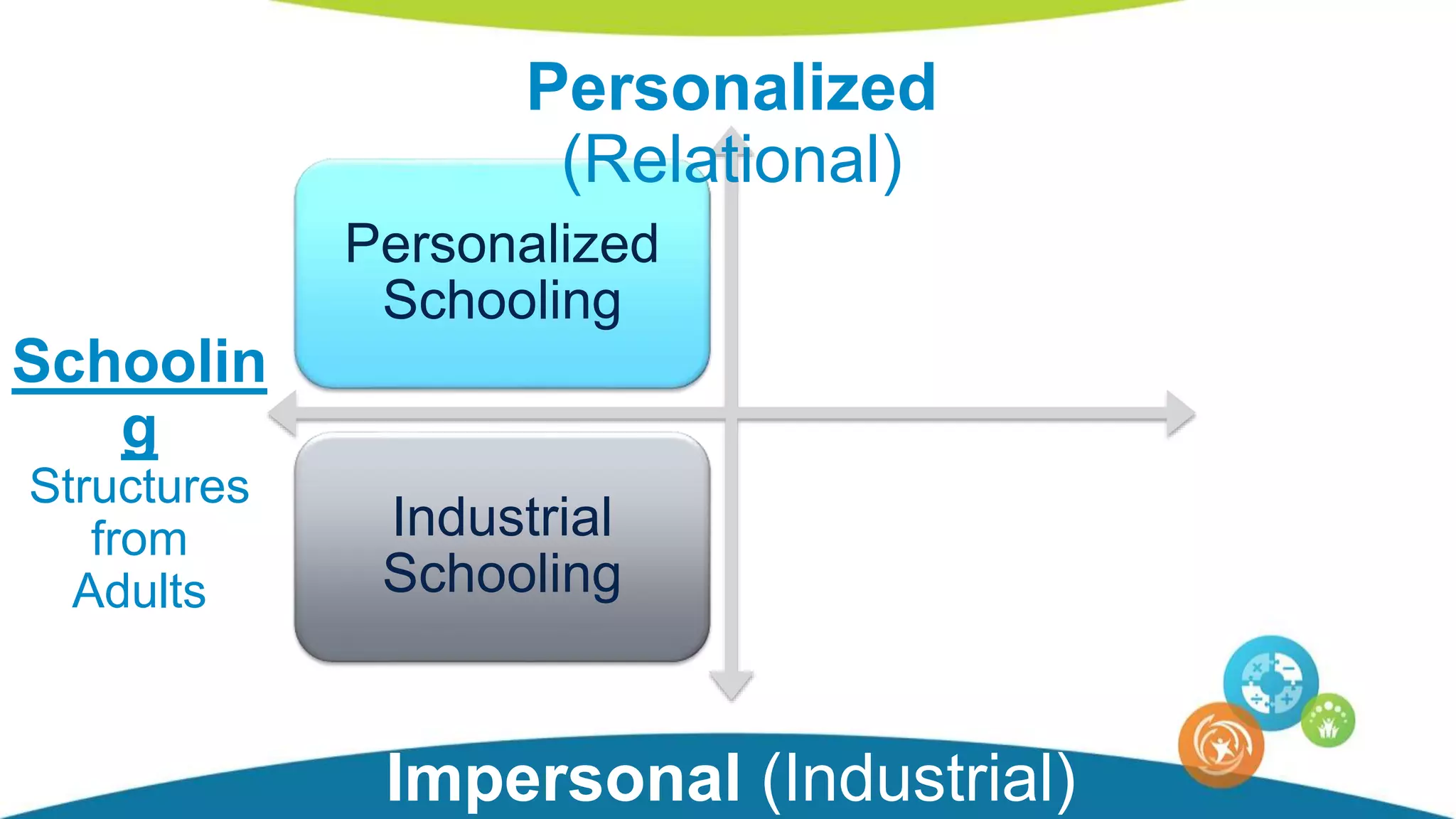
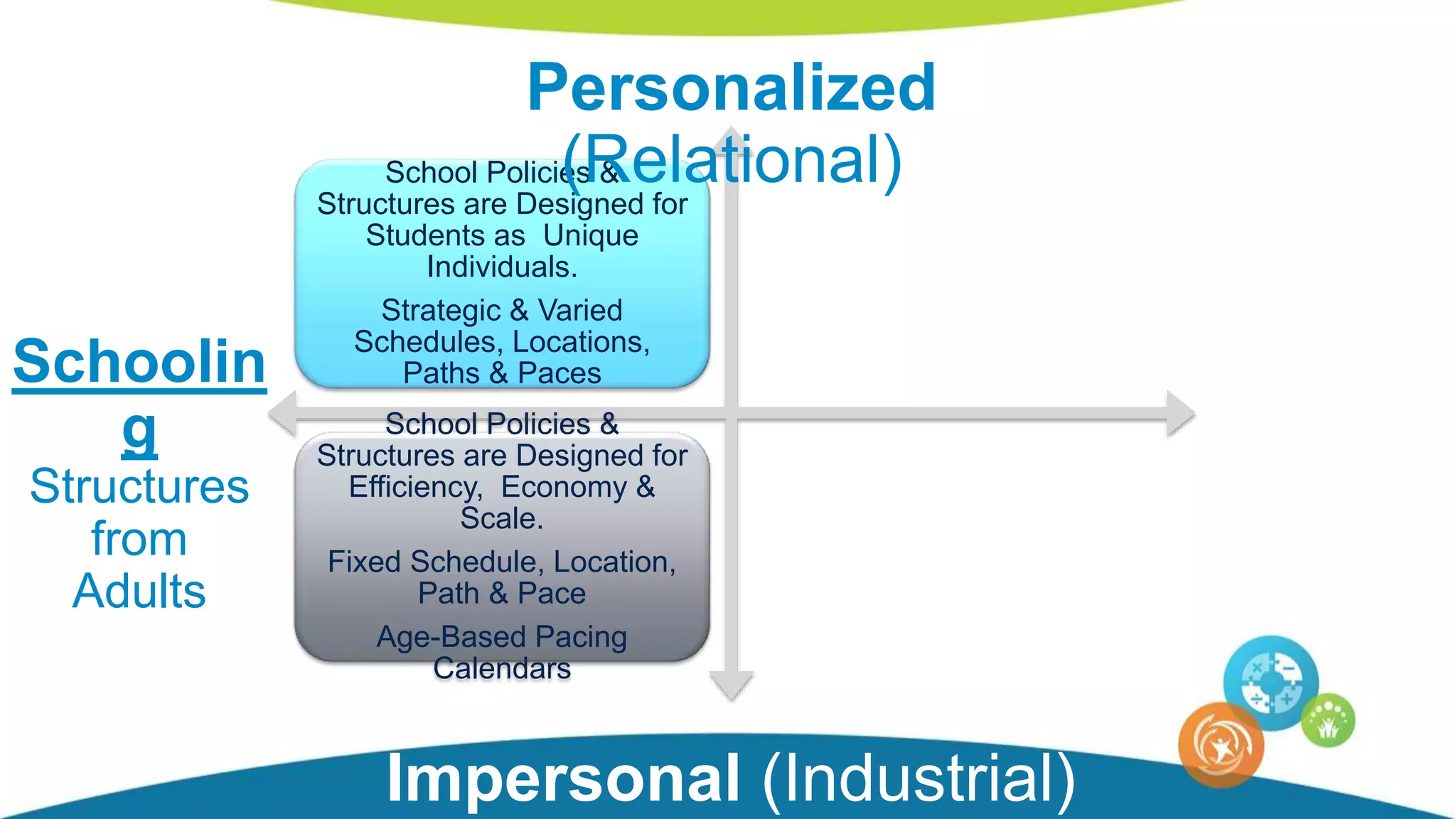
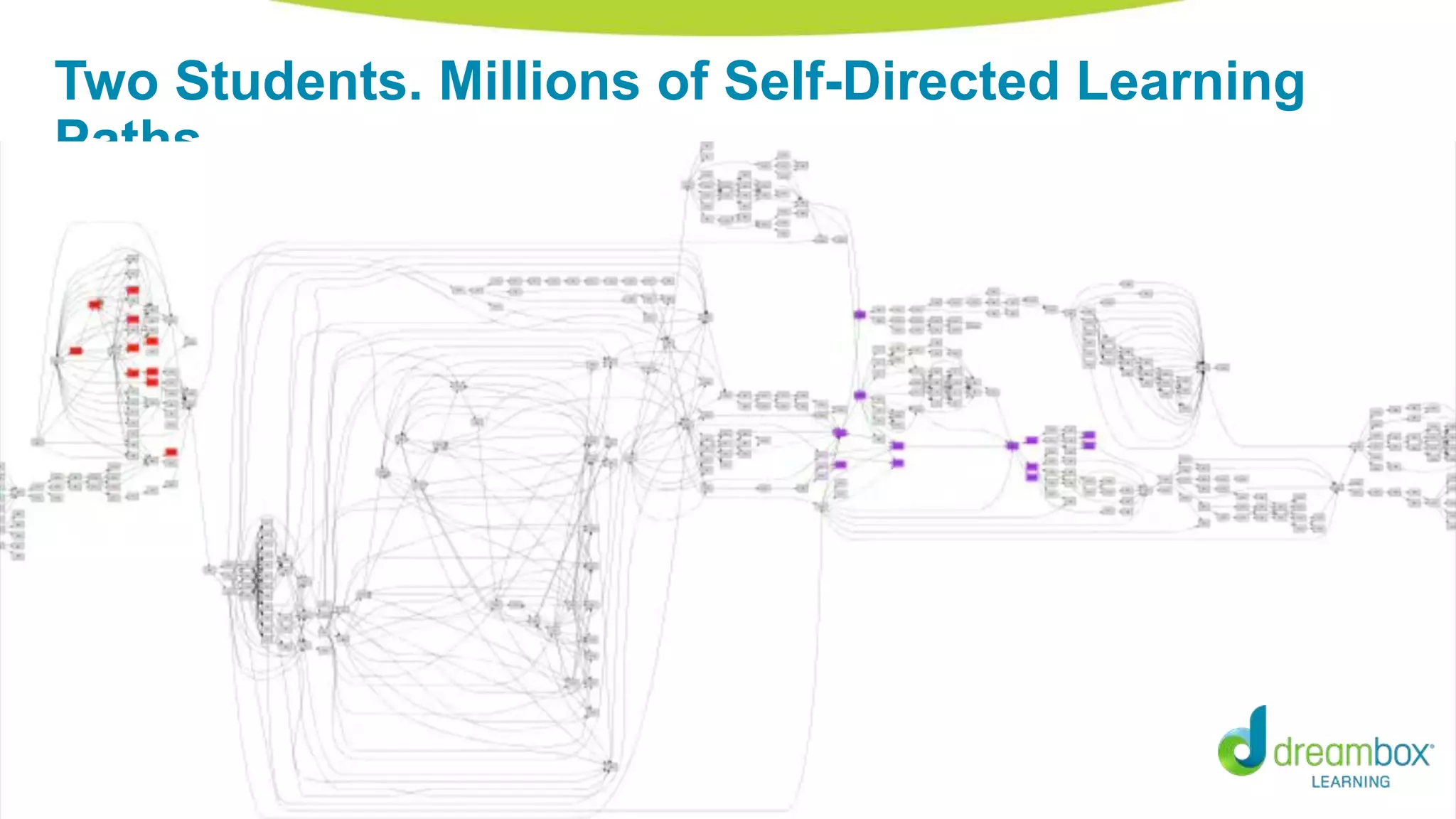
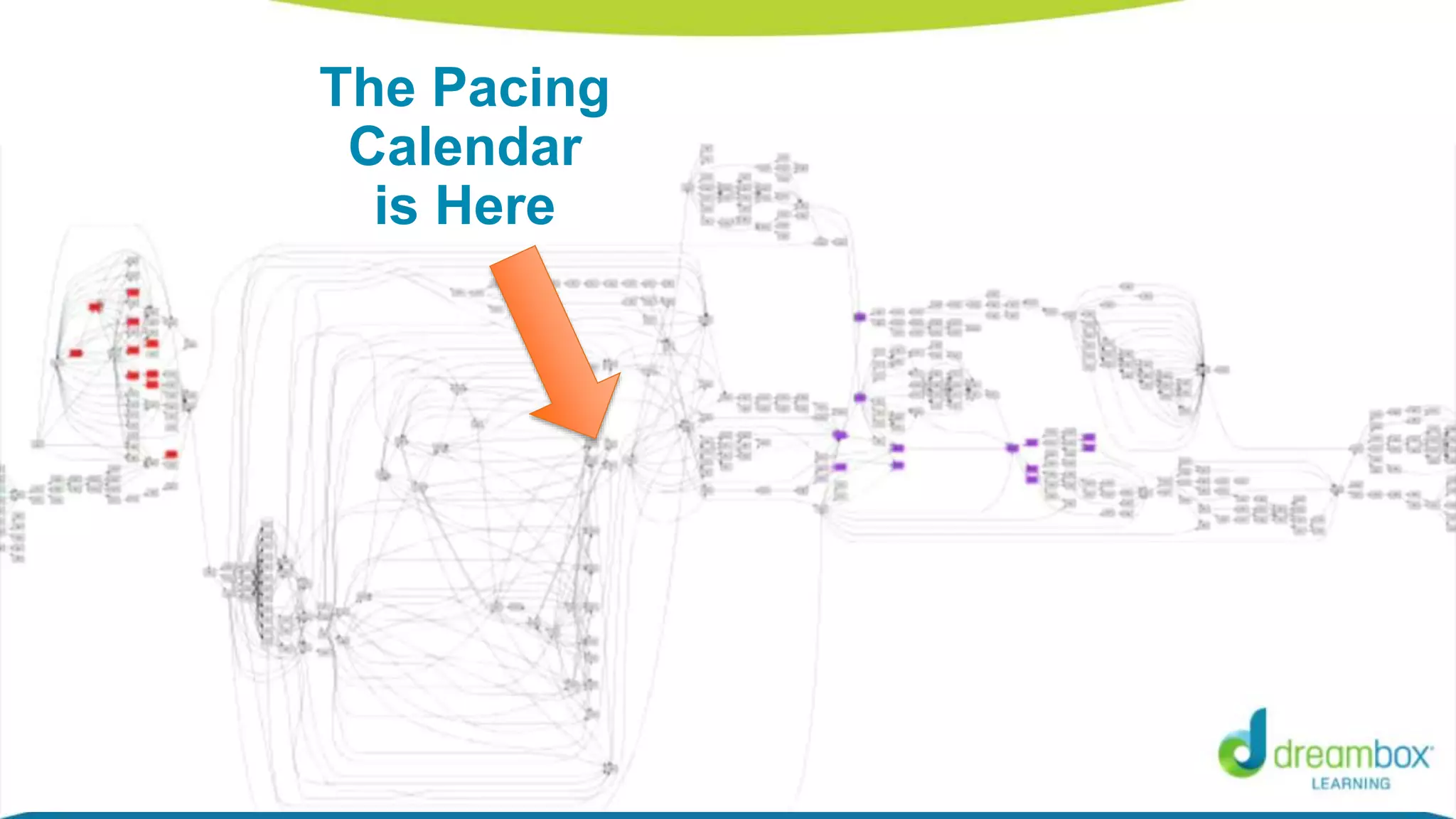
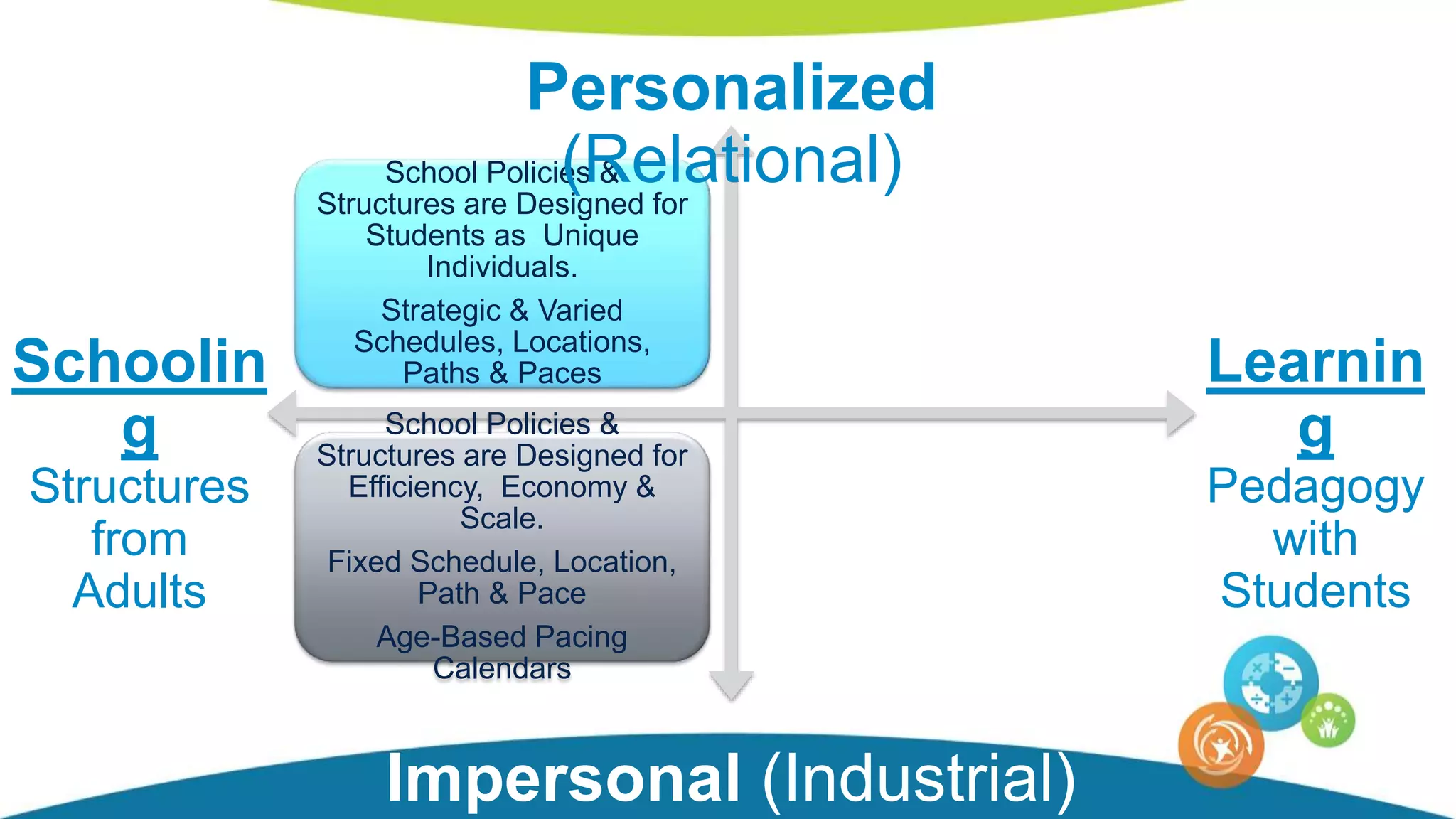
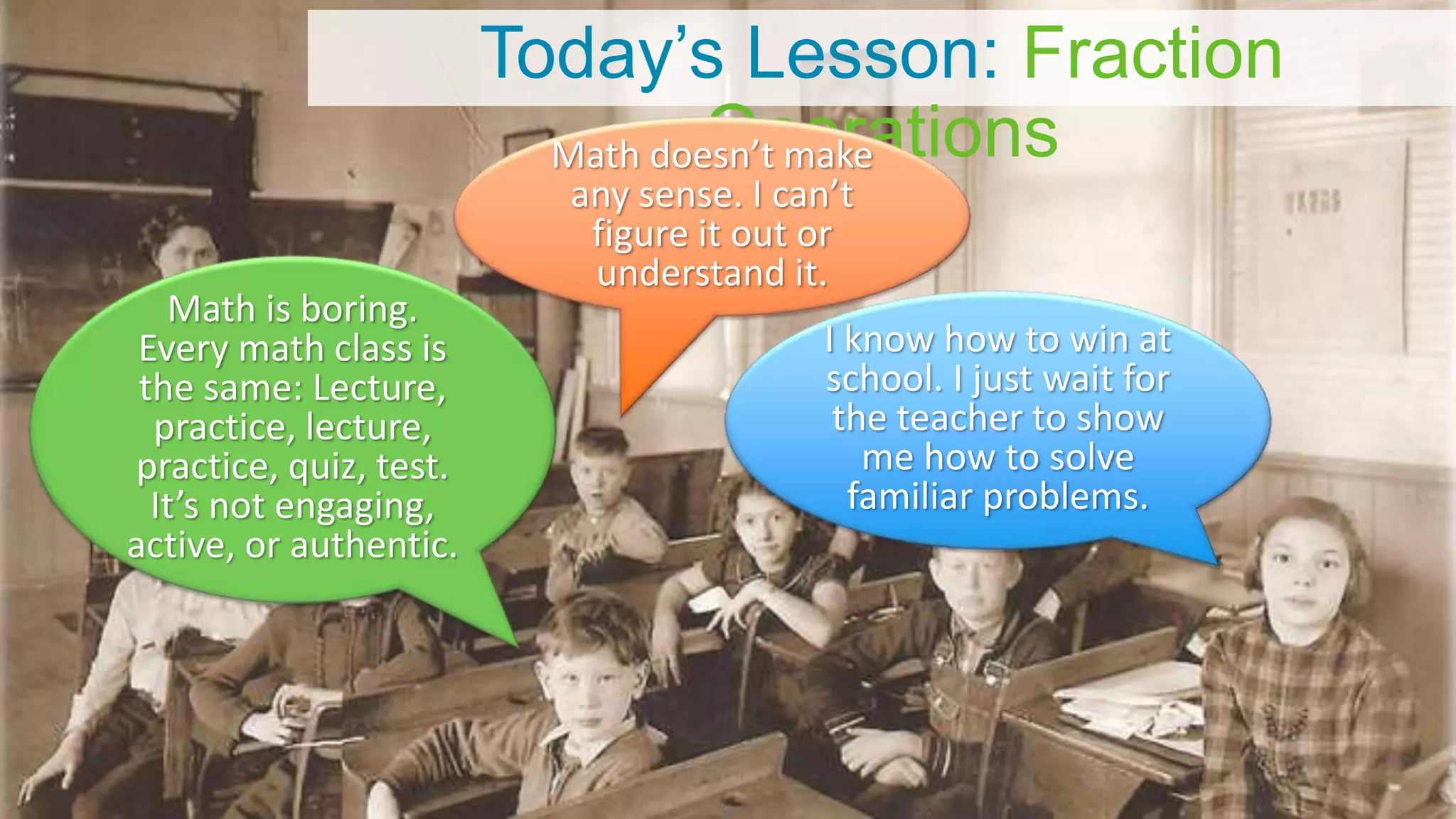
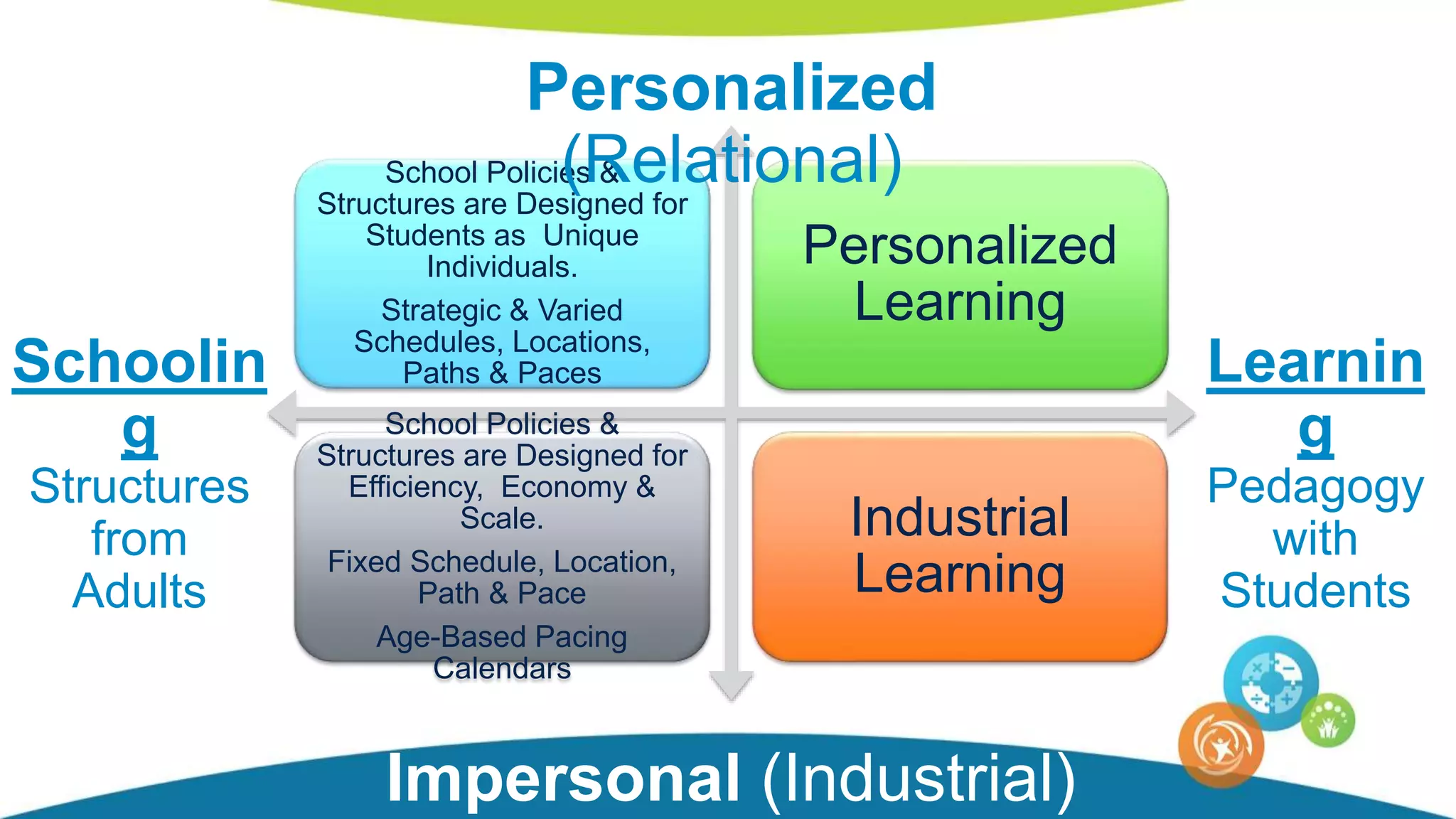
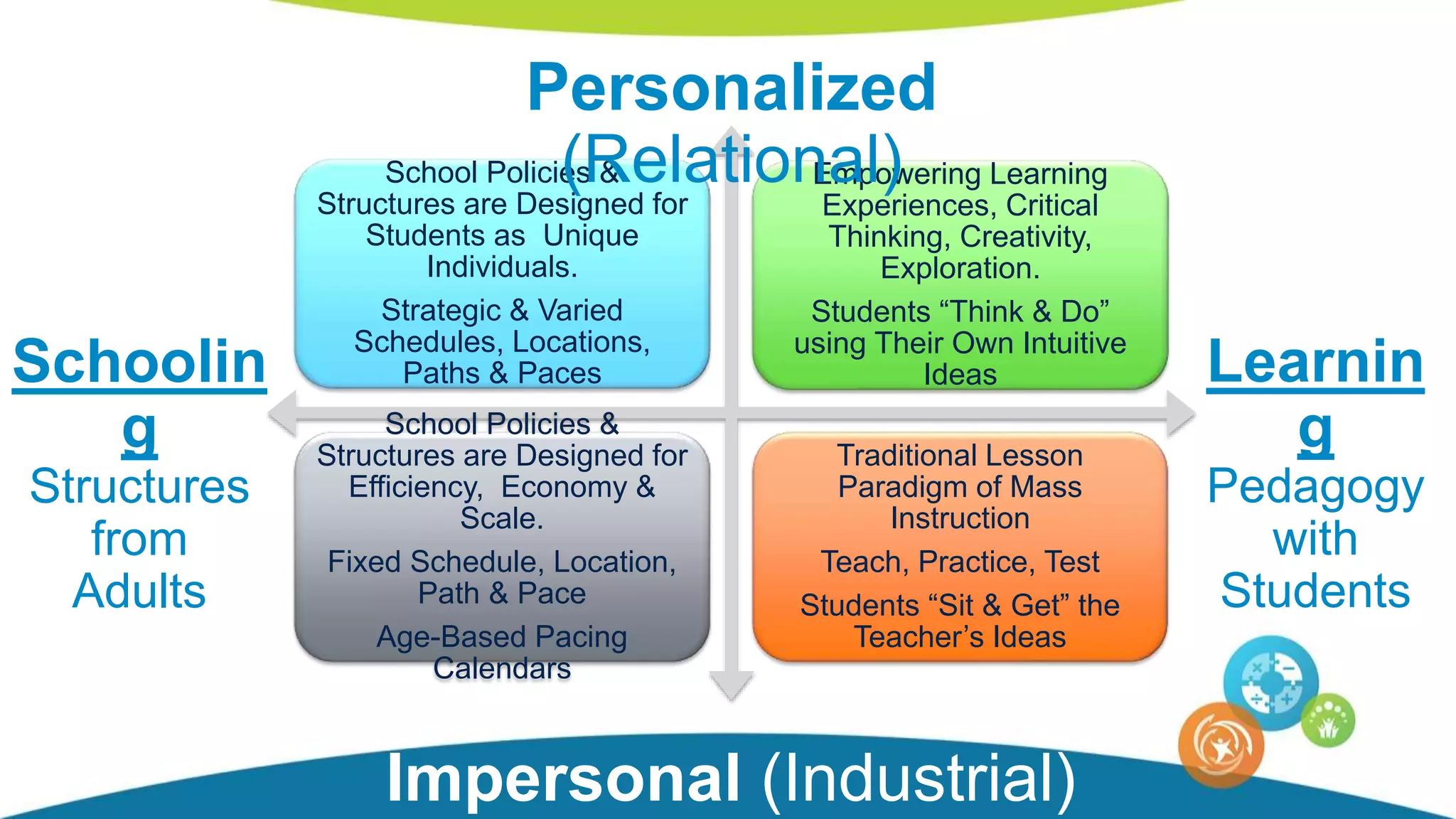
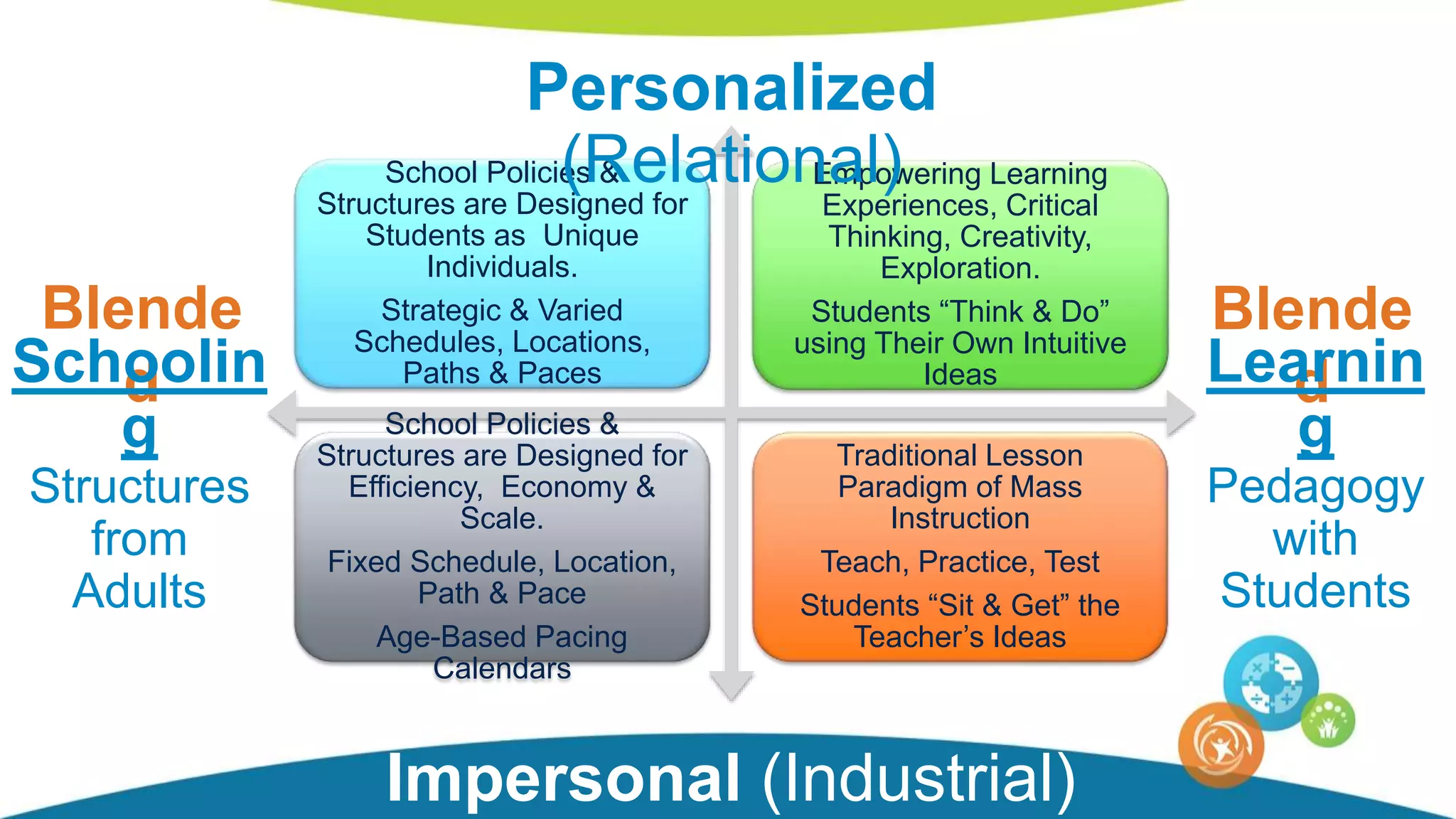
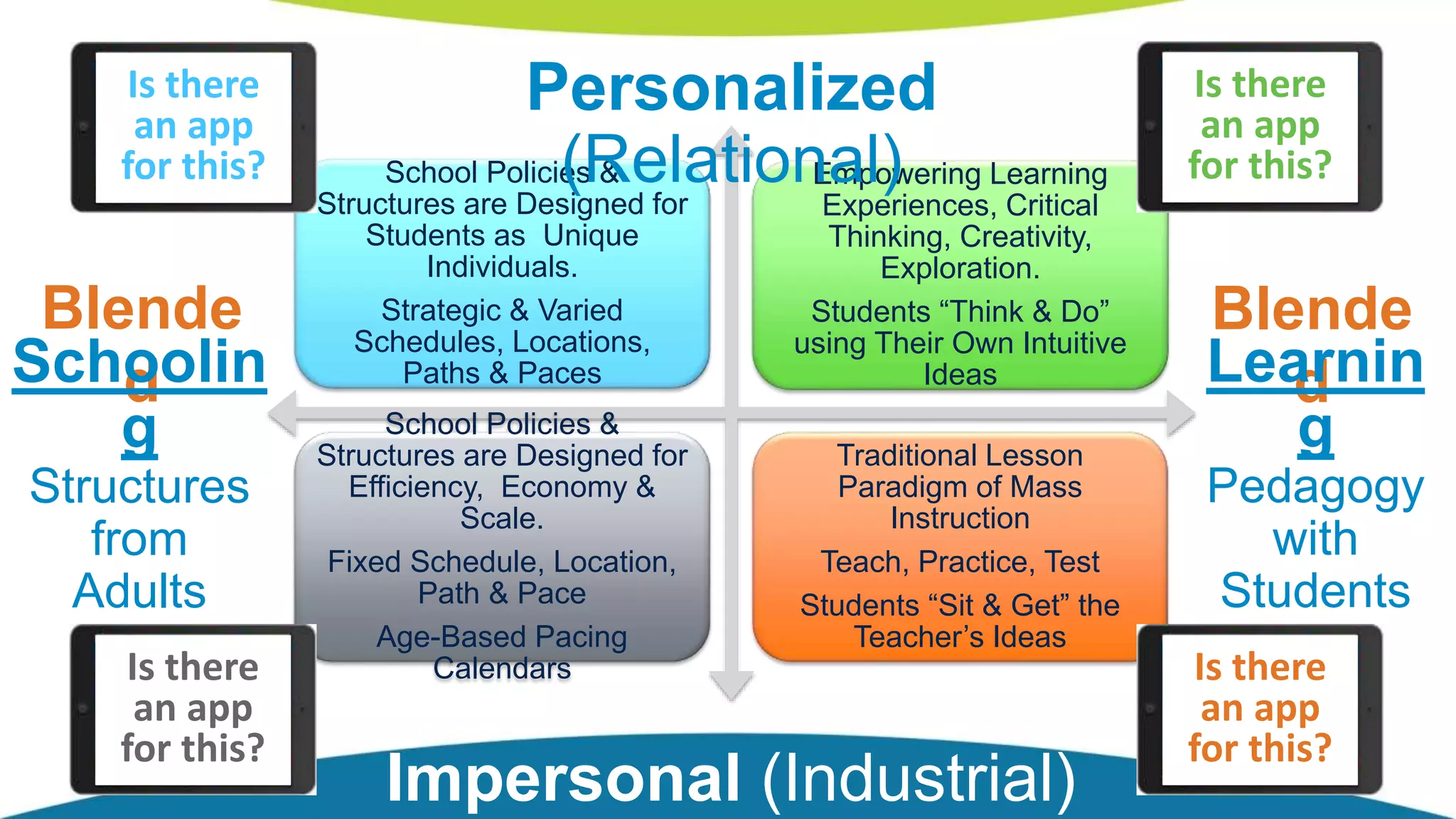
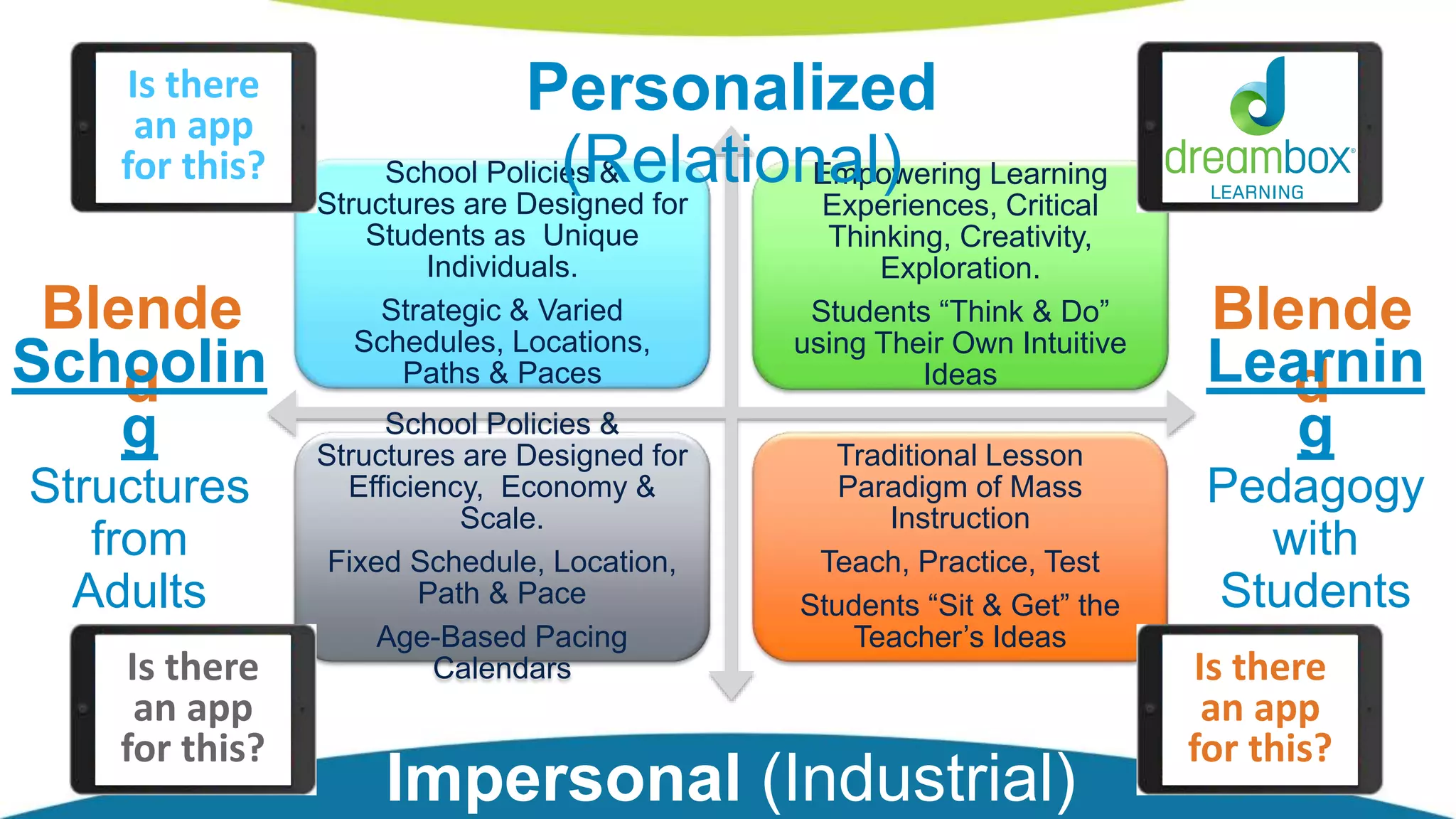
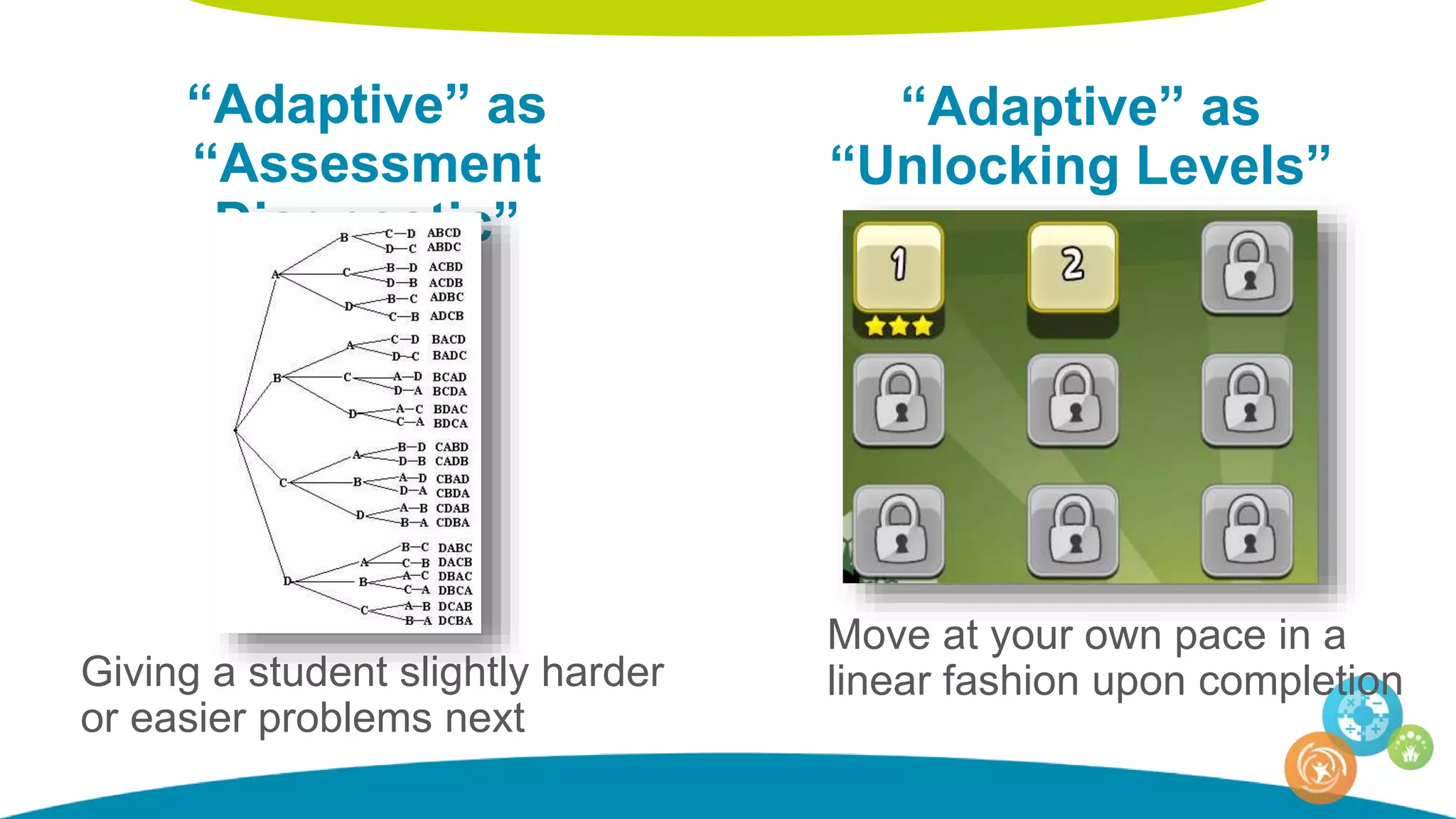
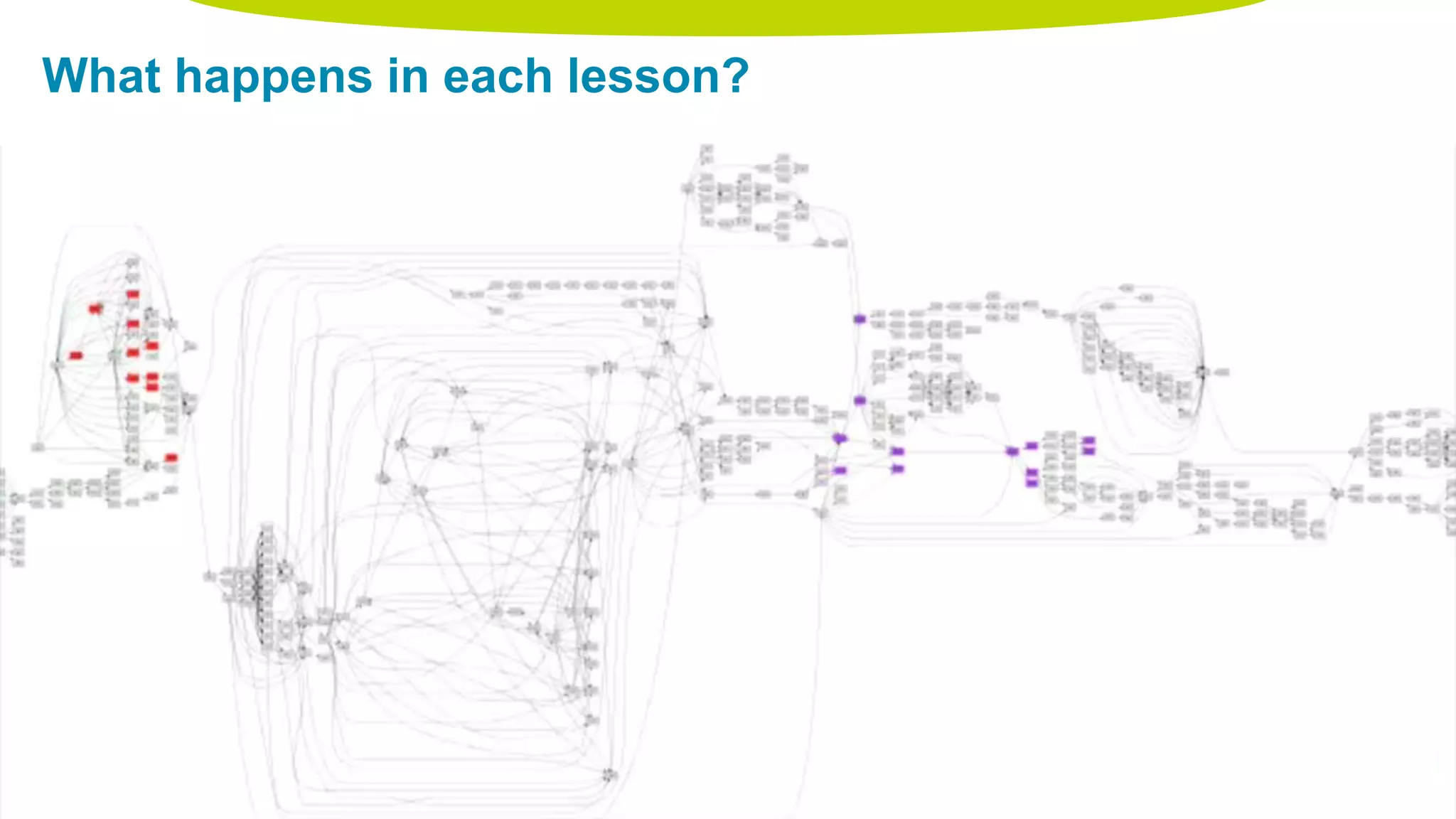
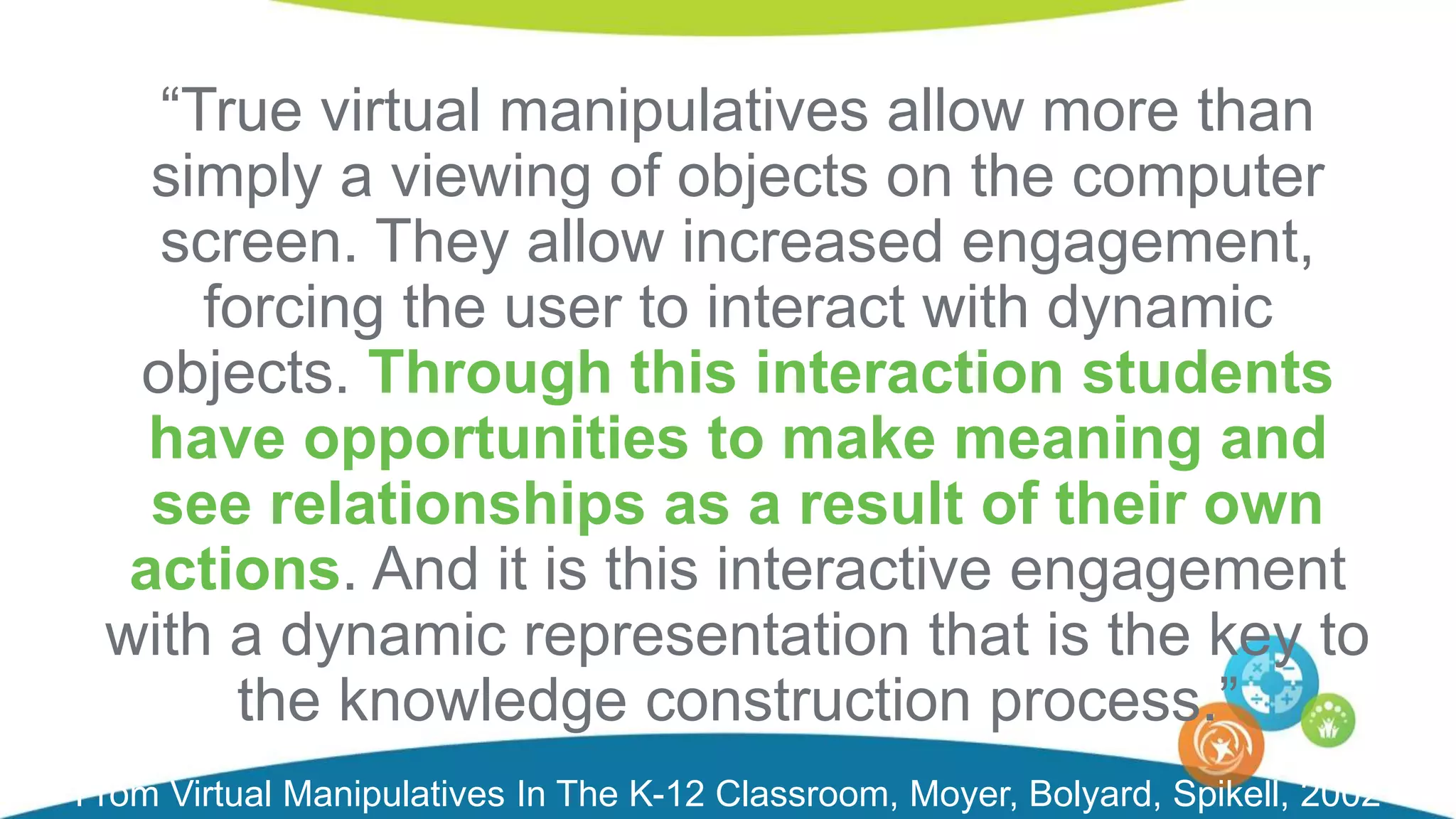
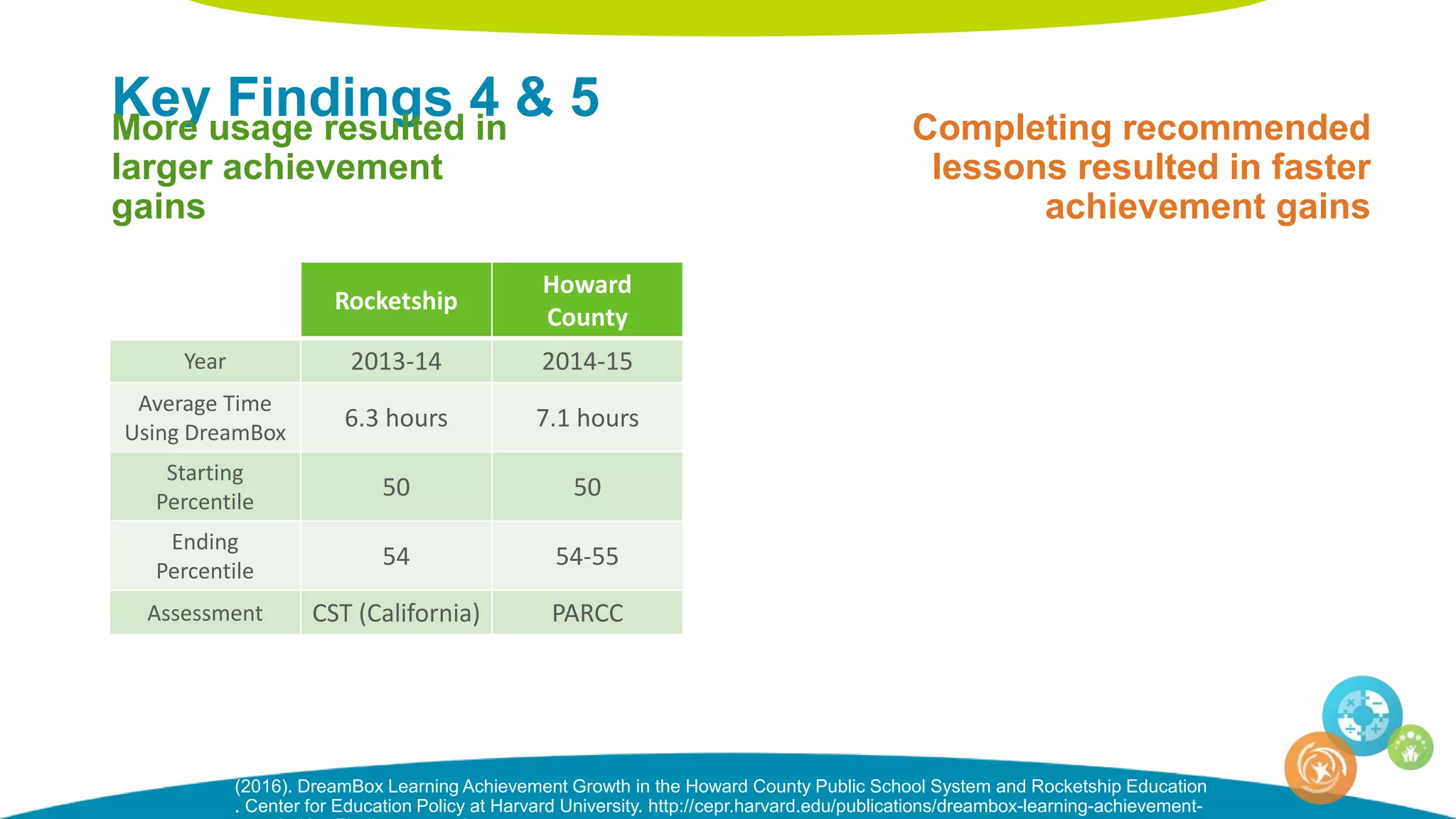
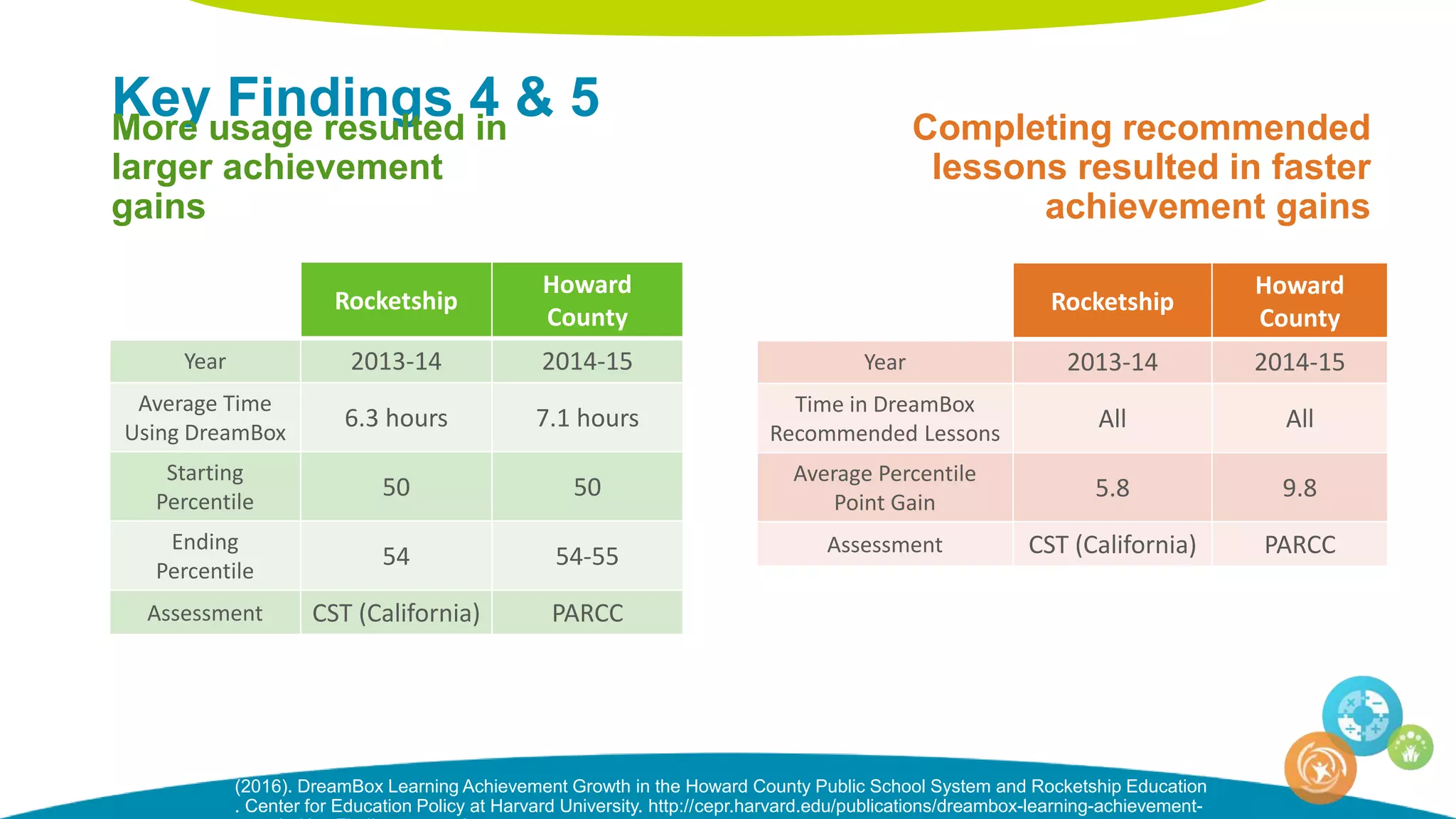
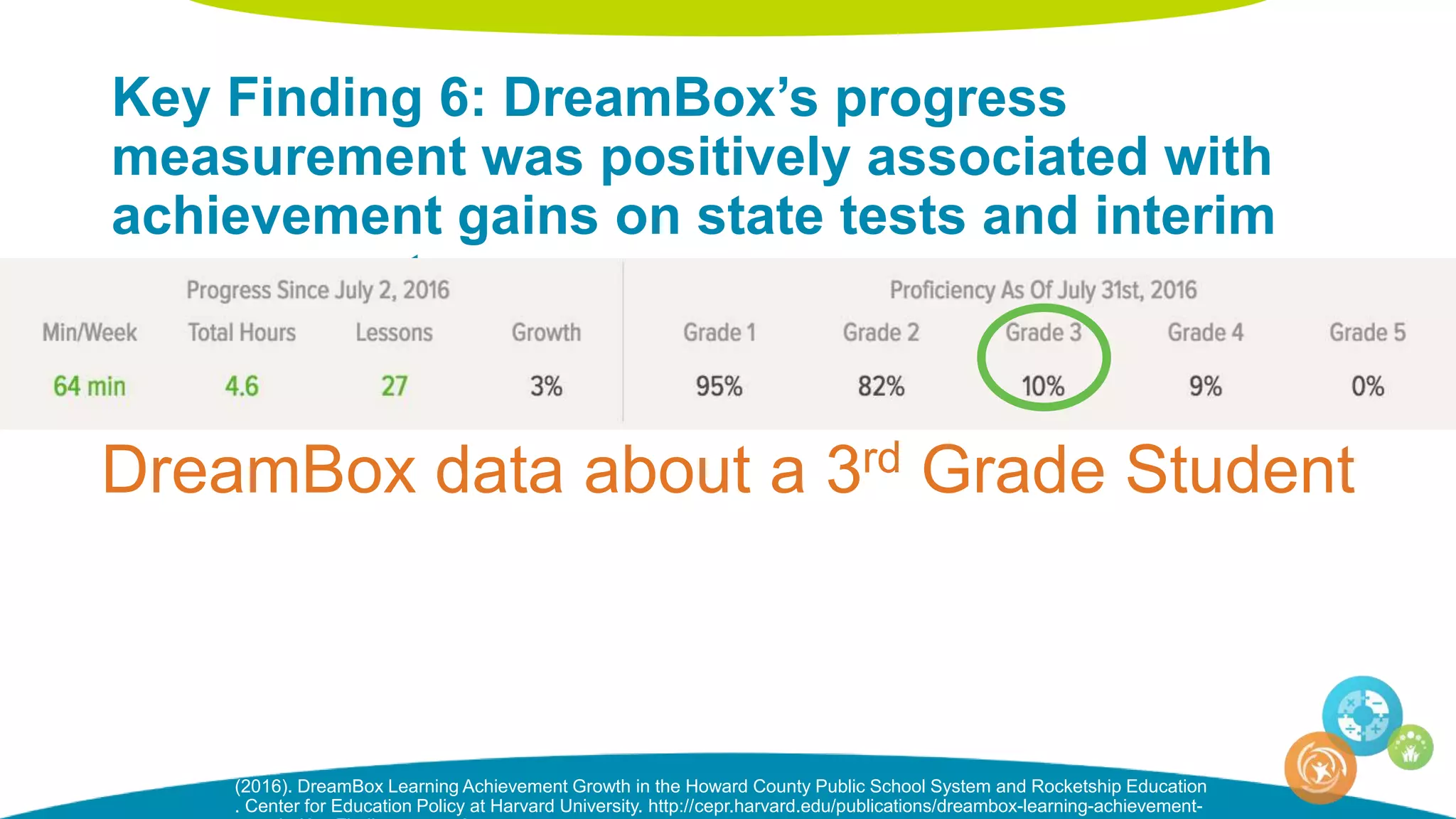
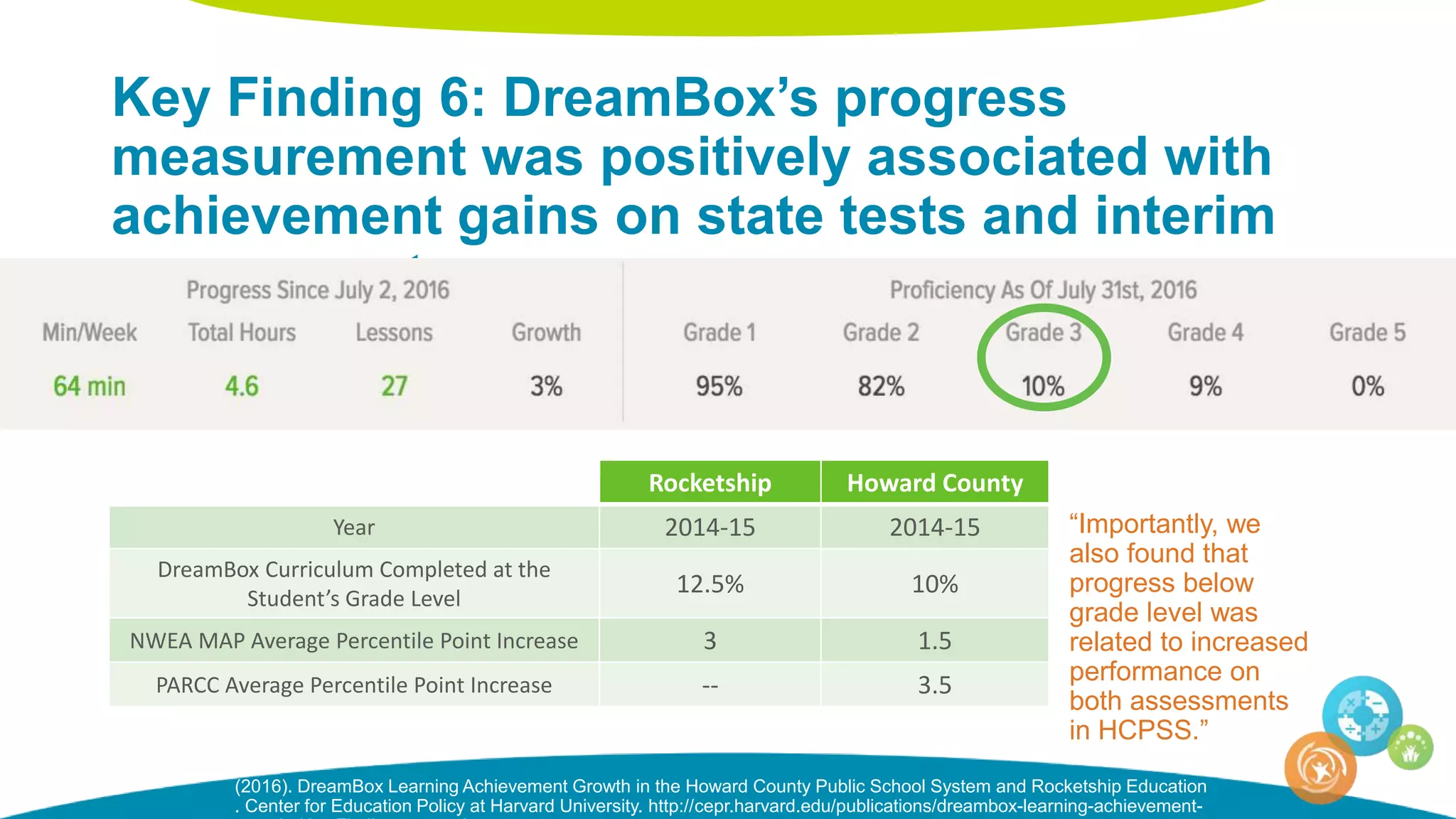
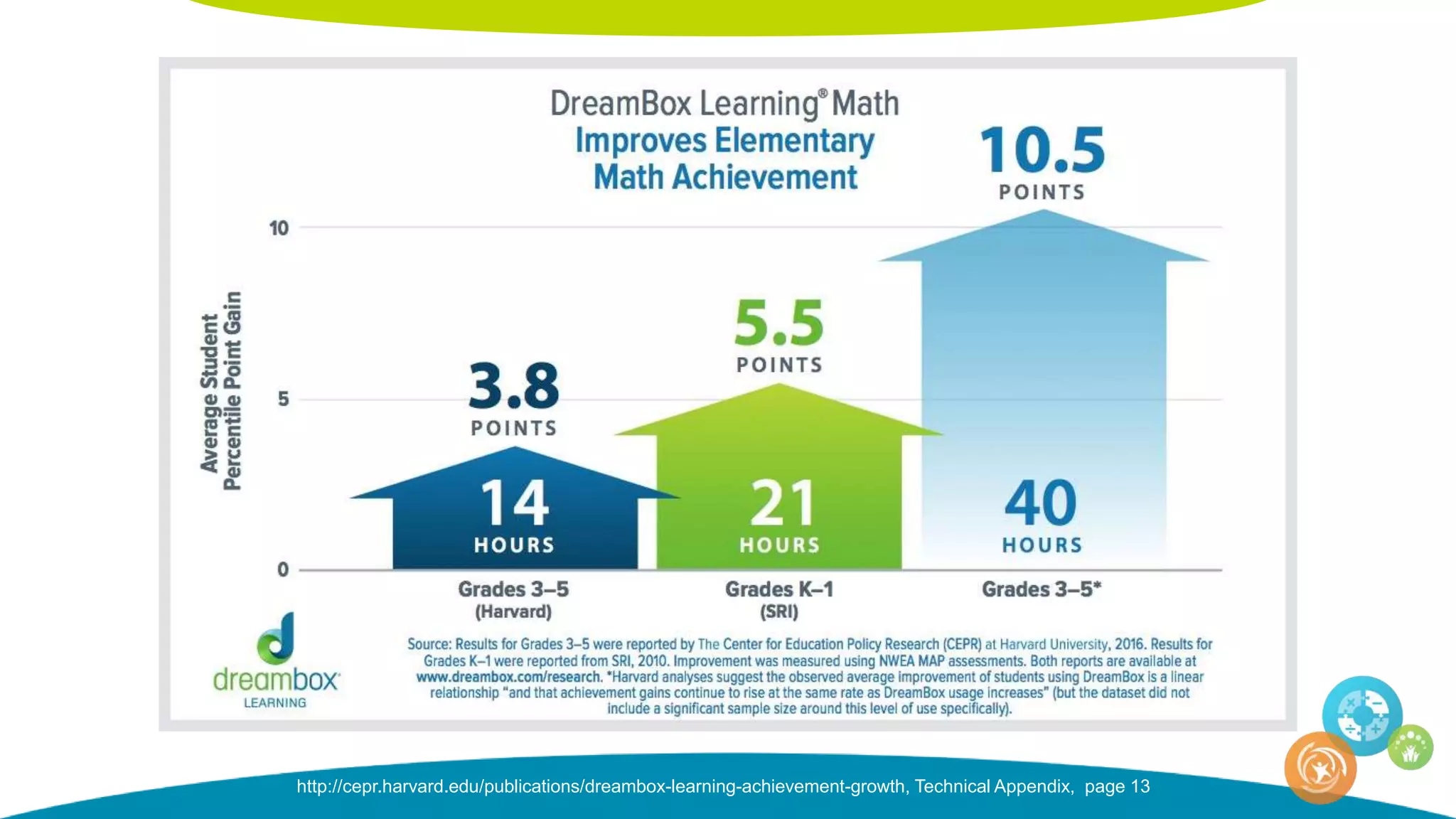
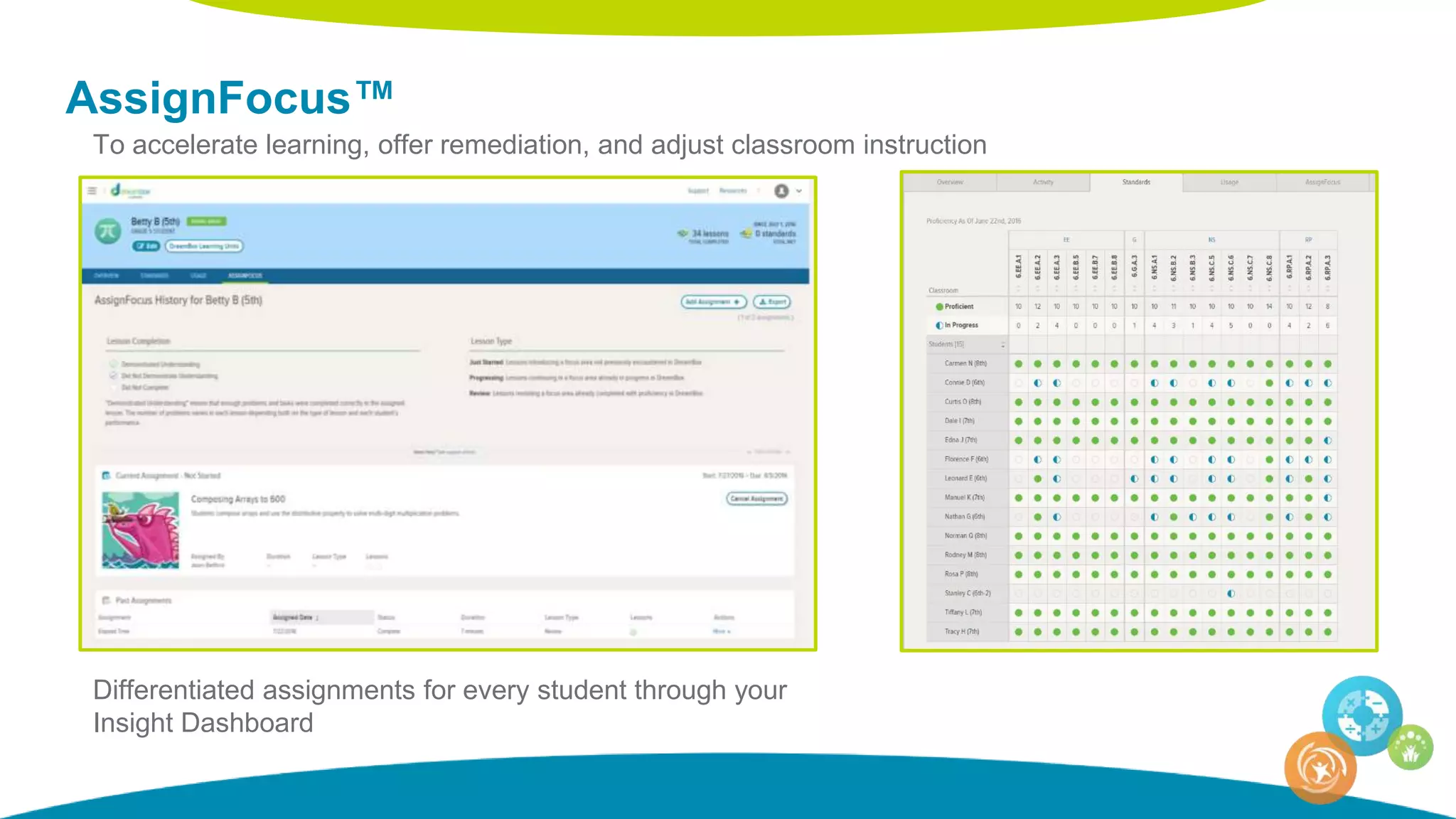
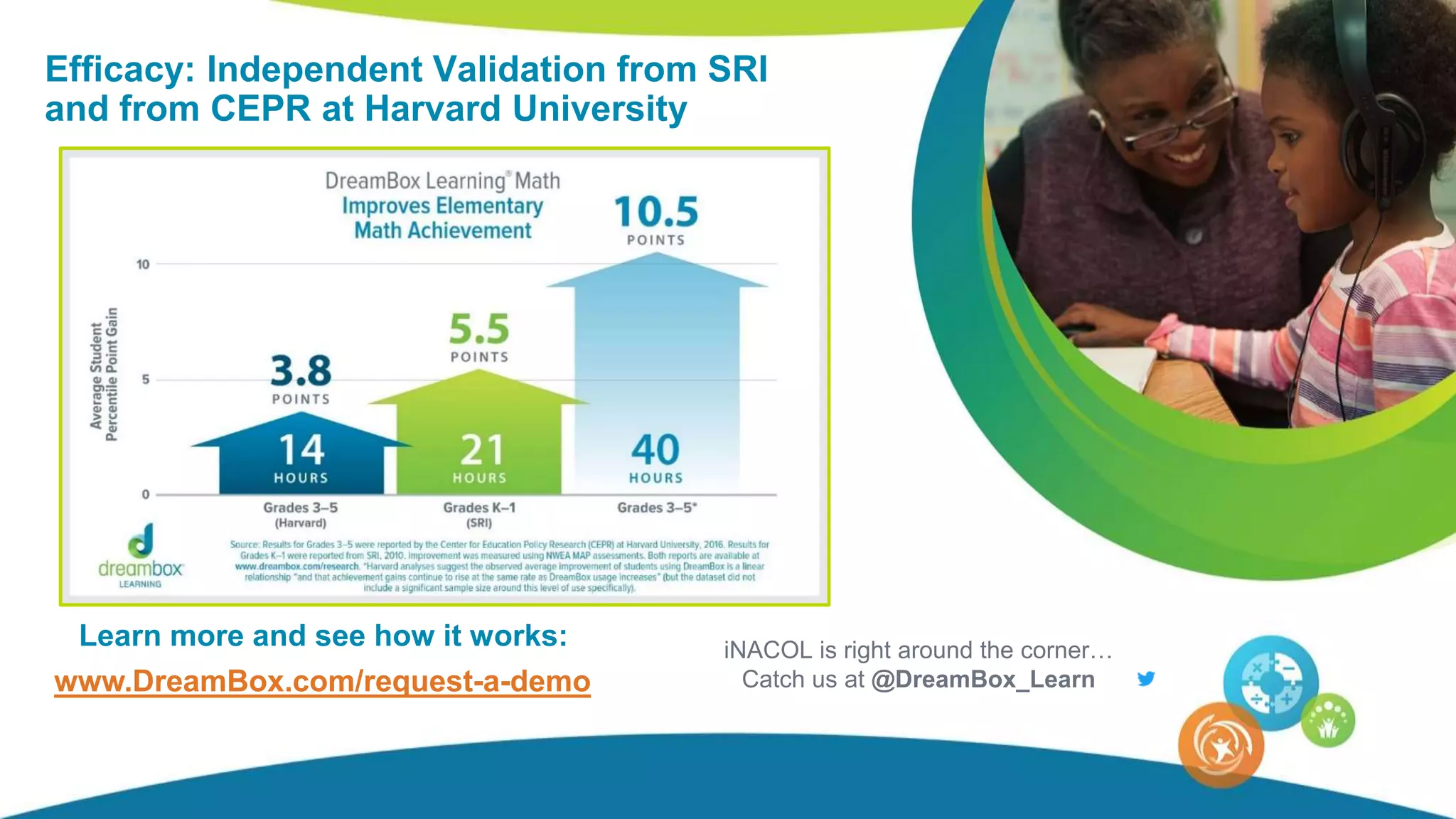
The document discusses personalized and adaptive math learning, highlighting the significance of such approaches in contemporary education. It presents recent research findings on the effectiveness of digital programs like DreamBox Learning and emphasizes the crucial role of teachers in implementing these programs to enhance student learning experiences. Key insights include the need for tailored educational practices and the positive association between program usage and academic achievement.