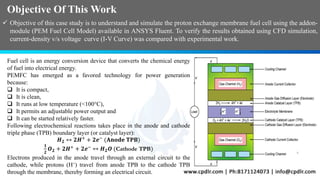
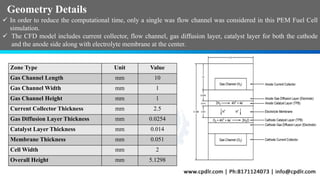
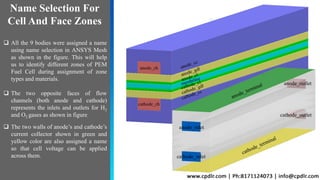
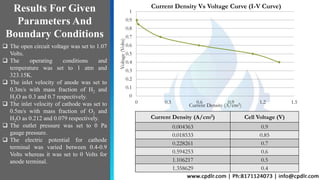
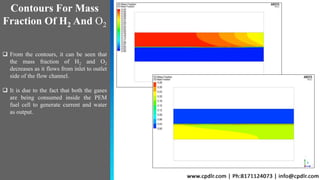
This document discusses the CFD simulation of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) using ANSYS Fluent, emphasizing its compactness, cleanliness, low operating temperature, adjustable power output, and quick startup. The study details the electrochemical reactions involved, the geometry of the PEMFC, and simulation parameters, including mesh details and boundary conditions. Results indicate a decrease in mass fractions of H2 and O2 as they flow through the channel, showcasing their consumption for current and water generation.