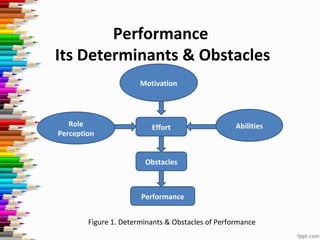
This document discusses performance appraisal. It defines performance appraisal as evaluating individual job performance as a basis for personnel decisions. It notes that performance appraisal is important because it encourages employees to maintain desired behavior knowing their performance is monitored. The key processes in performance appraisal are establishing standards, setting goals, measuring performance, comparing to standards, discussing results with employees, and taking corrective action. The document also outlines various appraisal methods and sources, as well as common errors and how to overcome them.