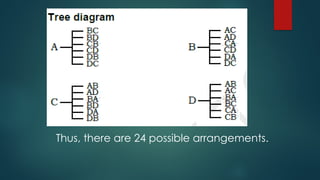
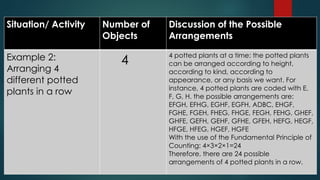
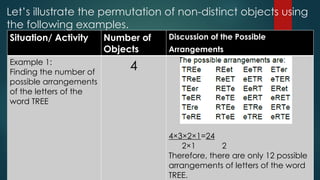
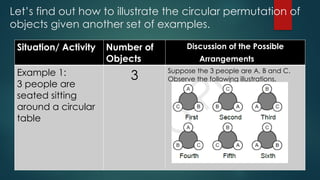
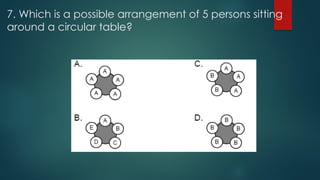
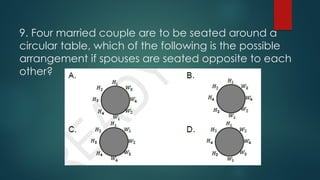
The document outlines techniques for counting permutations of objects, including making tables, tree diagrams, systematic listing, and the fundamental principle of counting. It discusses permutations of distinct and non-distinct objects, providing examples and exercises that illustrate these concepts. Additionally, it covers circular permutations and their application in arranging objects in a circular manner.