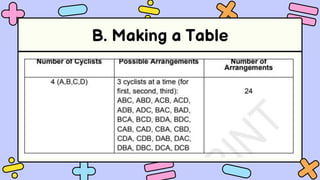
This document discusses different counting techniques including permutation, combination, systematic listing, making tables, tree diagrams, and the fundamental counting principle. It provides examples of how to use each technique to count outcomes. Specifically, it explains that permutation involves order while combination does not, and gives examples of situations that use each. It also works through examples of counting different outfits, ice cream orders, and pizza topping combinations using various counting methods.