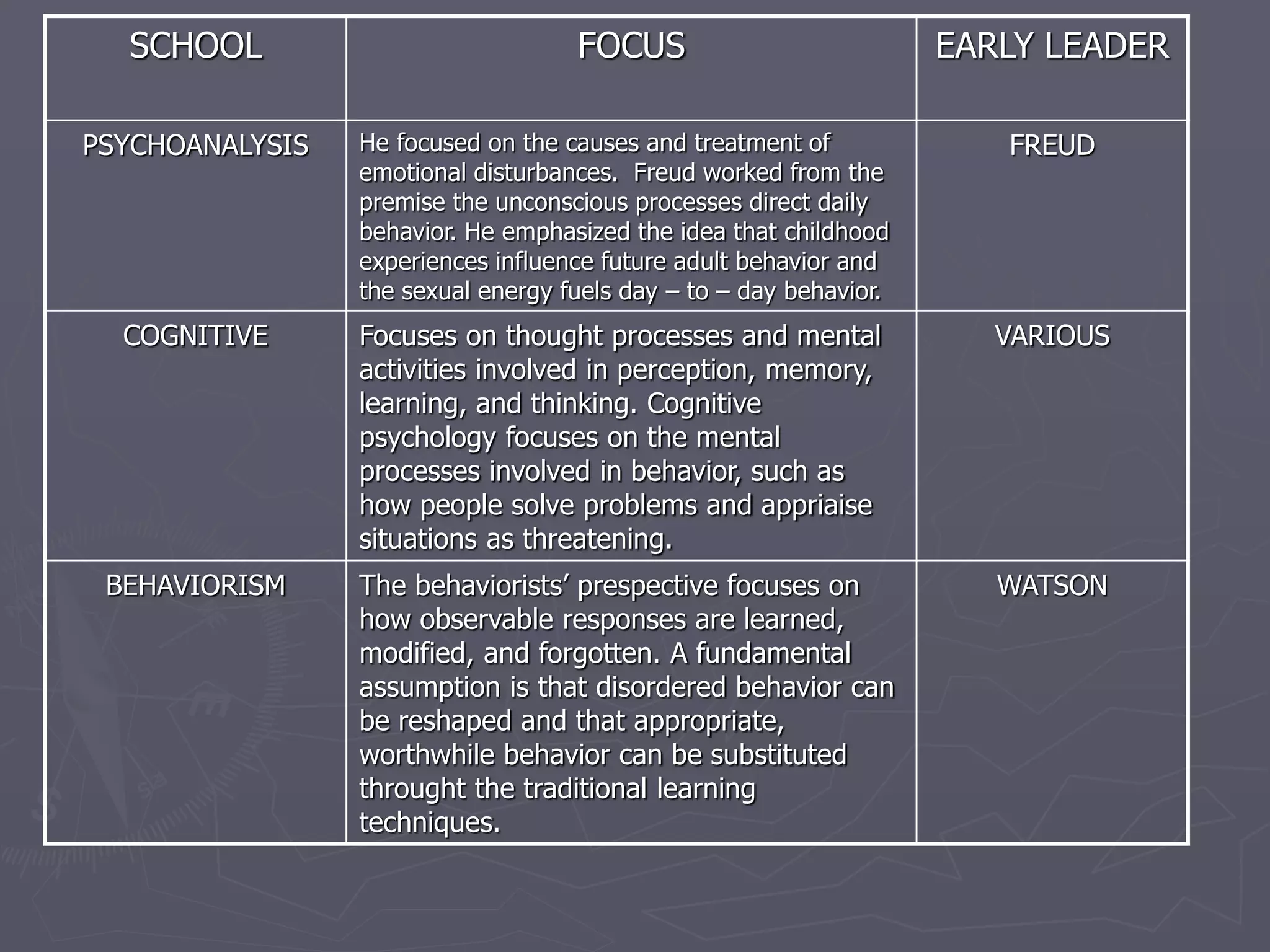
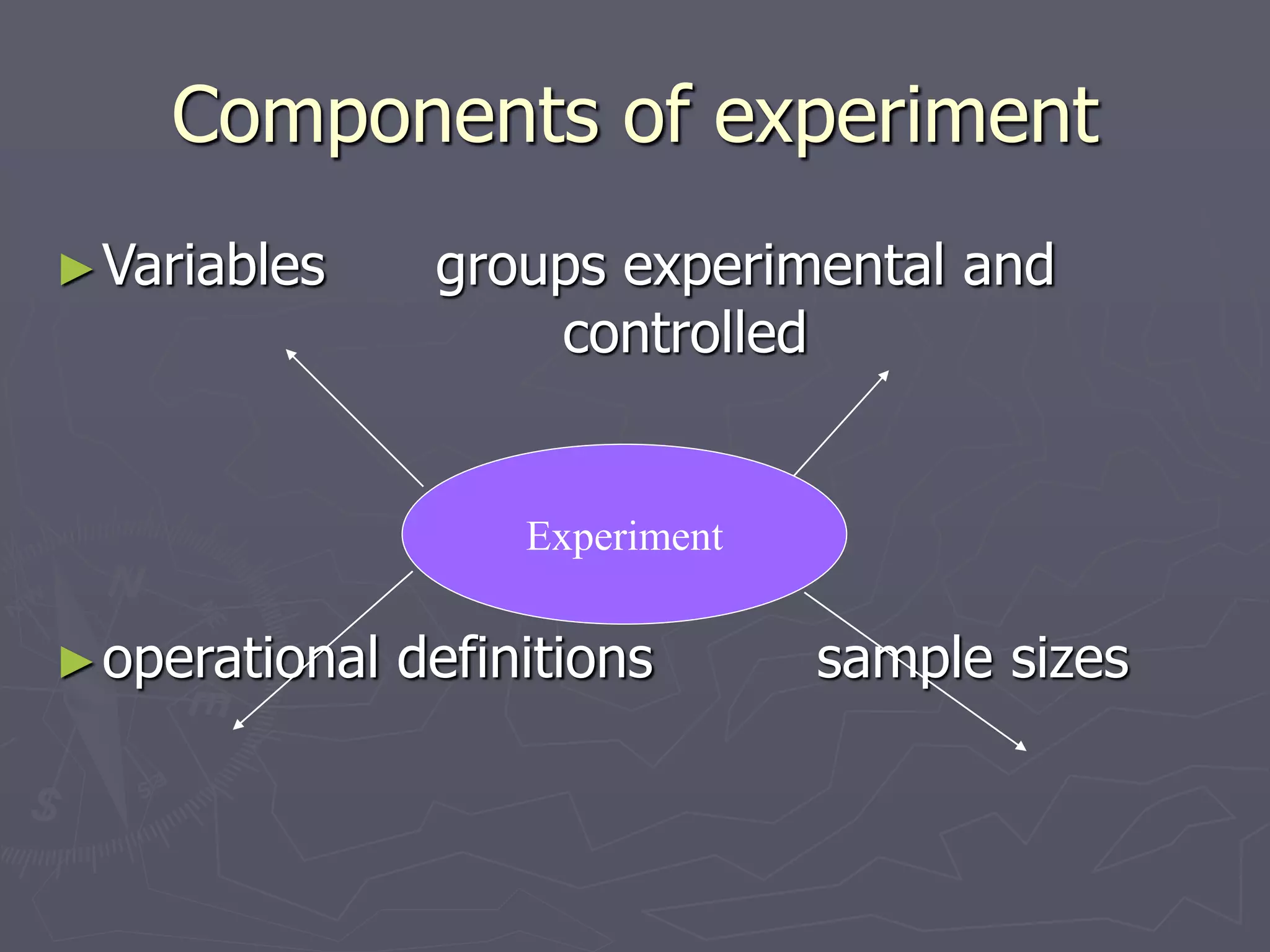
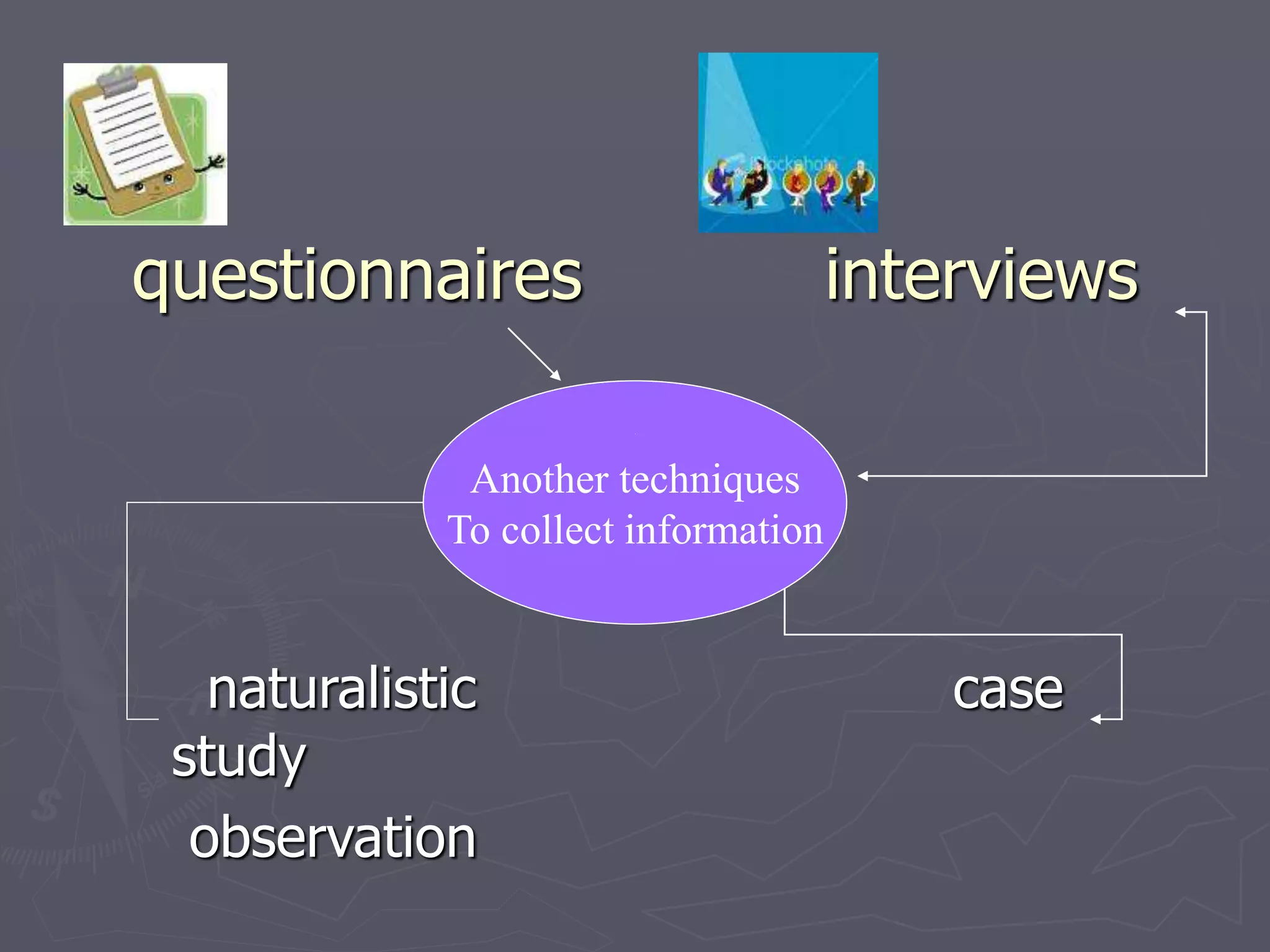
Psychology is the science of behavior and mental processes. It aims to describe, explain, predict, and potentially manage basic components of behavior. There are many approaches in psychology, such as structuralism, functionalism, gestalt, psychoanalysis, cognitive, behaviorism, humanistic, biological, and eclectic. While psychology uses various methods like experimentation, observation, questionnaires, and case studies, it is a unified science that seeks to understand behavior comprehensively. Psychologists work in various fields such as clinical, counseling, school, industrial, sports, and forensic psychology to promote well-being and solve problems using behavioral principles.