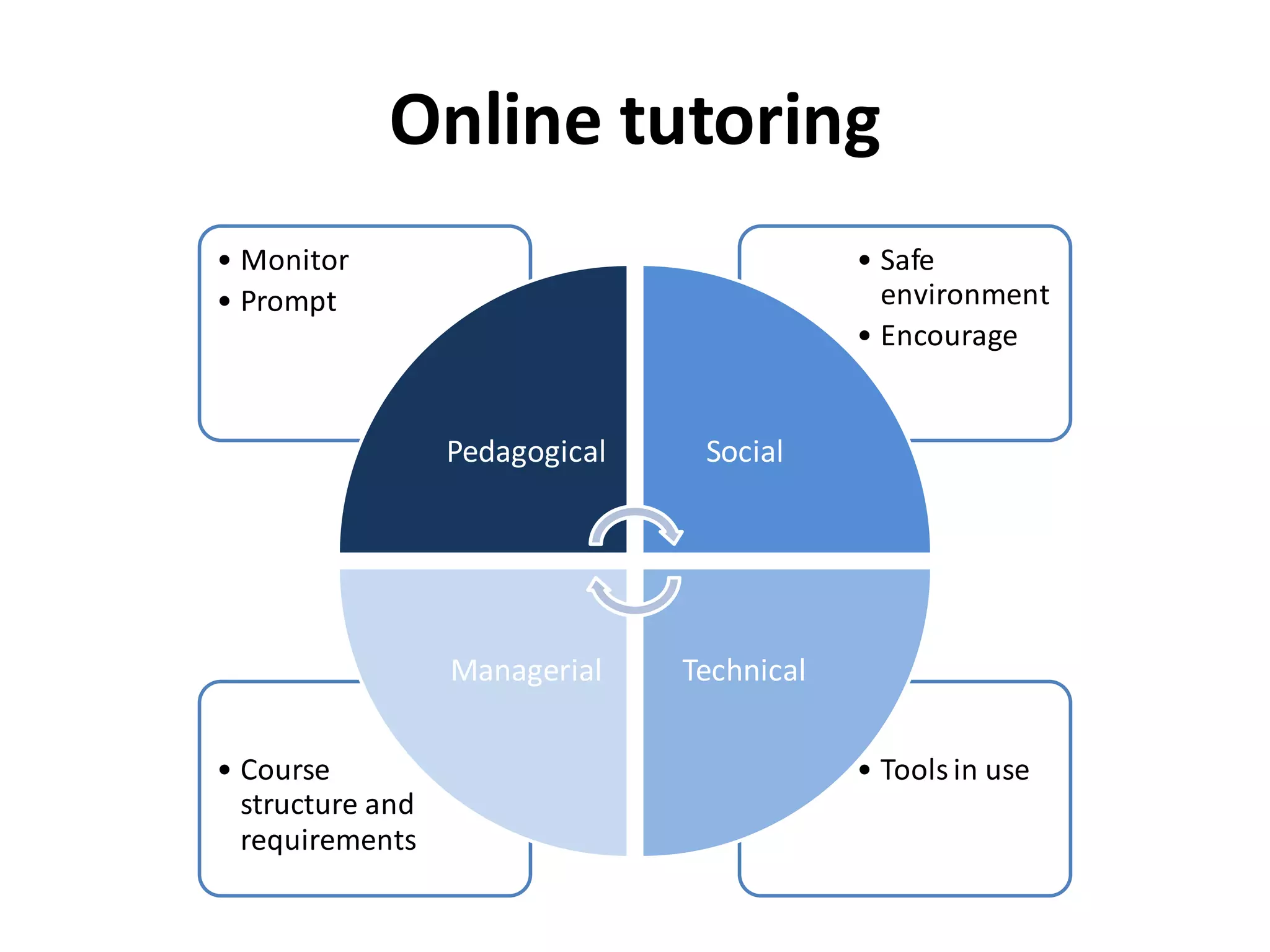
This document discusses collaborative learning in online and distance education. It defines collaborative learning as active knowledge construction through negotiation, explanation, and argumentation that empowers students to take responsibility for their own learning. Asynchronous collaborative learning involves backwards course design focused on what students will learn from activities rather than what the teacher delivers. It flips the classroom from lectures to discussions. Effective collaborative learning involves frequent interaction, feedback, and tasks situated in realistic contexts. While technology enables collaboration, it does not ensure it will occur spontaneously without experience and training. The role of the teacher is to guide inquiry, monitor understanding, and address dysfunctional group dynamics. Assessment should be part of the learning process, including individual and group assignments as well as participation.