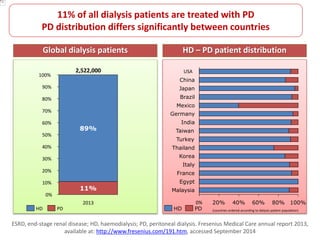
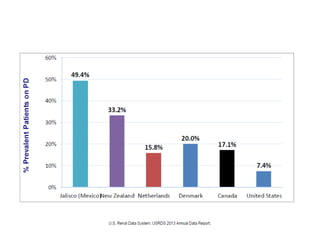
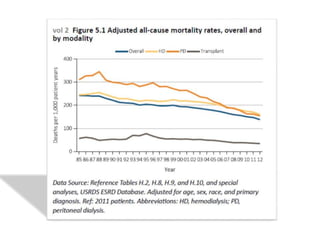
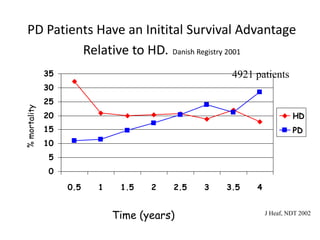
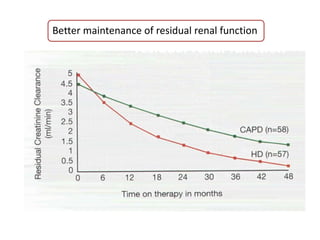
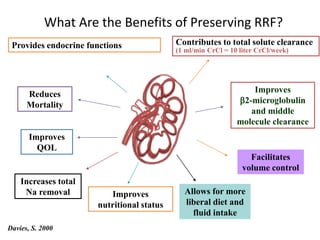
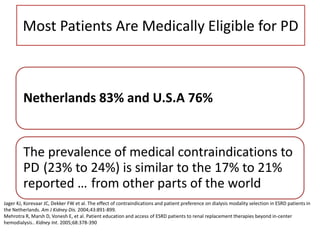
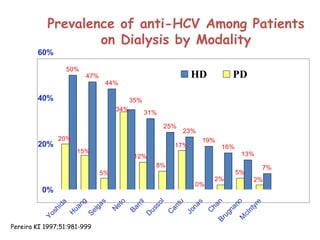
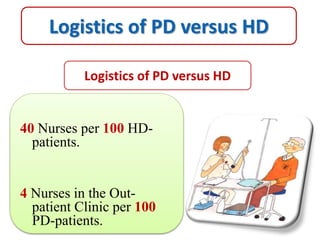
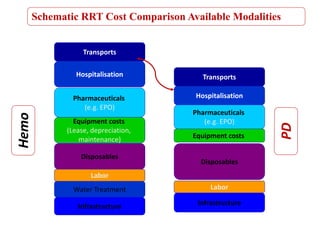
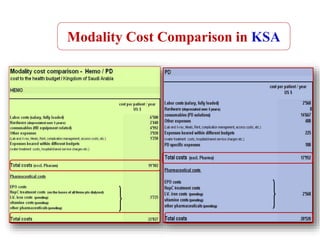
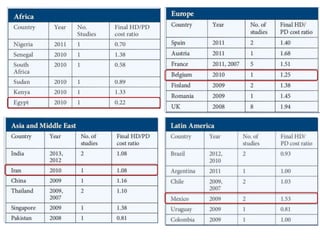
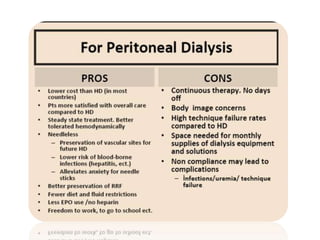
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) has several potential advantages over hemodialysis (HD), though patient and clinical factors must be considered when determining the optimal renal replacement therapy (RRT). PD is associated with better preservation of residual renal function, higher quality of life due to greater flexibility, and lower risk of infection. However, HD requires more nursing staff per patient. The "right modality at the right time" depends on individual patient characteristics and preferences as well as resource availability. Overall, PD can be a cost-effective first-line RRT option when integrated with HD.

![Prof. MacLeod:
4
“Patients whose kidney fail require life-saving treatment with
dialysis or with a kidney transplant.
Although dialysis is now very advanced, allowing more
patients to be treated successfully, it is also very expensive.
It is essential, therefore, to ensure that resources are used as
effectively as possible.”[1]
[1] Khan I., MacLeod A. Towards cost-effective dialysis therapy in Europe: the need for a multidisciplinary
approach. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1997; 12: p. 2483](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pd-170120000609/85/peritoneal-dialysis-4-320.jpg)