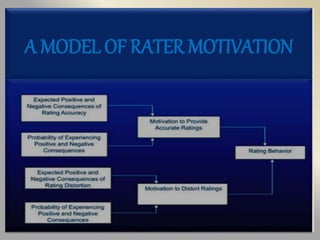
The document discusses performance appraisal forms and their components. It describes the typical sections in appraisal forms which include basic employee information, objectives and standards, competencies, achievements, development goals, stakeholder input, employee comments and signatures. It also discusses characteristics of effective forms like simplicity, relevancy, descriptiveness, adaptability and comprehensiveness. The document outlines factors to consider in rater training programs like providing information on how the performance system works, addressing rater motivations, and teaching skills like identifying, observing and evaluating performance.