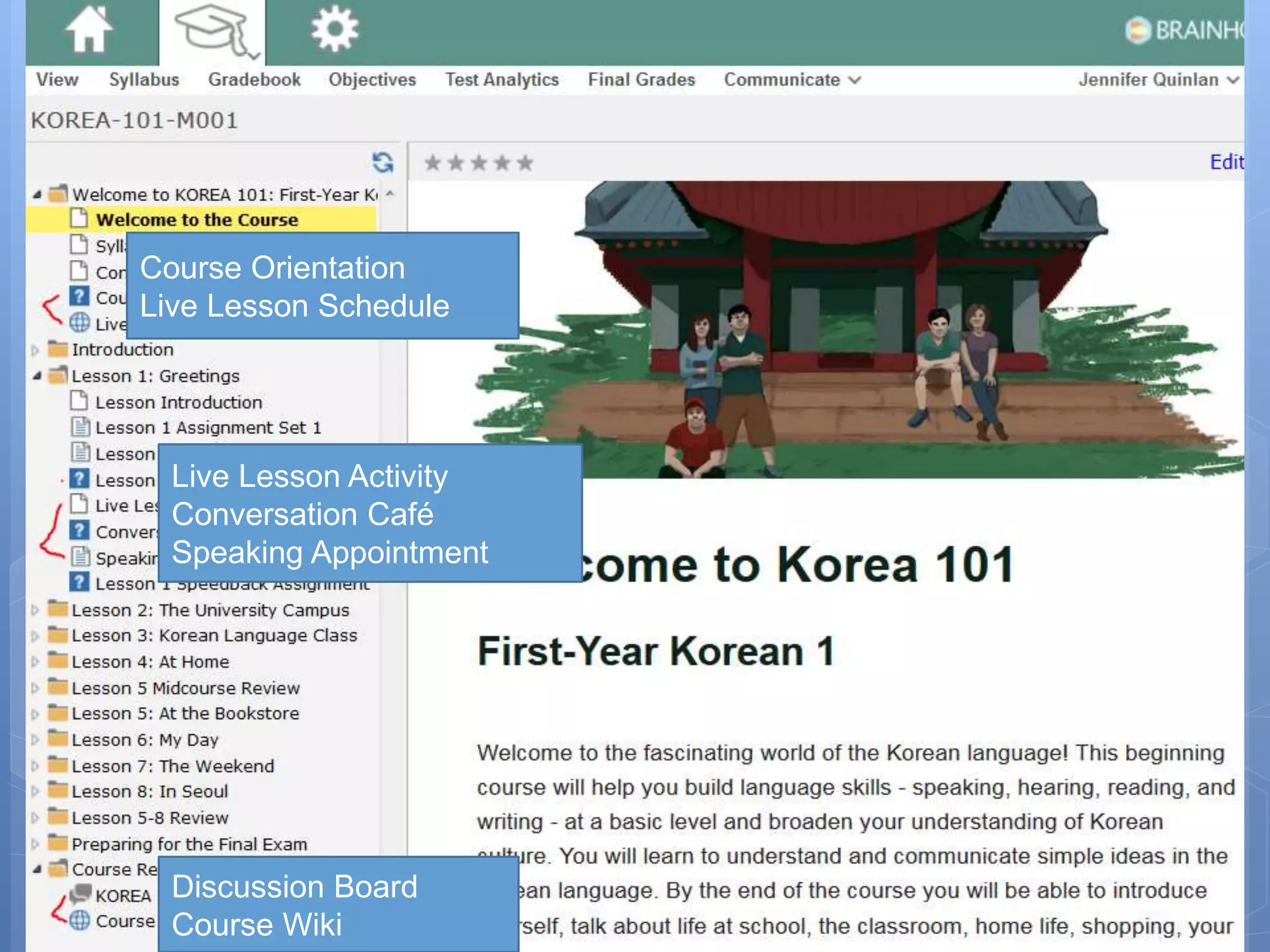
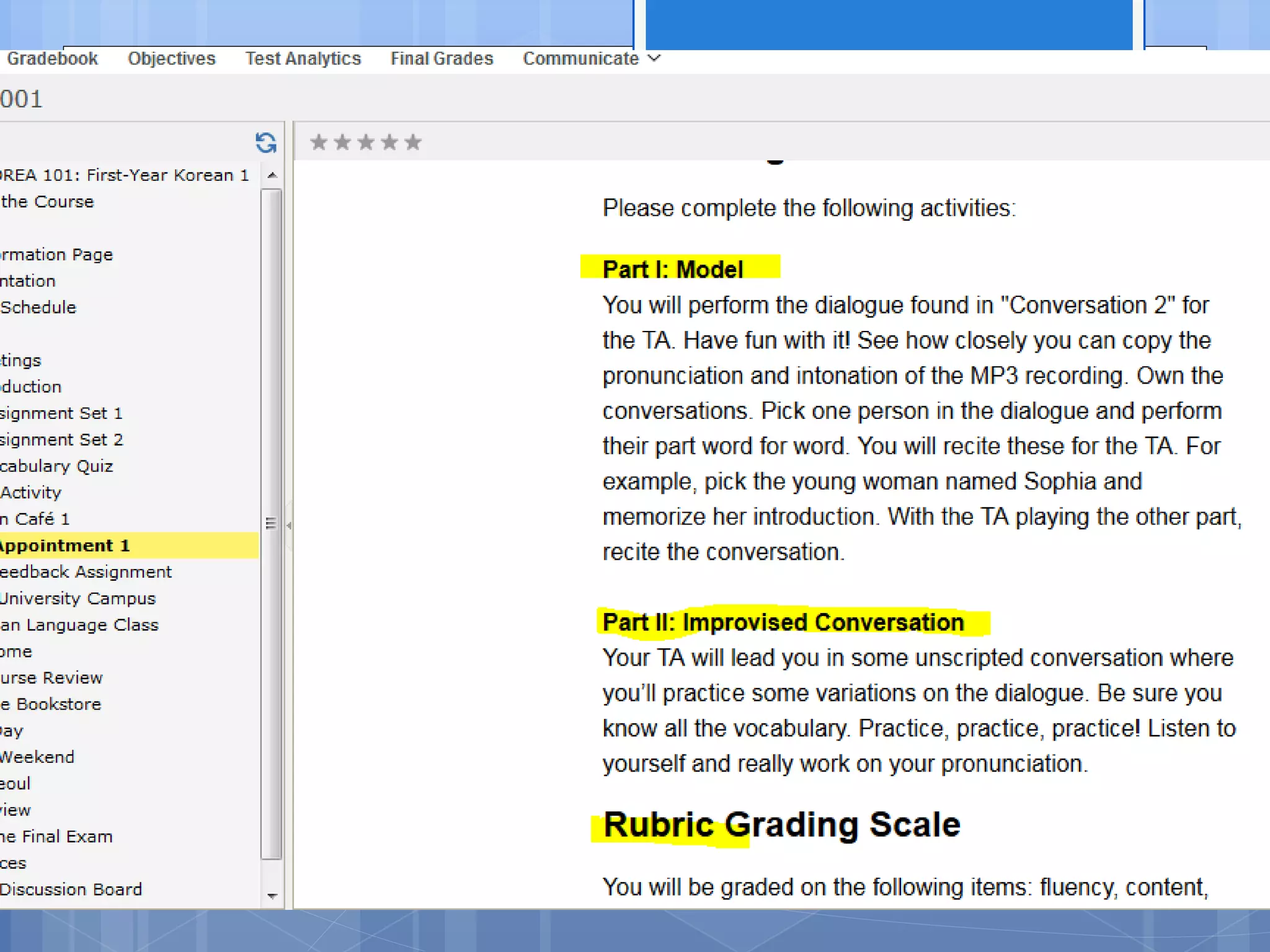
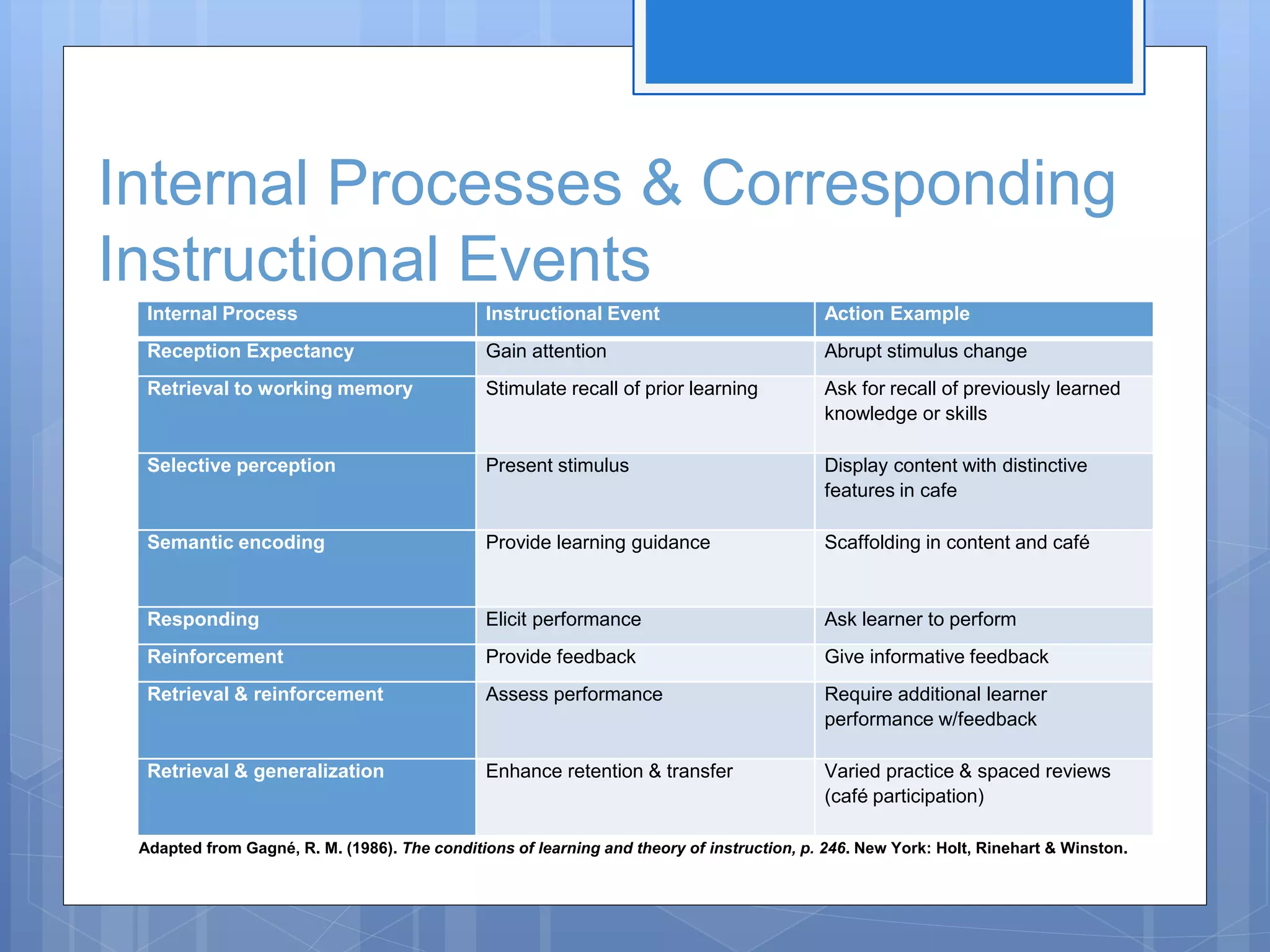
The document outlines the development and adaptation of asynchronous online world language courses at Brigham Young University, particularly focusing on Korean language instruction. It discusses the integration of technology to enhance student engagement and collaboration, employing the ADDIE instructional design model. The findings highlight the importance of course materials and methods that motivate students and improve learning outcomes, along with the necessity of evaluating pedagogical effectiveness.