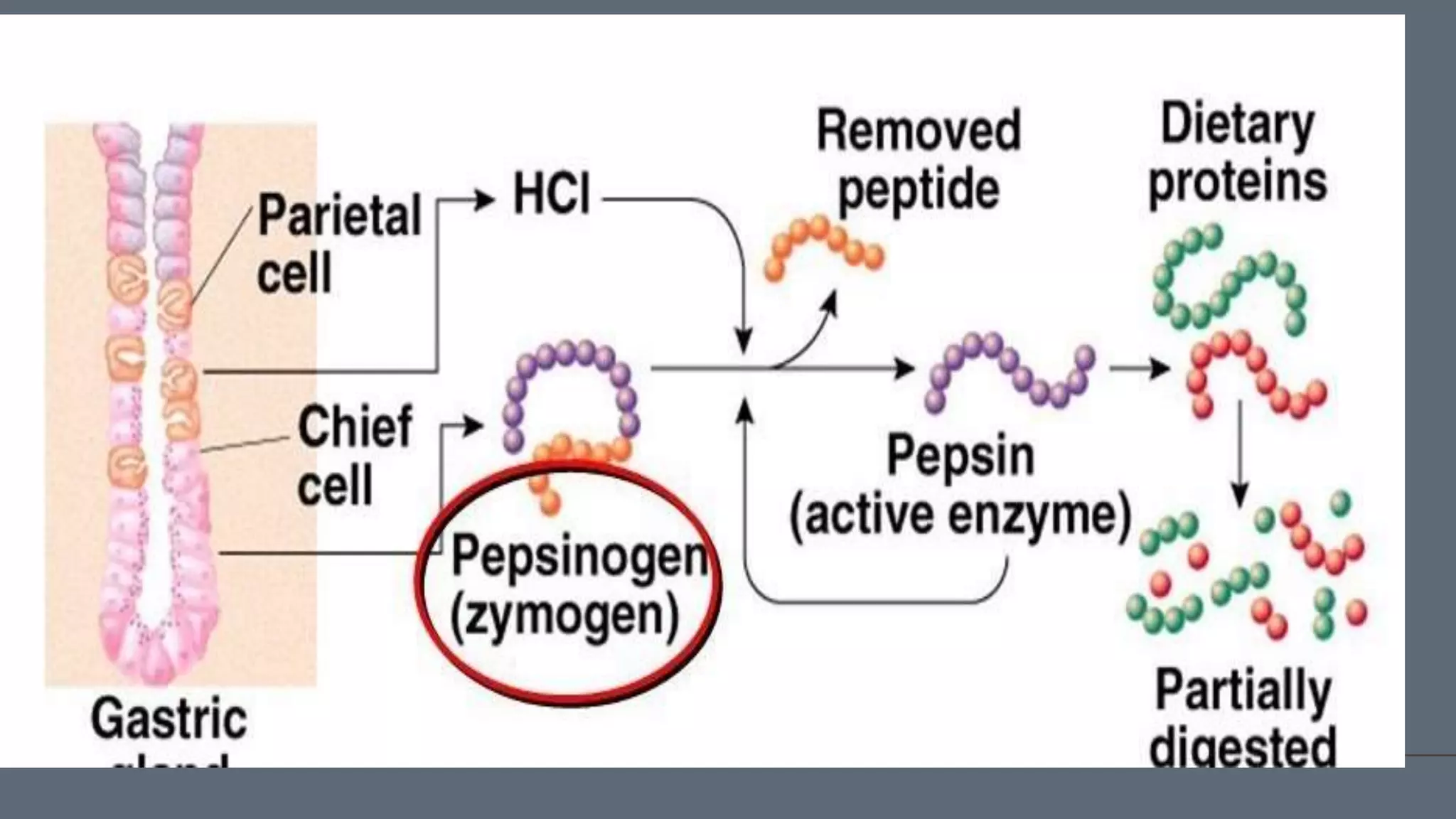
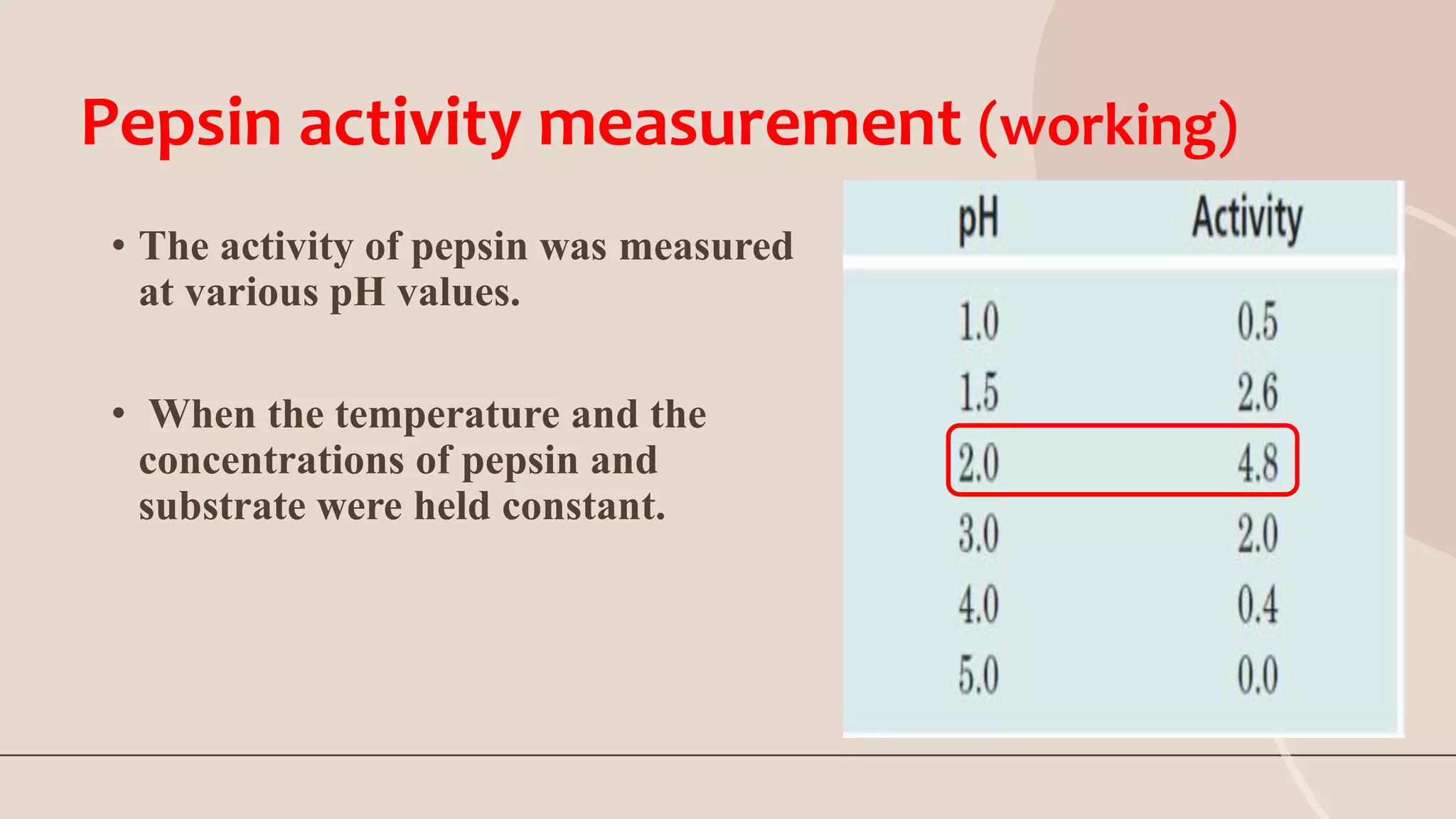
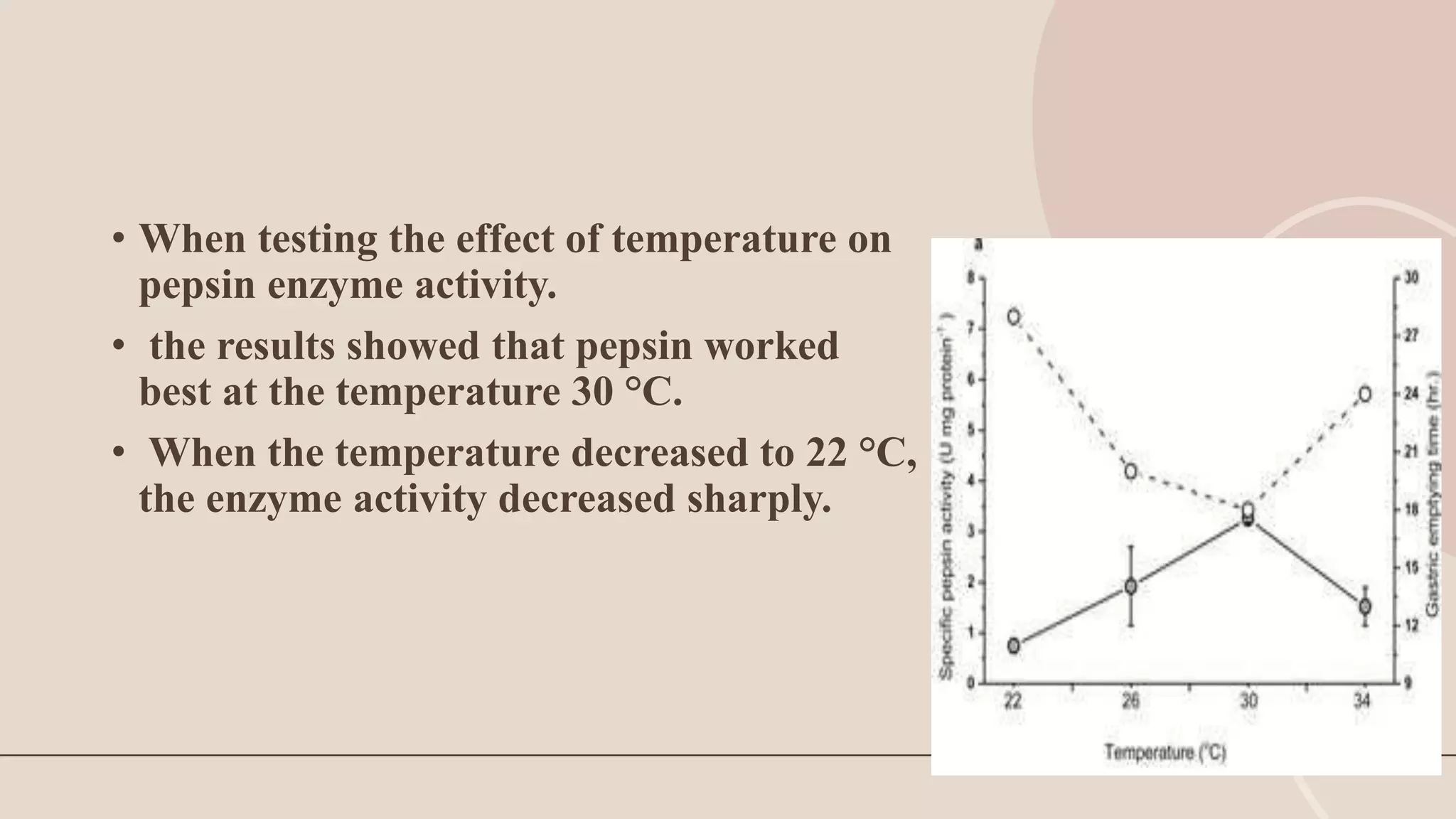
This document discusses pepsin, a proteolytic enzyme produced in the stomach. Pepsin is secreted as the inactive proenzyme pepsinogen and is activated by hydrochloric acid in the stomach. It breaks down dietary proteins into peptides and amino acids to aid in absorption. Pepsin is found in animal sources like pigs and sheep. It is also used to coagulate milk in cheese production. Detecting pepsin in saliva or sputum can help diagnose reflux diseases. Deficiencies in pepsin can impair digestion and nutrient absorption.