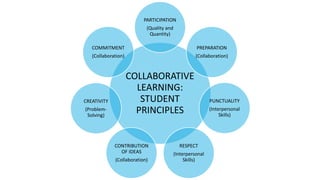
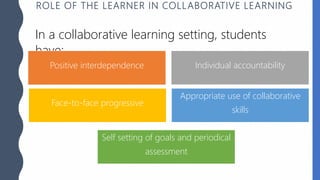
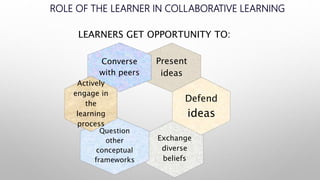
The document discusses collaborative learning, which involves groups of learners working together to solve problems or complete tasks. Some key points:
- Collaborative learning has principles like students teaching each other and taking responsibility for their own and others' learning.
- The teacher takes a facilitating role rather than close monitoring. They provide instructions and allow student groups to work independently.
- When used effectively it can develop students' thinking and social skills while increasing retention, but some students may feel uncomfortable in groups or some may dominate without letting others contribute.