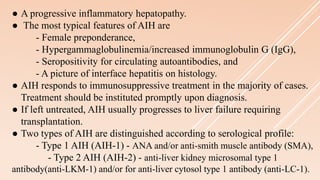
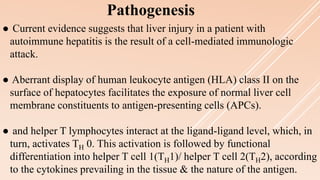
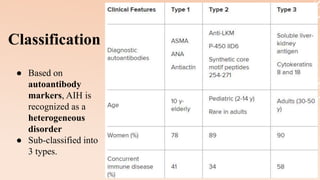
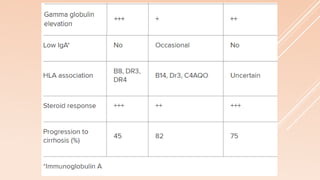
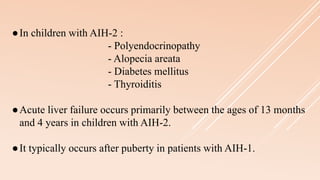
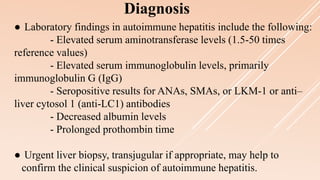
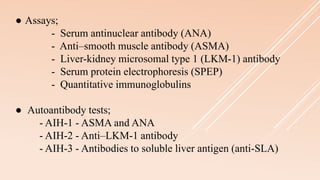
Pediatric autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a progressive liver inflammatory disorder predominantly affecting females, typically presenting with hypergammaglobulinemia and autoantibodies. It can lead to liver failure if not treated promptly and can be classified into two main types based on autoantibody profiles. Effective treatment involves immunosuppressive therapies, and patients may require liver transplantation in severe cases.









![● Cirrhosis and complications of cirrhosis;
- Ascites,
- Coagulopathy,
- Hepatic coma
● Portal hypertension
● Esophageal varices
● Malnutrition (with poor growth in children)
● Overlap Syndrome[Tx. - Ursodiol + Immunosuppressants]
Complications](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pediatricautoimmunehepatitis-rivin-200423095351/85/Pediatric-Autoimmune-Hepatitis-Rivin-15-320.jpg)
![● Many causes of chronic liver diseases including;
- α1 -antitrypsin deficiency,
- Wilson disease,
- Viral hepatitis,
- Hepatotoxic drugs,
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type I (APS-1),
- Autoimmunity in hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection,
- Immune-mediated drug-induced hepatitis,,
- Cryptogenic hepatitis,
- Overlap syndrome [primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC)
and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)]
Differential Diagnoses](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pediatricautoimmunehepatitis-rivin-200423095351/85/Pediatric-Autoimmune-Hepatitis-Rivin-16-320.jpg)

![● The presence of heterogeneous hepatic echotexture on abdominal
ultrasound or abnormal contrast enhancement on abdominal CT
imaging may suggest the presence of active inflammation or
necrosis.
● The appearance of an irregular nodular liver may confirm the
presence of cirrhosis.
● Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) to rule
out coexisting primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) [When alkaline
phosphatase levels are 7-8 times reference values or gamma glutamyl
transferase levels are 2-3 times reference values + a patient with autoimmune
hepatitis and ulcerative colitis]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pediatricautoimmunehepatitis-rivin-200423095351/85/Pediatric-Autoimmune-Hepatitis-Rivin-20-320.jpg)