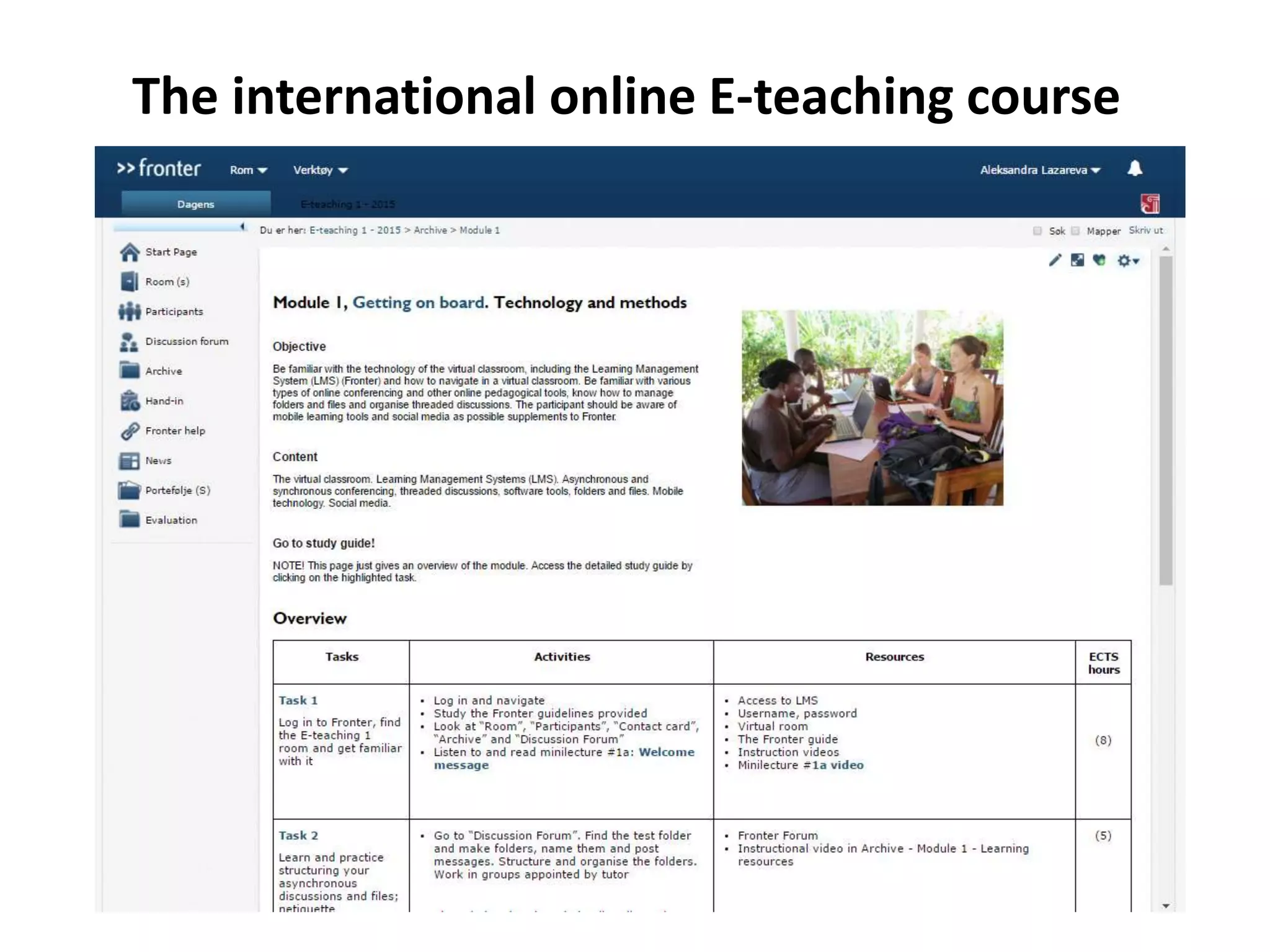
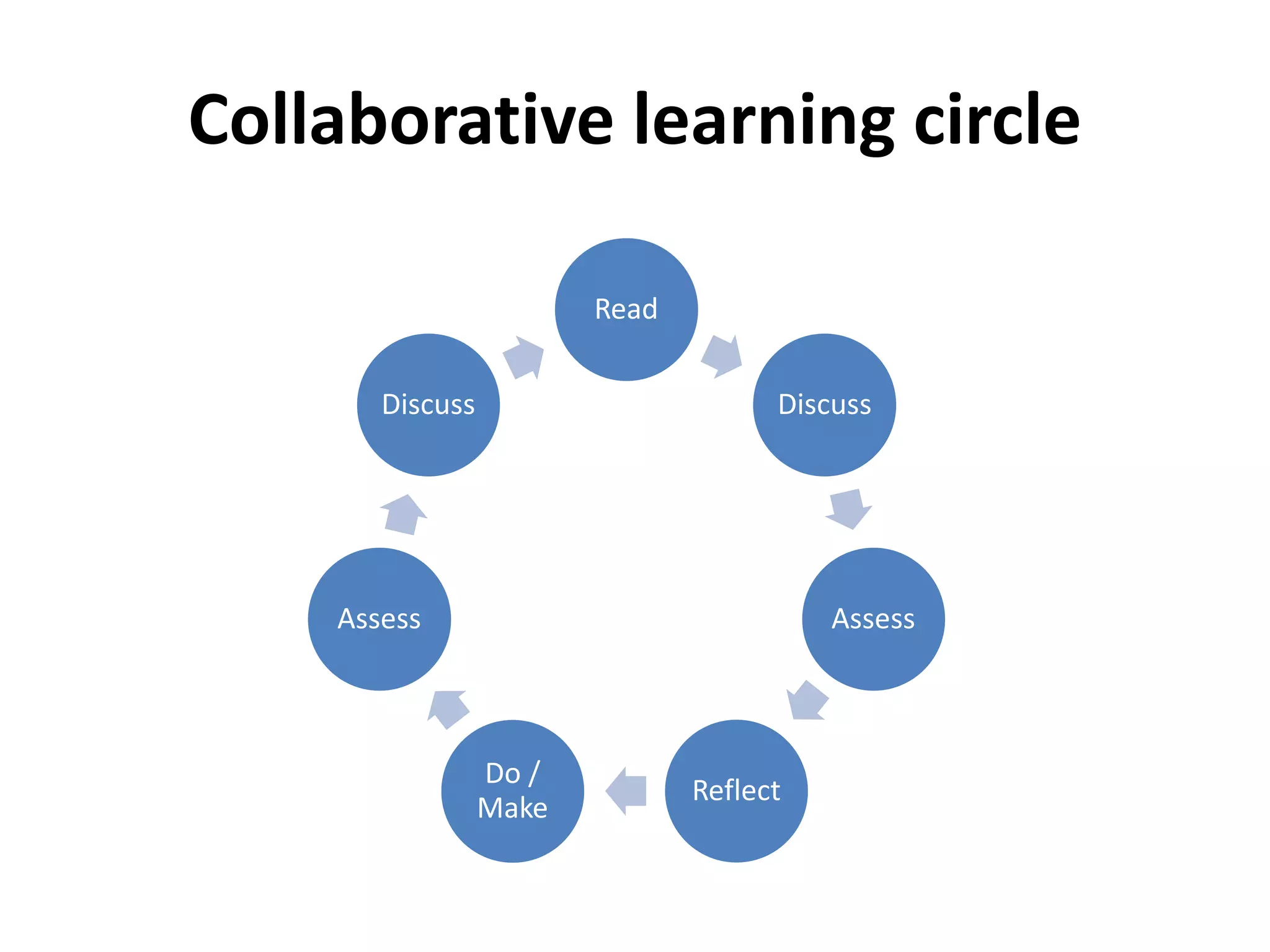
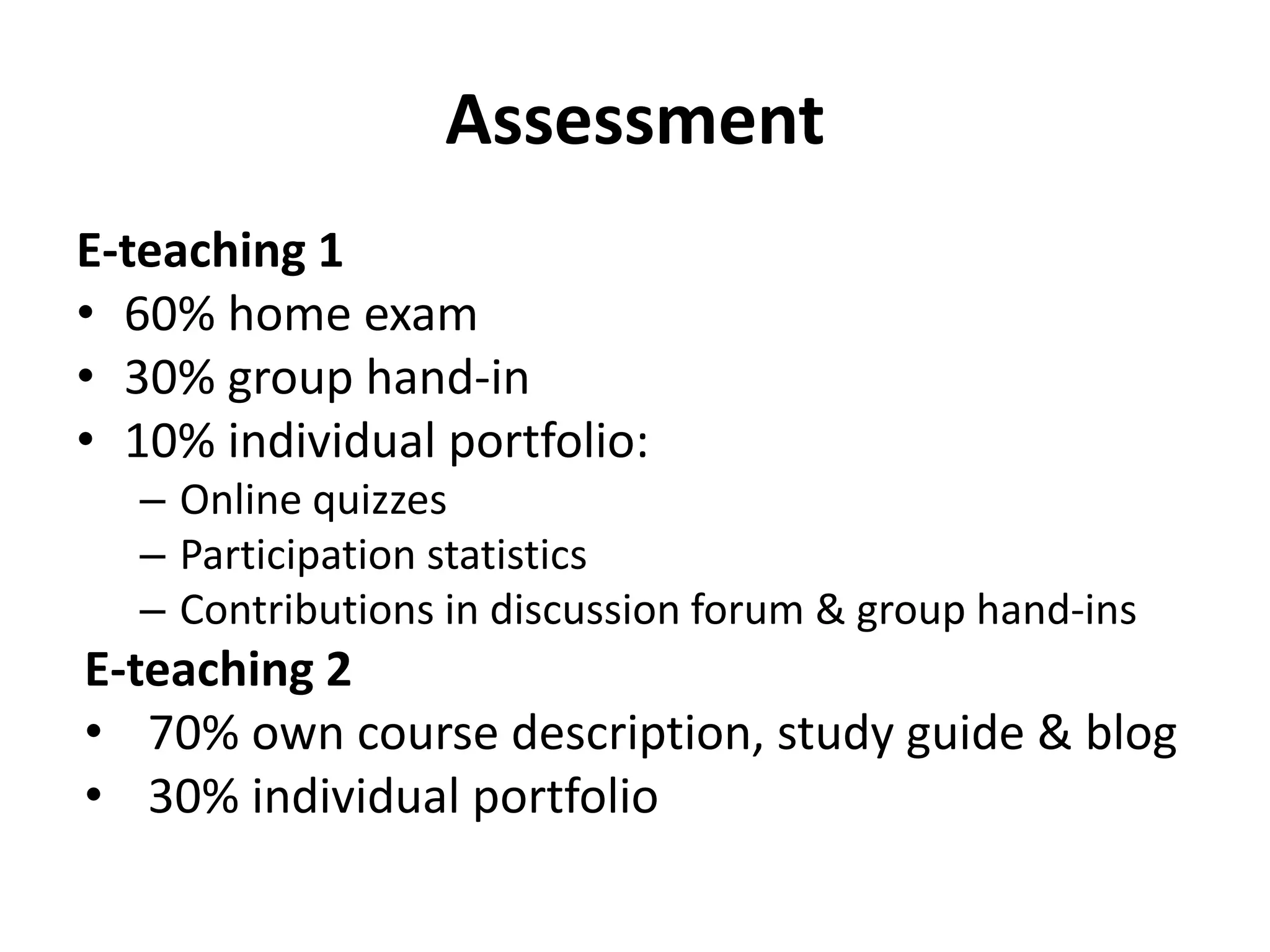
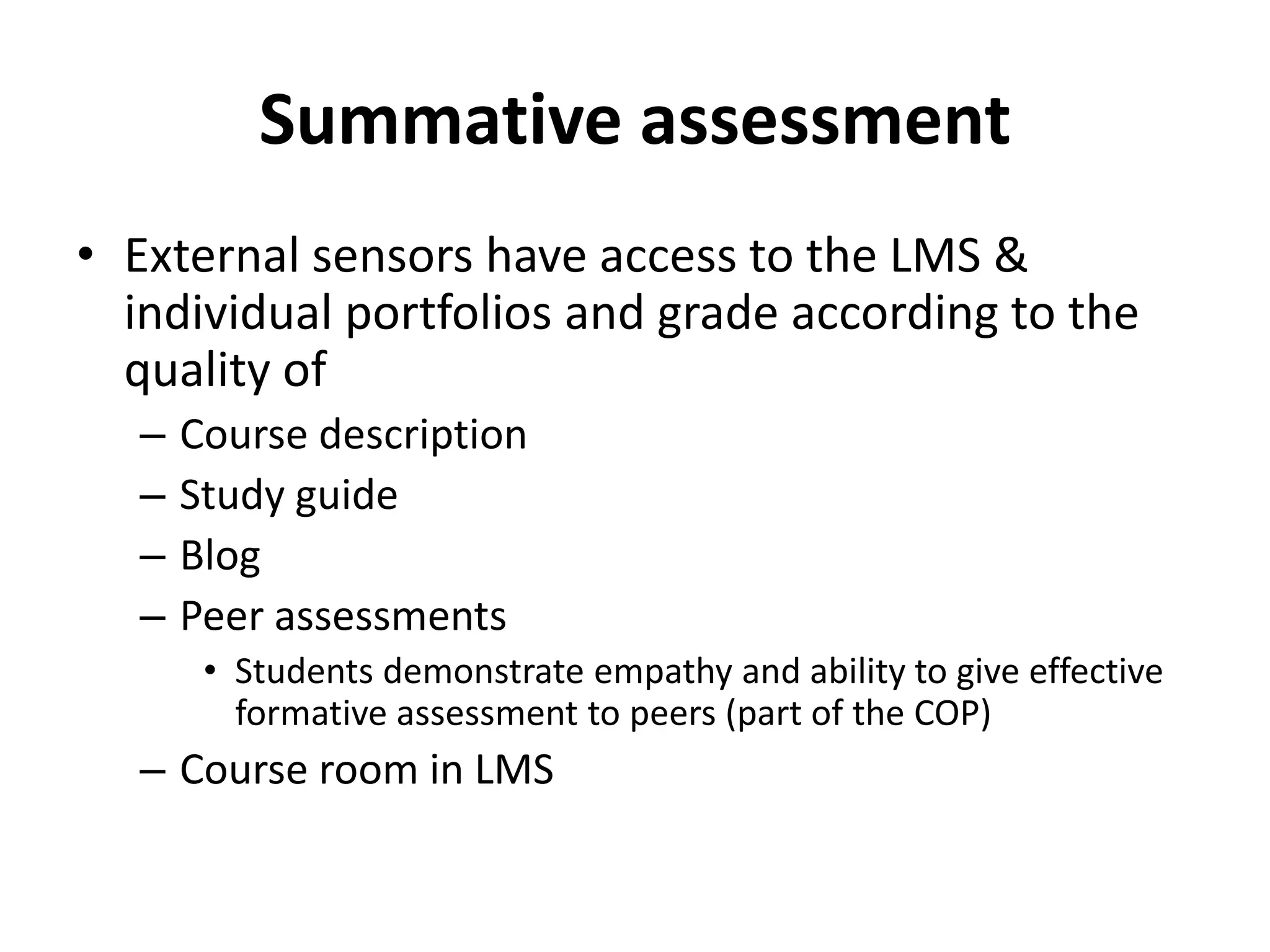
The document discusses peer assessment in online collaborative learning, emphasizing the importance of social interaction and deep learning through constructive alignment of content, process, and assessment. It outlines challenges for both teachers and students, highlighting the need for effective collaboration and communication strategies in diverse learning environments. Additionally, it describes the structure and assessment methods of international online e-teaching courses, focusing on active student engagement and formative feedback.